Process to make calcium oxide or ordinary portland cement from calcium bearing rocks and minerals
a technology of calcium oxide and portland cement, which is applied in the field can solve the problems of inefficiency, drawbacks, and considerable challenges of the art of producing cement materials, including ordinary portland cement, and achieve the effect of less energy intensiv
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
to Make Calcium Oxide or Ordinary Portland Cement from Calcium Bearing Rocks and Minerals
[0058]Conventional cement is made by thermally decomposing CaCO3 into CaO and then mixing it with other materials including Al2Si2O5(OH)4, Fe2O3, and CaSO4. Thermal decomposition occurs at ˜900C and final OPC production occurs at ˜1450C. Most of the energy required and CO2 emissions for cement making come from the thermal decomposition of limestone:
CaCO3→CaO+CO2ΔH=178(non spontaneous) (FX5).
[0059]Conventional cement requires 2.7-6 GJ / tonne OPC and produces 0.7-1.3 tonne CO2 per tonne of OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement). The normal cement process emits a lot of CO2 and take a lot of energy.
[0060]Included in this discloses is a process to produce CaO from any calcium-bearing rock or mineral. In nature, acid (e.g. H2CO3 or H2SO4) weathers calcium bearing minerals to produce, typically, CaCO3 or CaSO4. The general weathering trend follows:
