Low hemolytic antibacterial peptide and its application
A peptide, antibacterial activity technology, applied in the field of antibacterial peptides, can solve problems such as limiting the development of treatment, achieve the effect of inhibiting growth, improving compatibility, treating or preventing bacterial or viral infection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1: Design, synthesis, purification and characteristics of peptides
[0084] The peptide analogs of the present invention and their nomenclature are shown in Table 1 below, and each amino acid is represented by three letters.
[0085] Table I
[0086]
[0087] C: Cyclic: L: Linear
[0088] All linear peptides were synthesized by solid-state synthesis using standard Fmoc: (N-(9-fluorenyl)methoxycarbonyl) in PAL resin (5-(4-Fmoc-aminomethyl-3, 5-dimethoxyphenoxy)-pentanoic acid-methylphenylhydramine resin) by chemical synthesis; and the Fmoc protecting group on these resins was synthesized with 20% hexahydropyridine / dimethylformamide (piperidine / DMF) Removal, the reaction time is about 1 to 1.5 hours, and then determined by water and ninhydrin test (ninhydrin test). Next, 95% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) was added and mixed for 1-1.5 hours, and the unprocessed peptide was excised from the resin; then analyzed and purified by reverse-phase high-performance liqui...
Embodiment 2
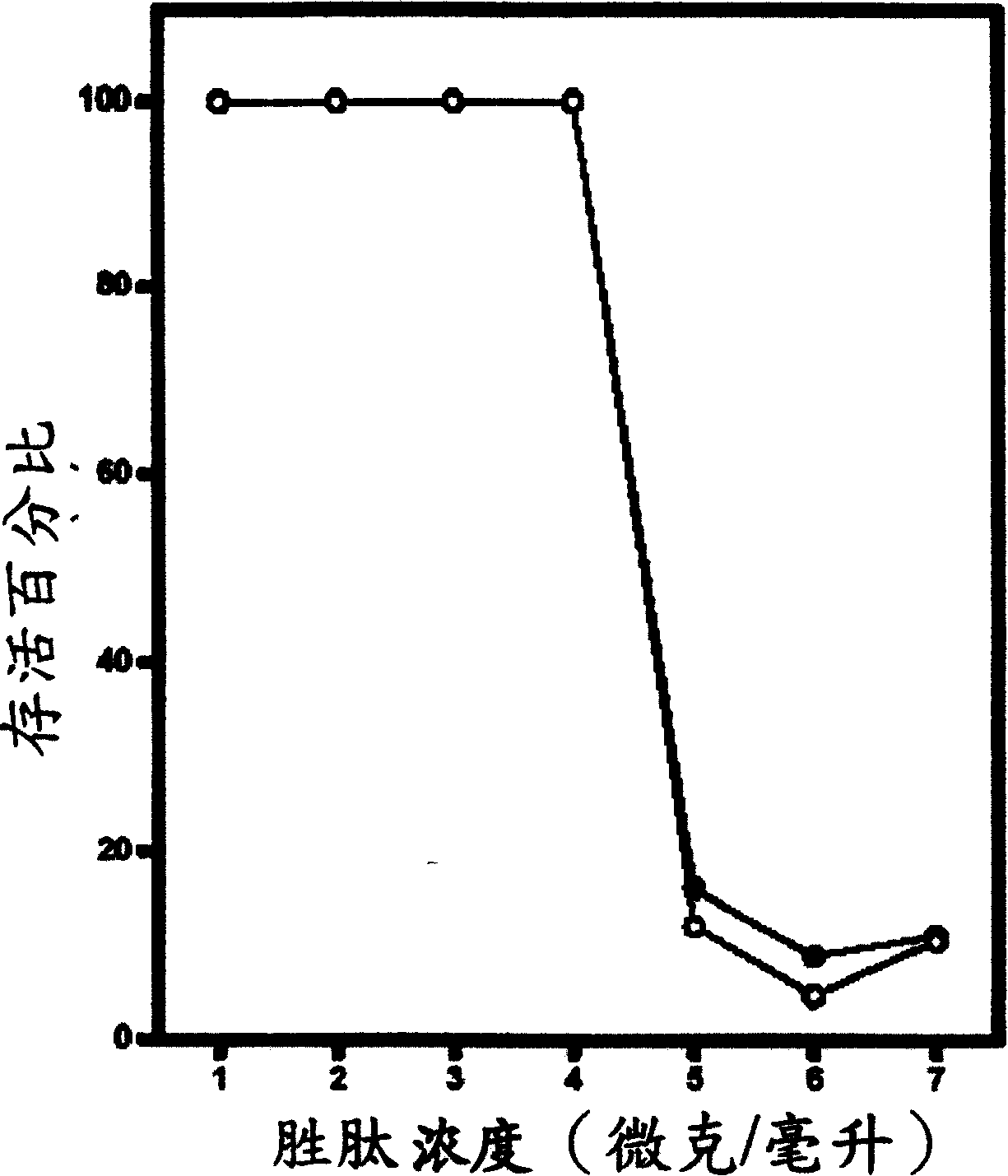
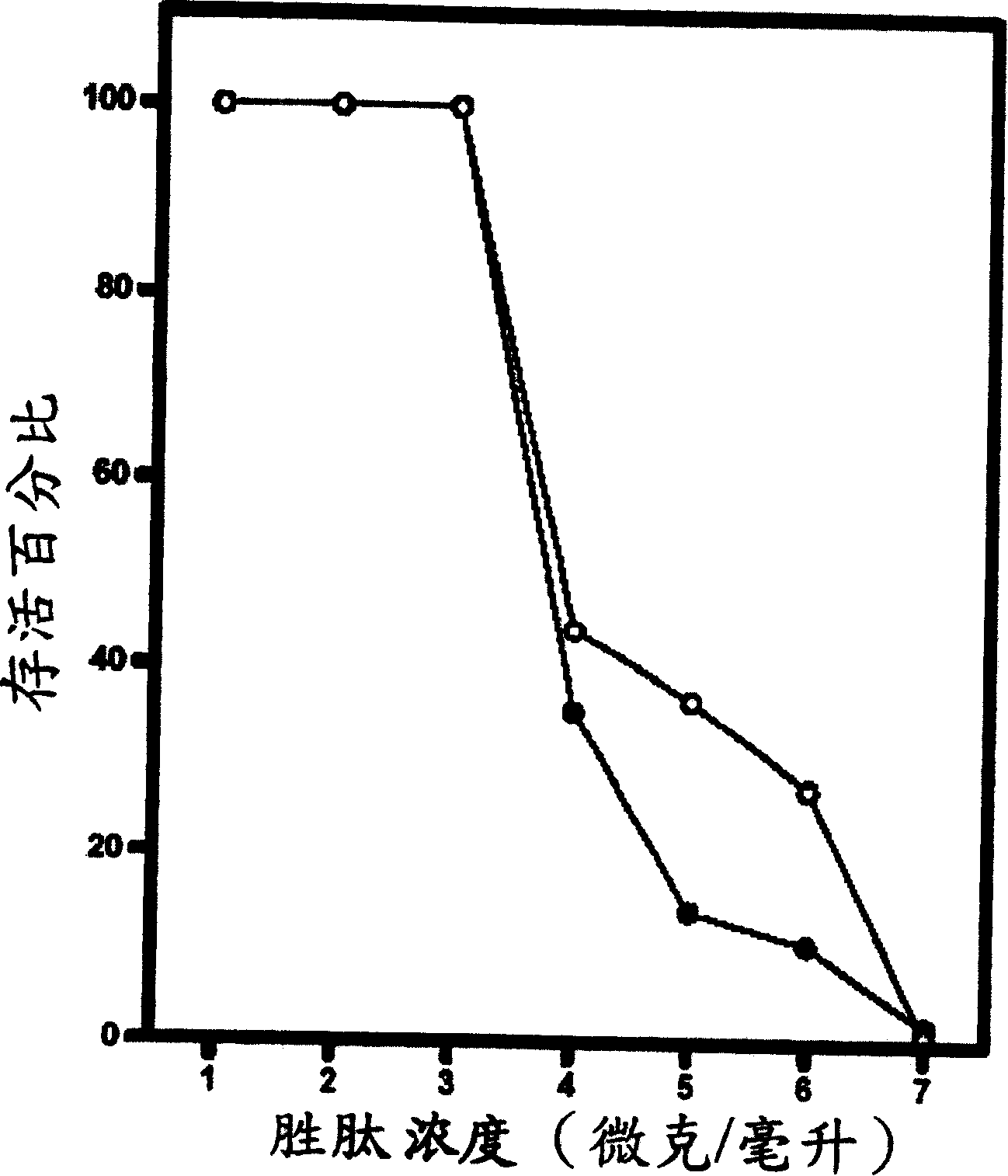
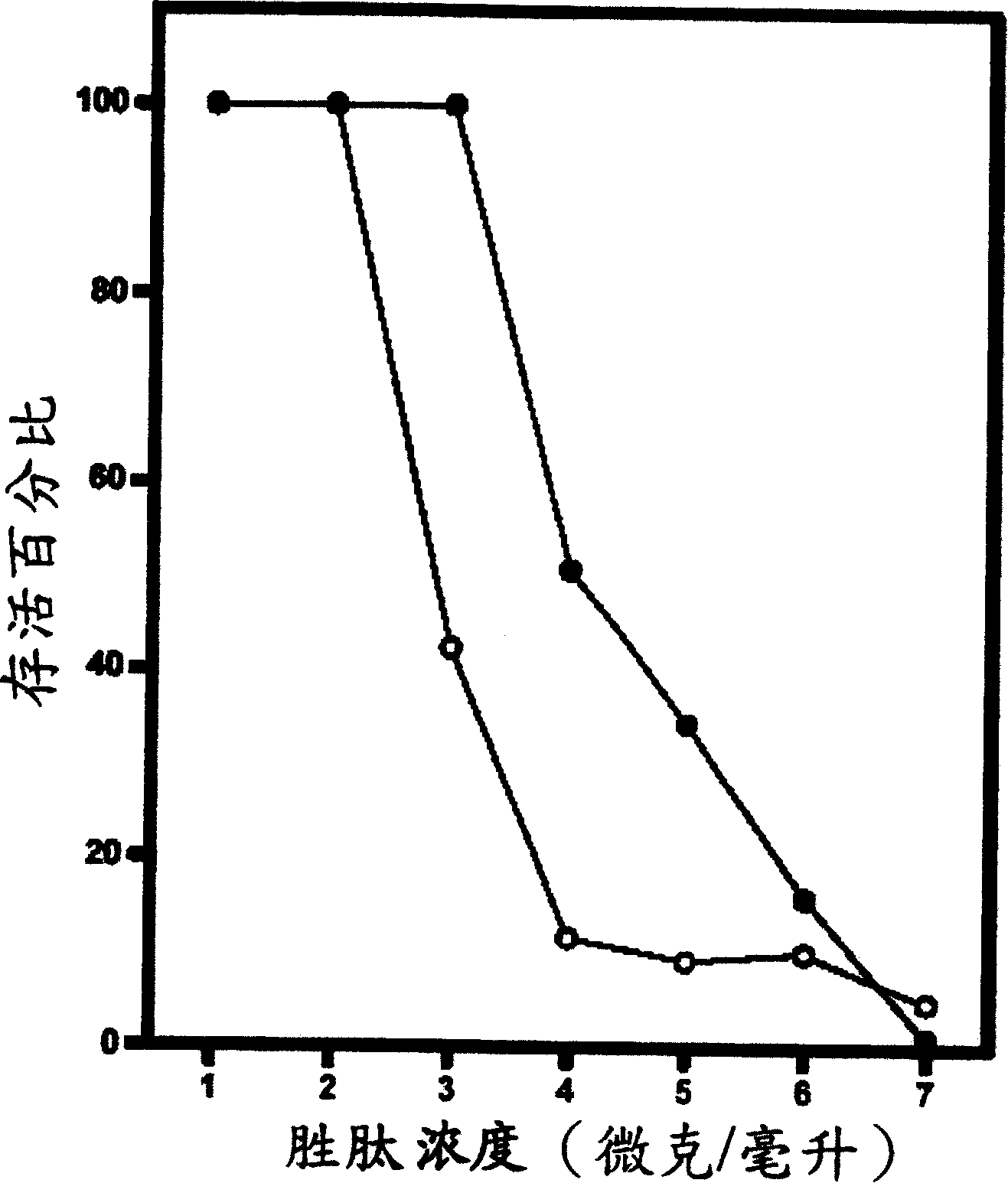
[0089] Example 2: In vitro peptide activity test
[0090] In general, in vitro peptide antibacterial activity can be tested using the standard National Council for Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS) bacterial inhibition assay or minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The so-called minimum inhibitory concentration refers to the minimum peptide concentration required to inhibit or reduce the growth of microorganisms. The organisms tested by the minimum inhibitory concentration analysis method are shown in Table 2:
[0091] Table II
[0092]
[0093]
[0094] Simply put, the overnight cultured bacterial solution was diluted with Meuller-Hinton growth medium to contain approximately 10 5 The inoculum of each colony; the peptide was also serially diluted twice, and then added to the diluted bacterial solution. After culturing at 37°C for 18 hours, analyze its turbidity; the minimum inhibitory concentration of each peptide was measured three times at different times, an...
Embodiment 3
[0100] Example 3: Analysis of Membrane Penetration
[0101] Peptide outer membrane penetration was determined by the 1-N-phenylnaphthylamine (NPN) uptake test. Intact Escherichia coli cell NPN shows weak fluorescence absorption in a liquid environment; while it has a strong absorption value in a water-repellent environment, thus indicating that the NPN is water-repellent and can be used to directly measure the degree of outer membrane penetration. Under normal circumstances, Escherichia coli absorbs little or no NPN; in the presence of some membrane-penetrating compounds (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, polymyxin B, neomycin or Antimicrobial peptides), NPN will partially penetrate the outer membrane of bacteria and cause an increase in fluorescence absorption.
[0102] The experimental steps are briefly described as follows: Add 1 ml of overnight cultured bacteria solution to 50 ml of culture solution, shake and culture at 37 degrees to OD 600 Equal to 0.4-0.6, centrifuge t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com