Method of making a transitor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
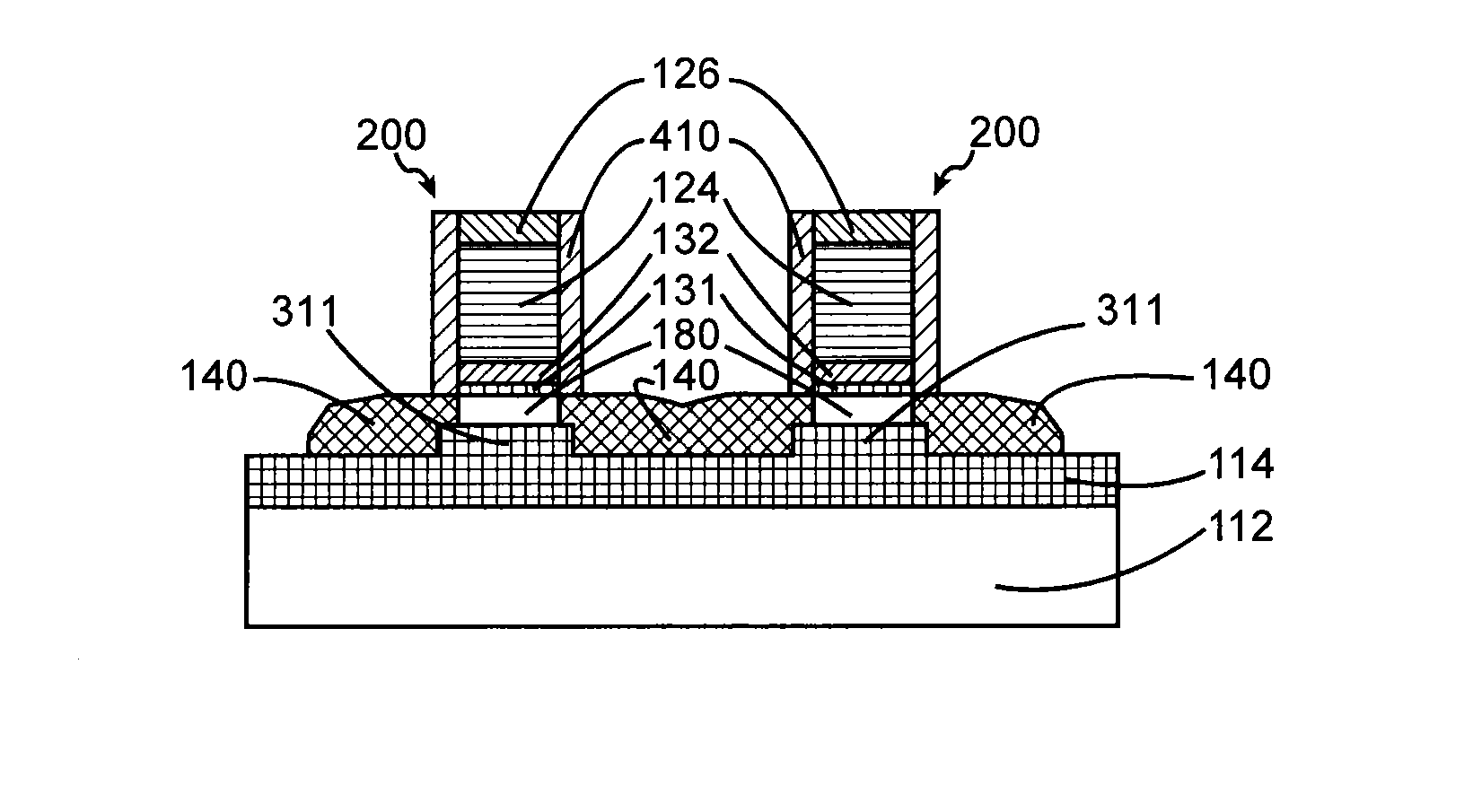
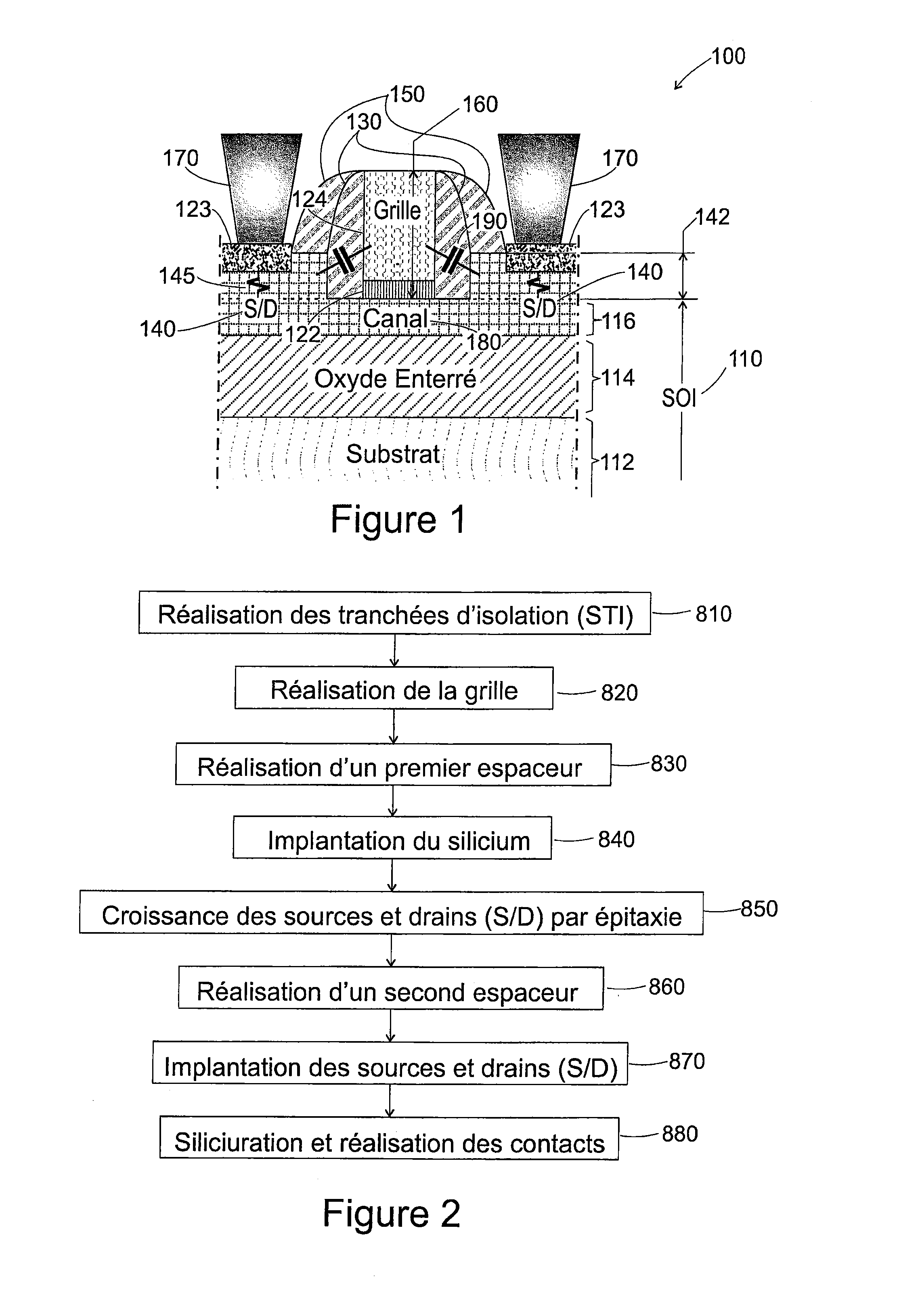
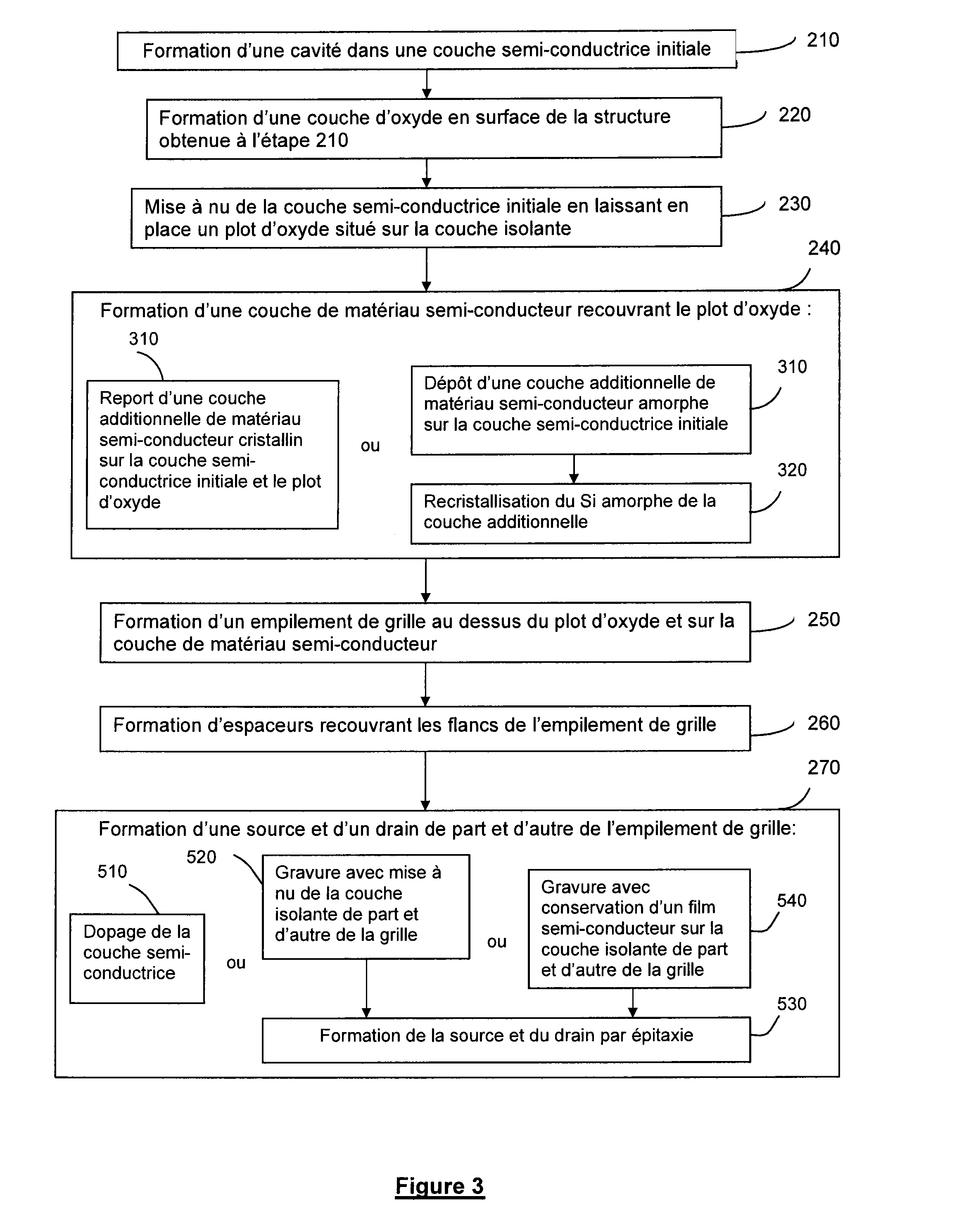
[0056] said etching of at least the additional layer of semiconductor material removes, on either side of the gate stack, the entire thickness of the additional layer of semiconductor material and the entire thickness of the initial semiconductor layer. Preferably, the etching is stopped on the insulating layer. Thus the etching bares the insulating layer on either side of the gate stack. The formation of the source and drain is effected by epitaxy from the semiconductor material remaining in place. This epitaxy is preferentially directed downwards, that is to say from the channel and in the direction of the substrate.
second embodiment
[0057]In a second embodiment, said etching preserves, on either side of the gate stack, a film formed by at least a portion of the thickness of the initial semiconductor layer and optionally by a portion of the additional layer of semiconductor material. Thus the etching is partial in that it does not bare the insulating layer on either side of the gate stack. Advantageously, in this case, the epitaxy is initiated by the lateral ends of the channel and / or by the film of semiconductor material left in place, on either side of the gate stack, on the insulating layer at the end of the etching. Typically only a top portion of the assembly formed by the additional layer of semiconductor material and the initial semiconductor layer is removed. Said top portion removed by anisotropic etching typically has a thickness of between 1 nm and 20 nm.
[0058]According to a first embodiment, the formation of at least one cavity is effected by etching only part of the thickness of the initial semicond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com