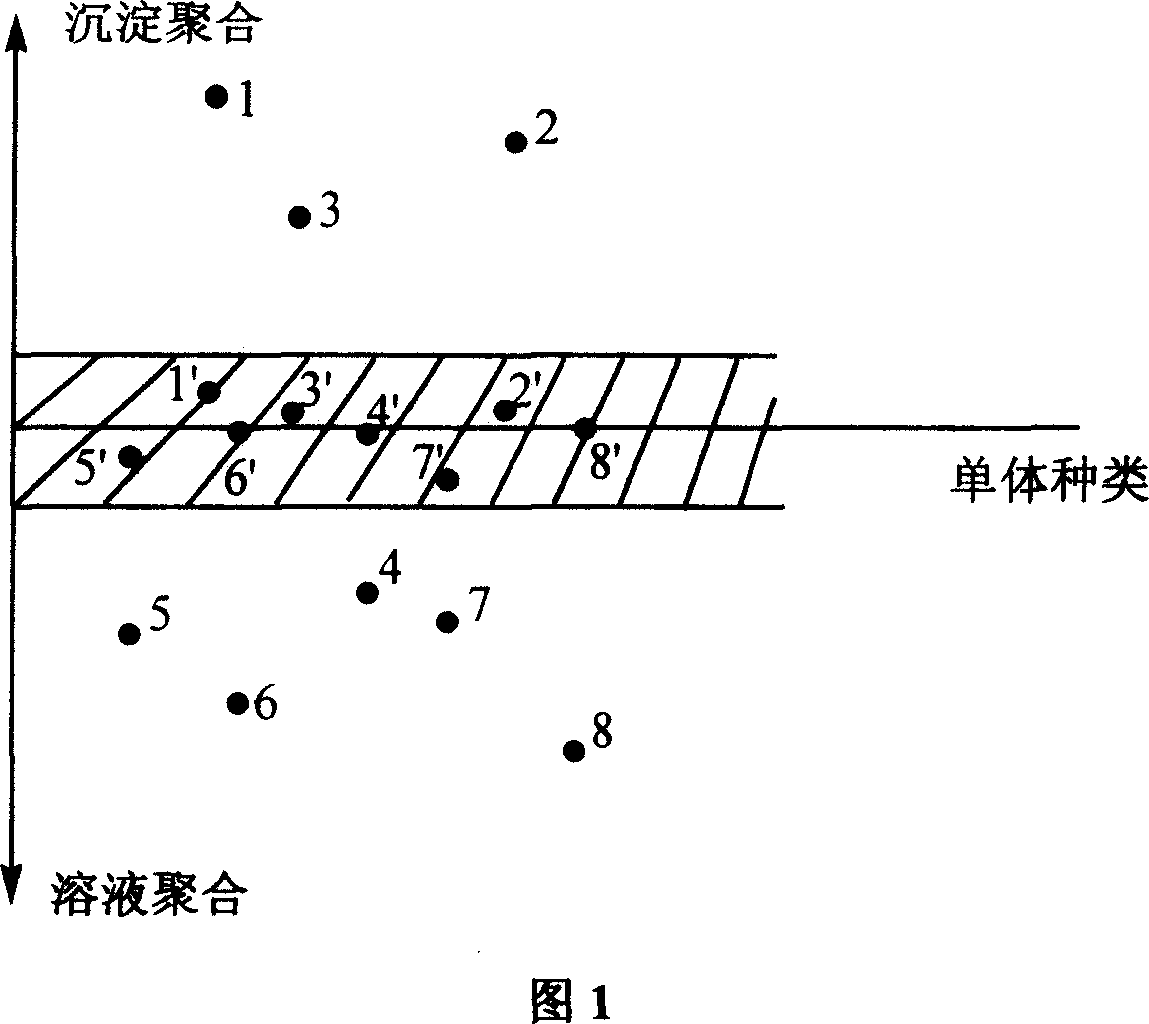
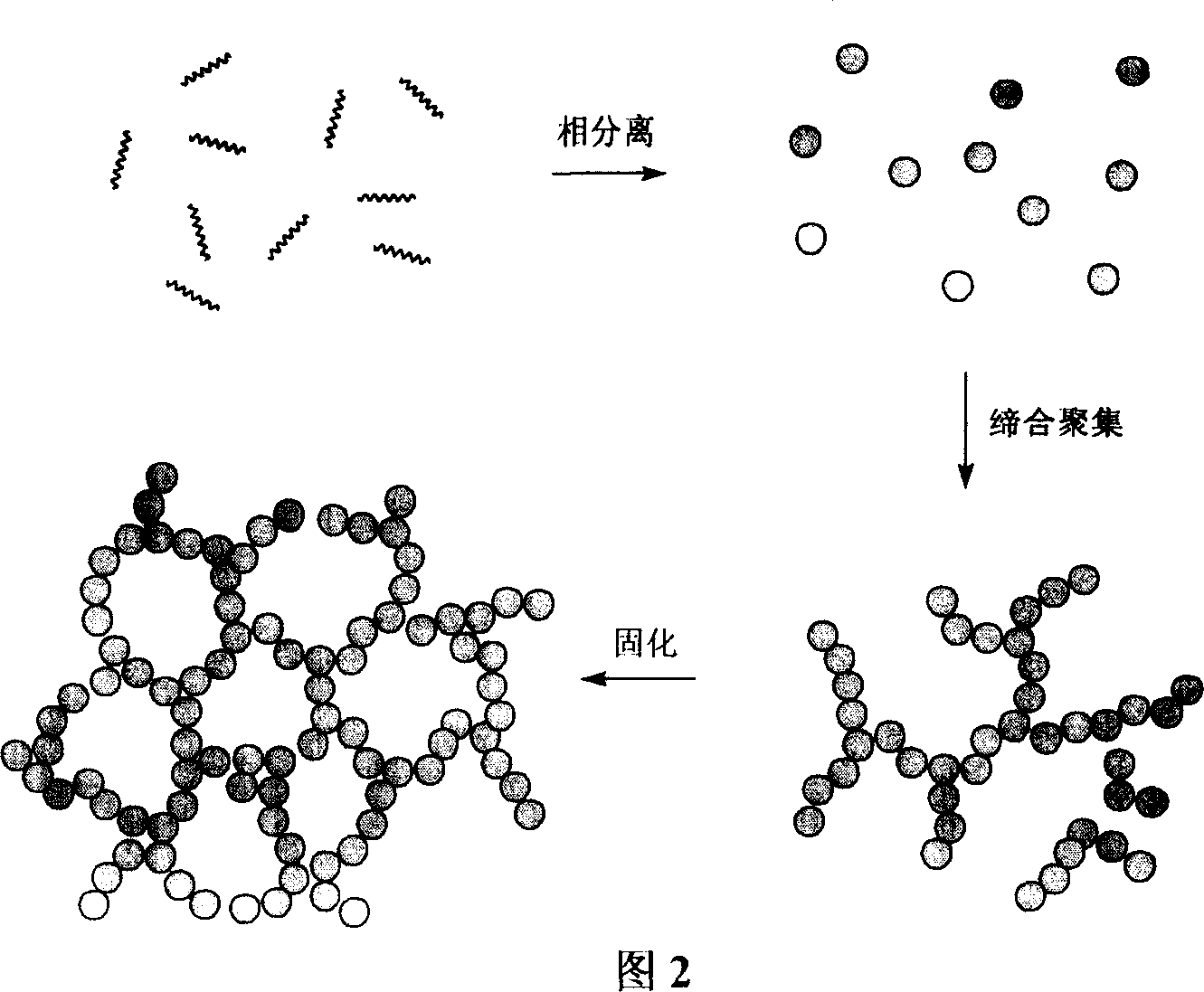
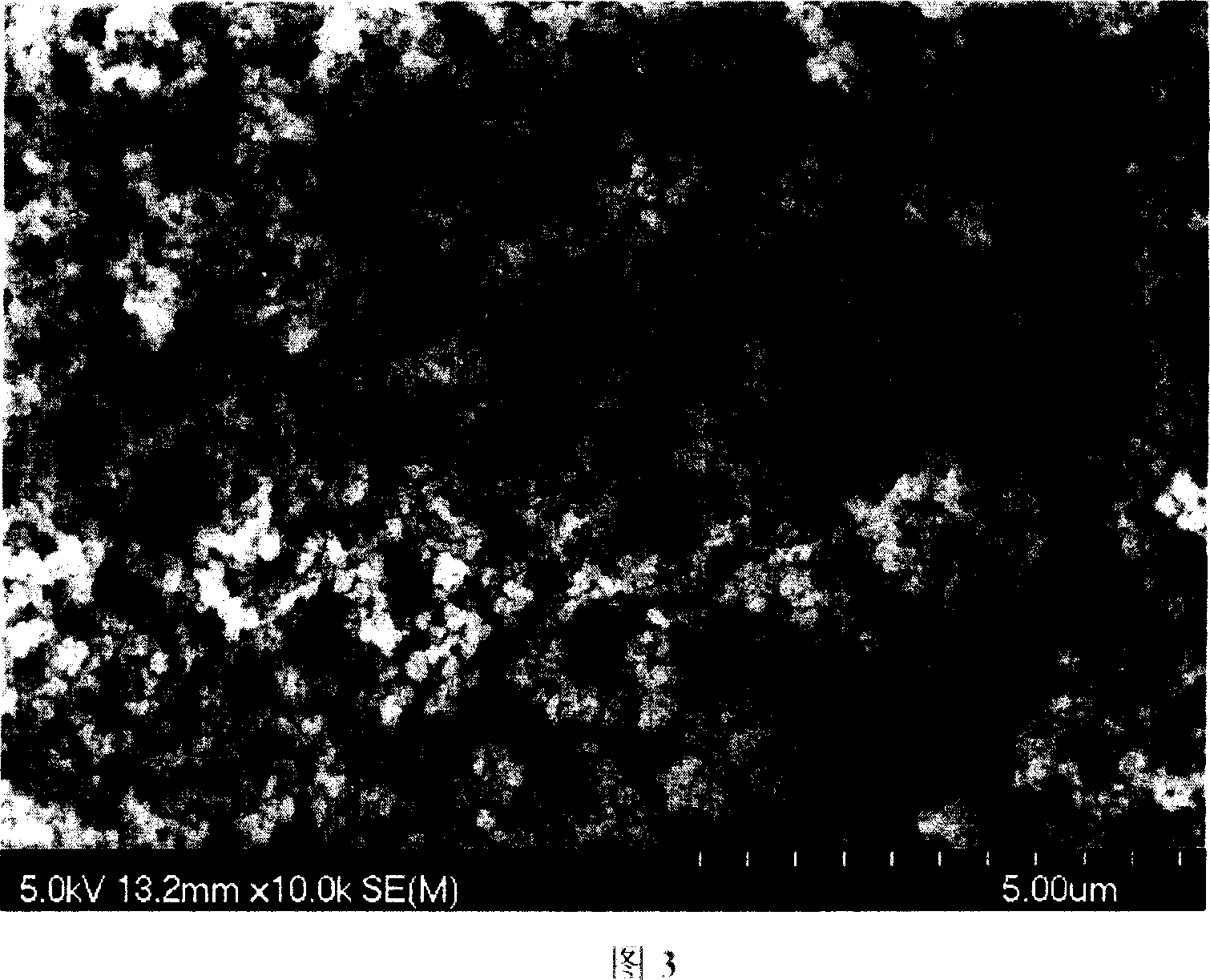
Method of preparing line type polyolefin cellular material
A linear polyolefin and porous material technology, applied in the field of linear olefin polymer porous materials, can solve the problems of difficulty in obtaining bulk porous polymer materials and narrow technical application areas, achieving unlimited shape, simple preparation and molding technology, Versatile effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Slowly add the olefinic monomer containing the initiator: 10 grams of styrene (S) is dissolved in 30 grams of polyethylene glycol 1000 and 10 grams of dioxane medium to obtain a clear solution, and react and polymerize at 60 ° C for at least 6 hours , the viscosity of the solution increases continuously, and then phase separation gradually occurs. During the phase separation, the system gradually turns milky white, and finally condenses into a jelly-like block. Put it into