H2CO3+CaAl2Si2O8+H2O→CaCO3+Al2Si2O5(OH)4 (FX6);
or
H2SO4+CaAl2S...
example 2
Thermal Decomposition of Limestone to Make Lime or Cement
[0065]Lime is used directly as a commodity chemical as well as the primary constituent of cement which is the most consumed human made material on the planet. Lime is currently produced via the thermal decomposition of limestone in an air atmosphere (FX16).
CaCO3→CO2+CaO (FX16);
This heat of decomposition of this reaction is 178 kJ / mol
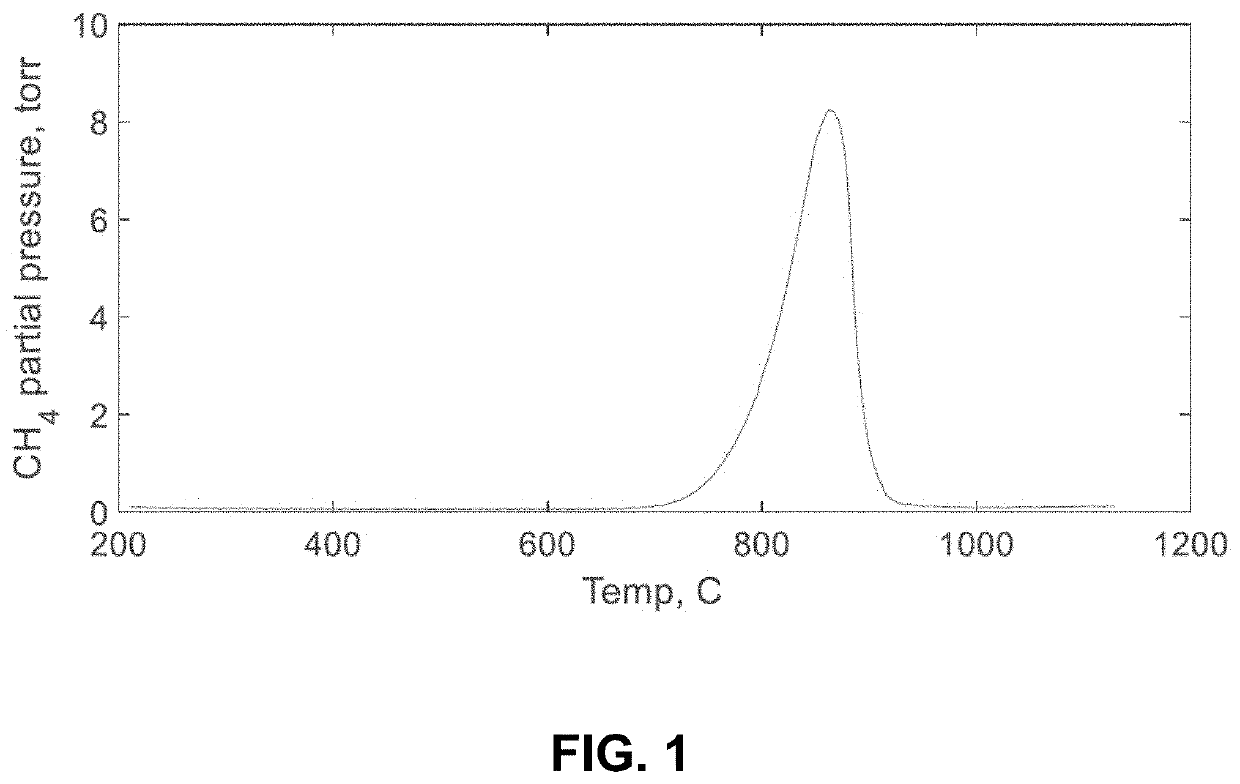
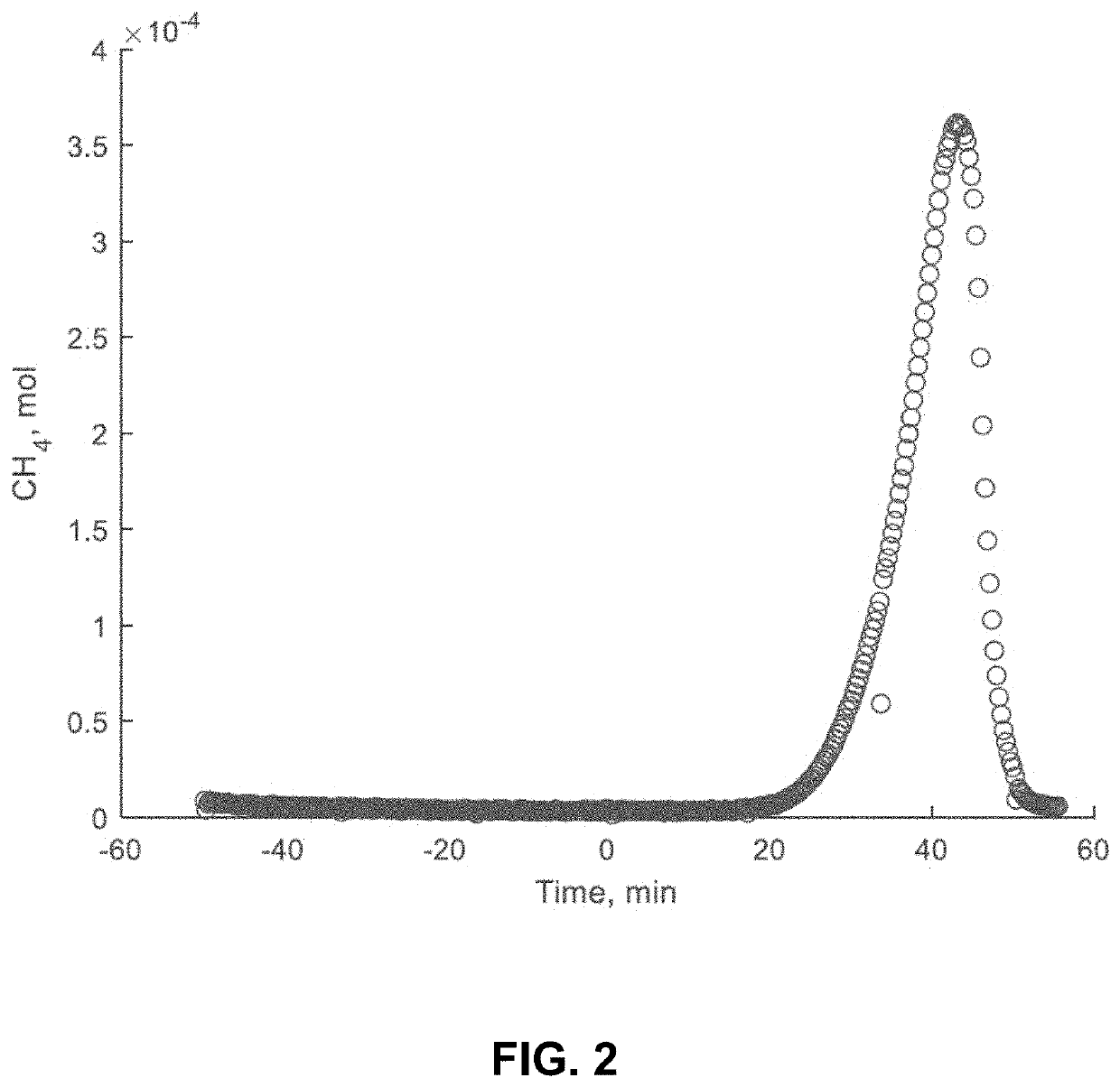
[0066]Included in this invention is a process to produce cement from limestone via reductive thermal decomposition with hydrogen. The first step in the process may follow the following reactions:
CaCO3+4H2→CH4+2H2O (FX17A);
or
CaCO3+2H2→CH4+O2(FX17B);
[0067]Water content of the reacting gas influences whether the reaction proceeds according to FX17A, FX17B, or both. CaCO3 can react with H2 to either make CaO+CH4+O2 or CaO+CH4+2H2O. If H2O is formed, 4H2s are consumed. If O2 is formed, only 2H2s are consumed. This reaction can be driven to only consume 2H2s if there is a water atmosphere, for example.
