Dipole electrical stimulation employing direct current for recovery from spinal cord injury
a technology of direct current and spinal cord injury, which is applied in the direction of artificial respiration, therapy, physical therapy, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory connectivity and functional recovery of impaired spinal cord, damage to the nervous system, and very limited process, so as to improve the performance of skeletal muscles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first experiment
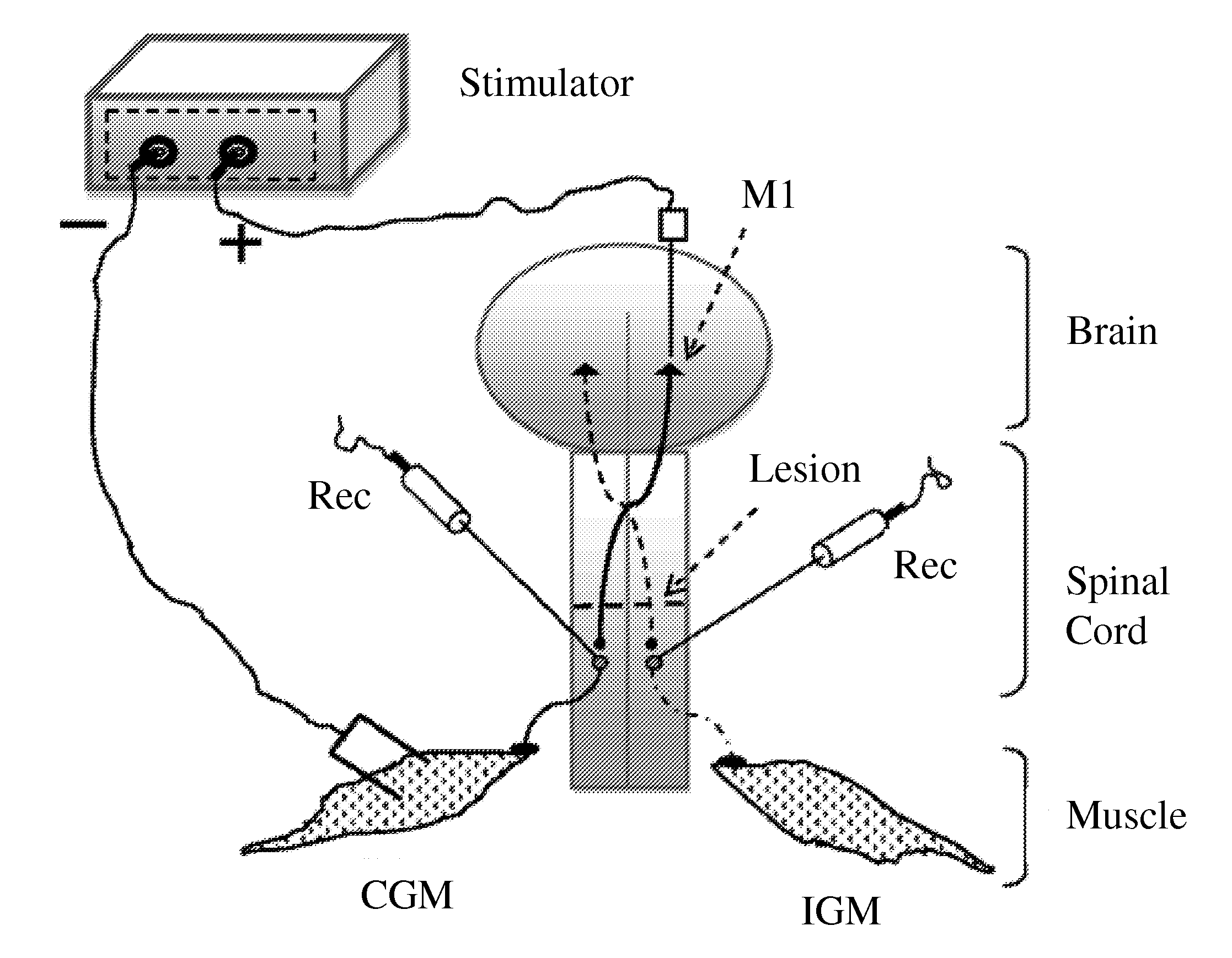
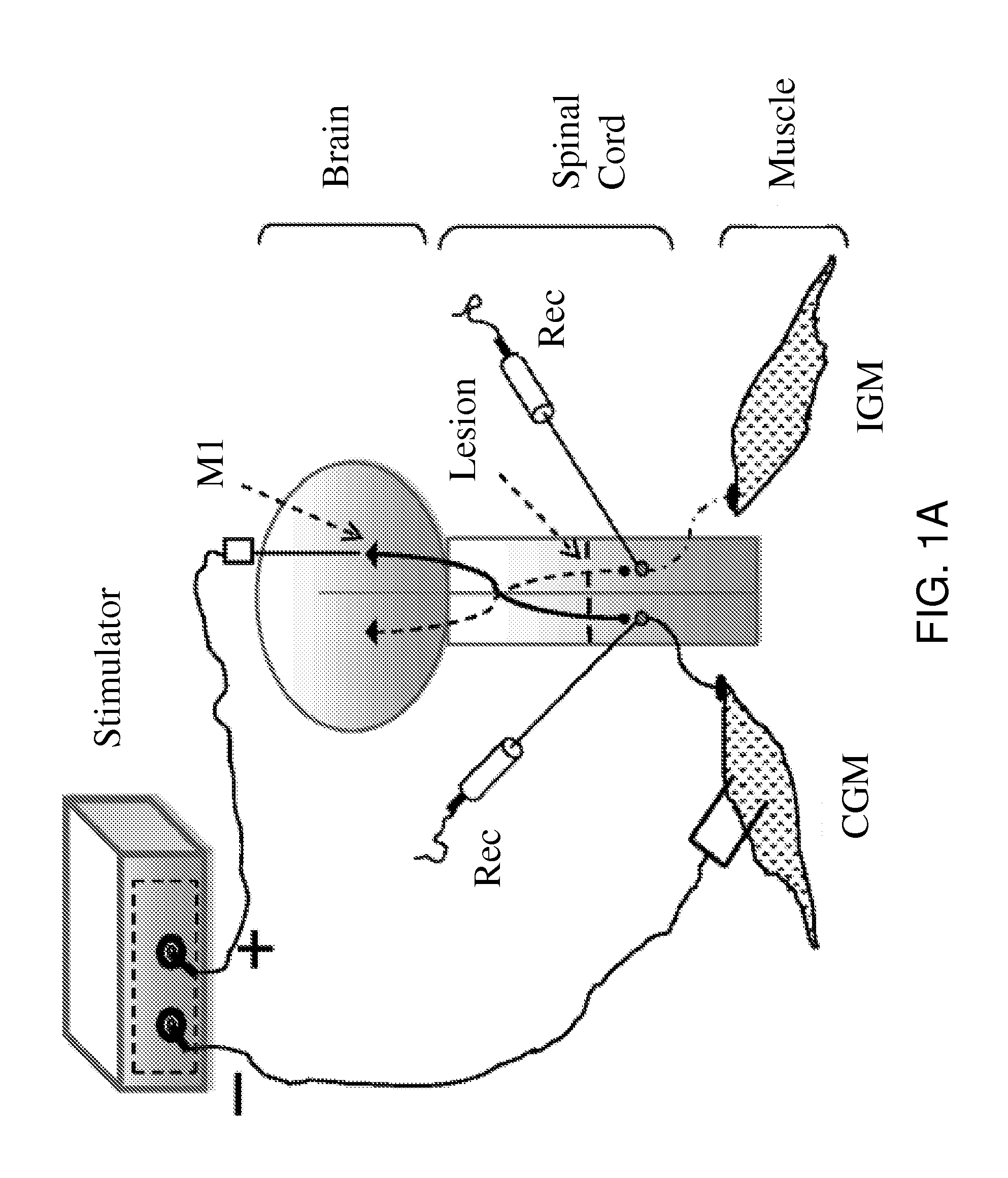
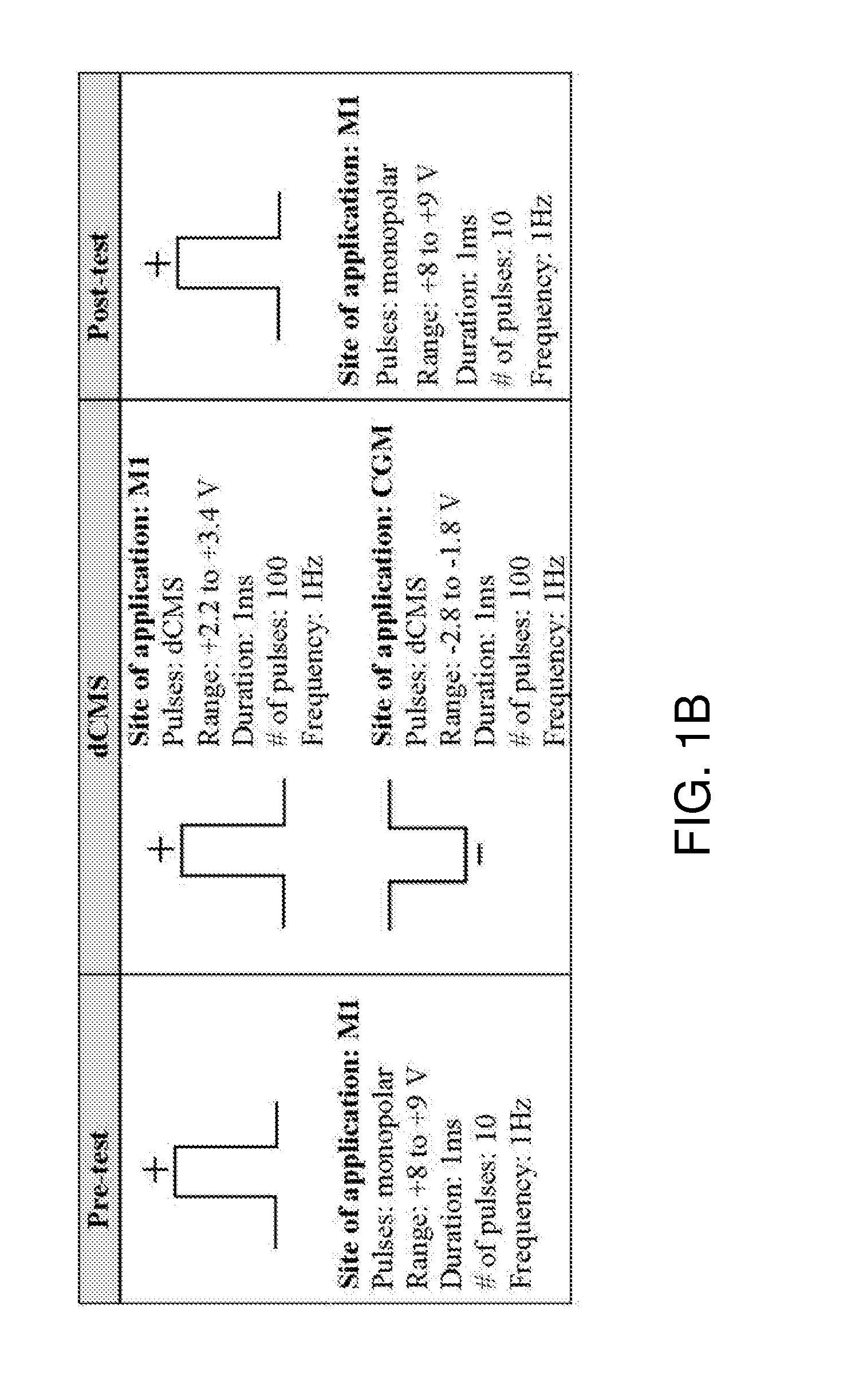
[0169]A new configuration of electrical stimulation is provided herein as it was tested in anesthetized control and spinal cord injury (SCI) mice. Constant voltage output was delivered through two electrodes. While the negative voltage output (ranging from −1.8 to −2.6V) was delivered to the muscle (two-wire electrode, 500 μm), the positive output (ranging from +2.4 to +3.2V) was delivered to the primary motor cortex (M1) (electrode tip, 100 μm). The configuration was named dipolar cortico-muscular stimulation (dCMS) and consisted of 100 pulses (1 ms pulse duration, 1 Hz frequency).