water, dissolve and remove polyethylene glycol, etc., to obtain a linear Polyolefin porous material. In the polymerization process, if the decomposition activation energy of the initiator is too high or the half-life is too long, the decomposition rate will be too low, which will prolong the polymerization time. However, if the activation energy is too low or the half-life is too short, the initiation is too fast, the temperature is difficult to control, and implosion may be caused; or the initiator d...
Embodiment 2~4
[0032] Slowly add the olefinic monomer containing initiator dibenzoyl peroxide (BPO): 10 grams of styrene (S) are dissolved in 30 grams of polyethylene glycol 1000 and dioxane mixed medium to obtain a clear solution. 60 ℃ constant temperature reaction polymerization for at least 6 hours, the viscosity of the solution increases continuously, then phase separation gradually occurs, forming a white gel, and finally solidifies into a block, put the solid into water, dissolve and remove polyethylene glycol, etc., to obtain a linear Polyolefin porous material. The weights of dioxane were 6 grams, 8 grams, and 12 grams respectively. The rest of the conditions and operations were the same as those in Example 1, and the corresponding linear polyolefin porous materials were prepared. The pore diameters are shown in Table 1.
[0033] Example 1
Embodiment 5
[0035] Slowly add olefinic monomers containing initiator azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN): 10 grams of acrylonitrile (AN) dissolved in 30 grams of polyethylene glycol 1000 and 8 grams of dimethylformamide (DMF) medium, Obtain a clear solution, react and polymerize at a constant temperature of 65°C for at least 6 hours, the viscosity of the solution increases continuously, then phase separation gradually occurs, forming a white gel, and finally solidifies into a block, put the solid into water, dissolve and remove polyethylene glycol etc. to obtain linear polyolefin porous materials. The average pore diameter is 0.45 μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com