[...
example 3
n of Gypsum and Cement Materials
[0072]Exemplary aspect 1: The production of ordinary portland cement (OPC) from any calcium containing starting material without the net production of acid-forming gases (e.g. SO2 and CO2). Examples of calcium containing starting materials include: basalt, igneous appetites, wollastonite, slag, fly ash, anorthosite, montmorillonite, bentonite, calcium-containing feldspar, anorthite, diopside, pyroxene, pyroxenite, mafurite, kamafurite, clinopyroxene, colemonite, grossular, augite, pigeonite, margarite, calcium serpentine, garnet, scheilite, OPC, concrete, any rock that has any Ca or CaO by mass especially rocks with >5%, >10%, or >15% CaO, any skarns, limestone, gypsum, appetite, or fluorapatite.
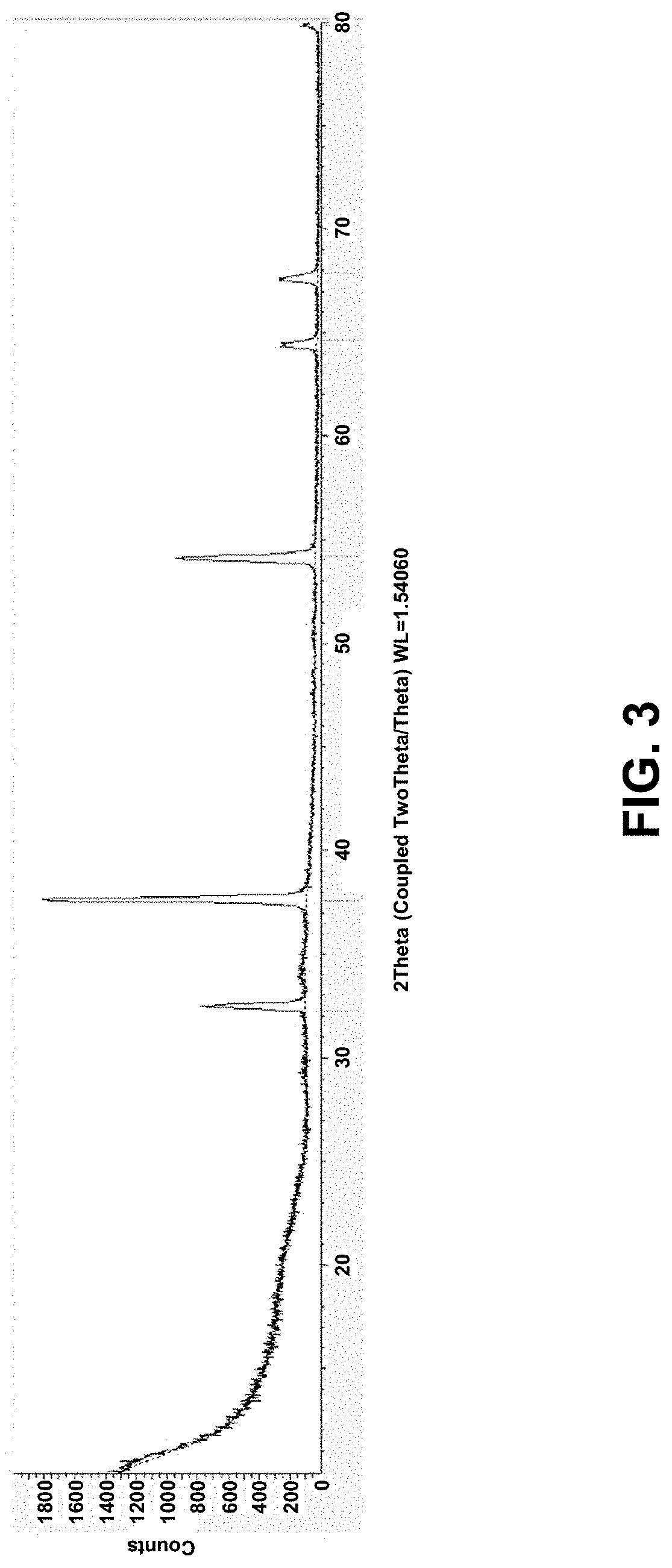
[0073]In certain embodiments, we do this by first producing >90% pure synthetic gypsum from the above calcium containing rocks (details in claim 2) and then thermally decomposing this gypsum to make CaO and then mixing it with the proper ratios of other materi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com