[0170]In experimental testing, constant voltage output was delivered through two electrodes. While the negative voltage output (ranging from −1.8 to −2.6V) was delivered to the muscle, the positive output (ranging from +2.4 to 3.2V) was delivered to the primary motor cortex (M1). The configuration consisted of 100 pulses (1 ms pulse duration, 1 Hz frequency). In SCI animals, after dCMS, muscle contraction...
second experiment
[0248]The application of dCMS on humans yielded similar results. A fourteen year old male with history of erb's palsy (right upper limb) had very weak external rotator muscles of the shoulder. The patient had no voluntary control over these muscles and could not rotate the shoulder outward. In addition, the shoulder external rotators were apparently moderately atrophied, which was determined by clinical observation. The dCMS was applied by situating the first point negative electrode on the muscles belly (the right supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles) and the second point positive electrode on the contralateral muscles (same group). The current passed in between the two locations on opposite sides of the body, forcing the current to cross the spinal cord. It is assumed that the current follows the least resistant pathway which most likely involved right muscles (supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles), the nerves innervating these muscles (the right suprascapular nerve from C5,...
third experiment
[0251]A nine-month-old child with quadriplegic paralysis due to chromosomal anomaly was treated with the same dCMS method as described in the second experiment. The child had been completely paralyzed without movement in the head, the neck, the trunk, and the upper and lower extremities. Over a course of three weeks, the child was treated in four dCMS treatment sessions that lasted 20 minutes each. After the four sessions, the child was able to make movement in all directions in the upper extremities. She could also move her fingers in all directions and hold a toy. She could hold her head up and turn her head around. Further, she was able to move her toes and lower extremities.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com