Crystalline glucose producing process based on whole membrane method
A technology for crystallized glucose and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of glucose, can solve the problems of not forming a crystallized glucose production process, and achieve the effects of saving equipment investment and operating costs, simplifying the process flow, and improving the quality of the filtrate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
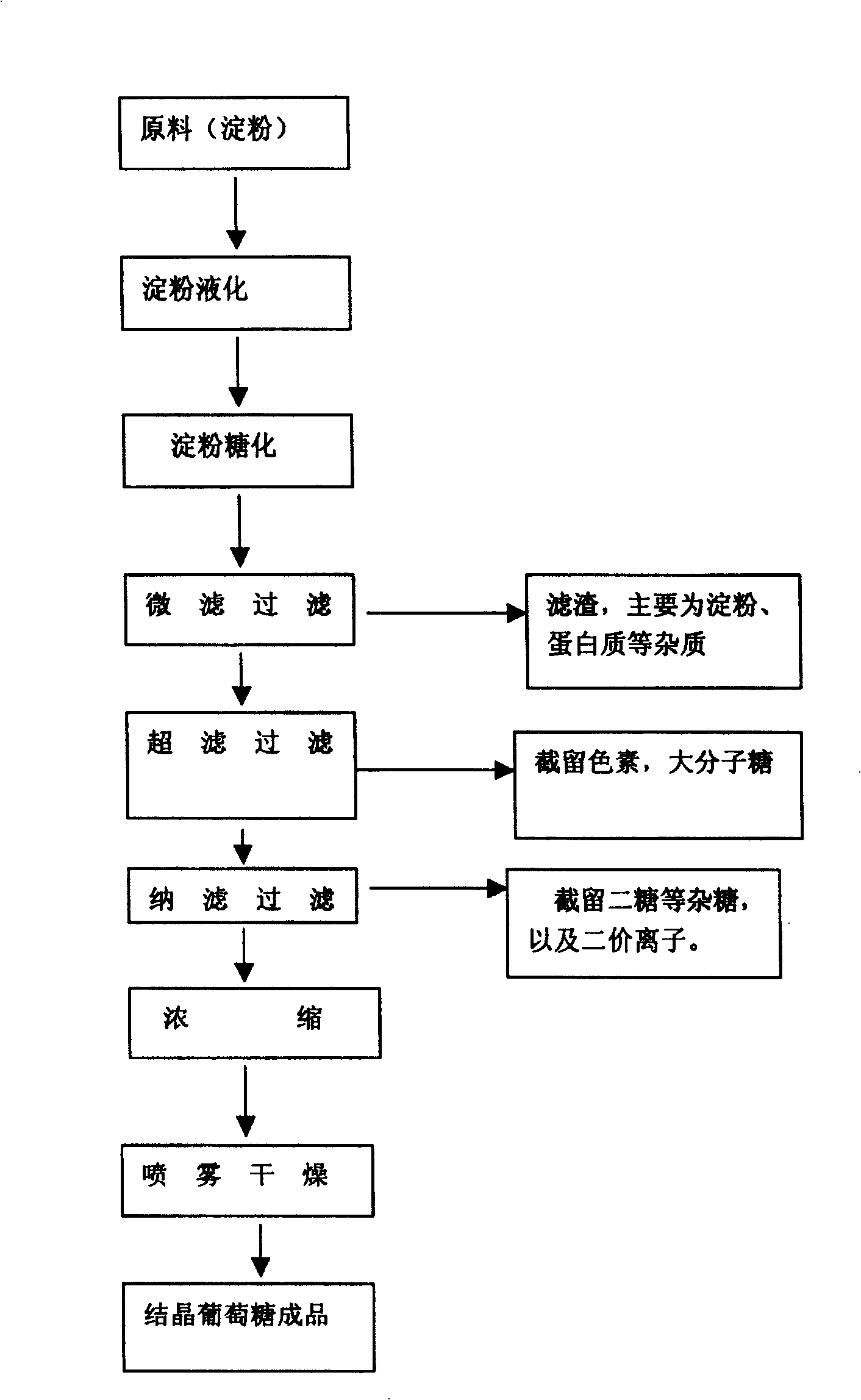
[0034] 1. Starch liquefaction: Mix 500Kg of raw starch with 1100Kg of water to prepare a 31% starch emulsion, then sterilize at 110-115°C to prepare a liquid starch emulsion for glucose production. Add α-high temperature liquefied amylase to the liquid starch material emulsion, and then hydrolyze it into a liquefied starch solution with a DE value (glucose value) of 14% to 25% (containing polysaccharides, dextrins, etc.).
[0035] 2. Saccharification: Cool the liquefied starch solution prepared in step 1 with a DE value (glucose value) between 14% and 25% to 35-38°C, then add compound glucoamylase and perform enzymatic hydrolysis under this temperature condition The liquefied starch solution was further enzymatically hydrolyzed into glucose. After 48 hours of enzymatic hydrolysis, the DE value of the saccharification solution was measured (or continuously measured) every 0.5 h. After 52 hours of enzymatic hydrolysis, when the DE value reached 98%, the enzymatic hydrolysis proc...
Embodiment 2
[0042] 1. Starch liquefaction: Mix 750Kg of raw starch with 1400Kg of water to prepare a 35% starch emulsion, then sterilize at 115°C to prepare a liquid starch emulsion for glucose production. Add α-high temperature liquefied amylase to the liquid starch material emulsion, and undergo a high-pressure injection of a liquefaction injector and a continuous liquefaction reaction with enzyme twice to hydrolyze it into polysaccharides and pastes with a DE value (glucose value) of 14% to 25%. Jing and so on.
[0043] 2. Saccharification: Cool the liquefied starch solution prepared in step 1 with a DE value (glucose value) between 14% and 25% to 40-42°C, then add compound glucoamylase and perform enzymatic hydrolysis under this temperature condition The liquefied starch solution was further enzymatically hydrolyzed into glucose. After 48 hours of enzymatic hydrolysis, the DE value of the saccharification solution was measured (or continuously measured) every 0.5 h. After 49 hours of ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] 1. Starch liquefaction: Mix 500Kg of raw starch with 1100Kg of water to prepare a 31% starch emulsion, then sterilize at 115°C to prepare a liquid starch emulsion for glucose production. Add high-temperature liquefied amylase to the liquid starch emulsion, and then hydrolyze it into polysaccharides and dextrins with a DE value (glucose value) of 14% to 25% through a high-pressure injection of a liquefaction injector and a continuous liquefaction reaction of adding enzyme twice. Wait.
[0051] 2. Saccharification: Cool the liquefied starch solution prepared in step 1 with a DE value (glucose value) between 14% and 25% to 42-45°C, then add compound glucoamylase and perform enzymatic hydrolysis under this temperature condition The liquefied starch solution was further enzymatically hydrolyzed into glucose. After 48 hours of enzymatic hydrolysis, the DE value of the saccharification solution was measured (or continuously measured) every 0.5 h. After 61 hours, when the measu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com