Hydrothermal synthesis method for lithium ion-cell anode material of ferric phosphate lithium
A technology of lithium ion battery and hydrothermal synthesis method, which is applied in the field of phosphate, can solve the problems of poor electrochemical performance, impure phase, and uneven particle size, and achieve improved electronic conductivity, good batch stability, and particle size The effect of uniform diameter distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
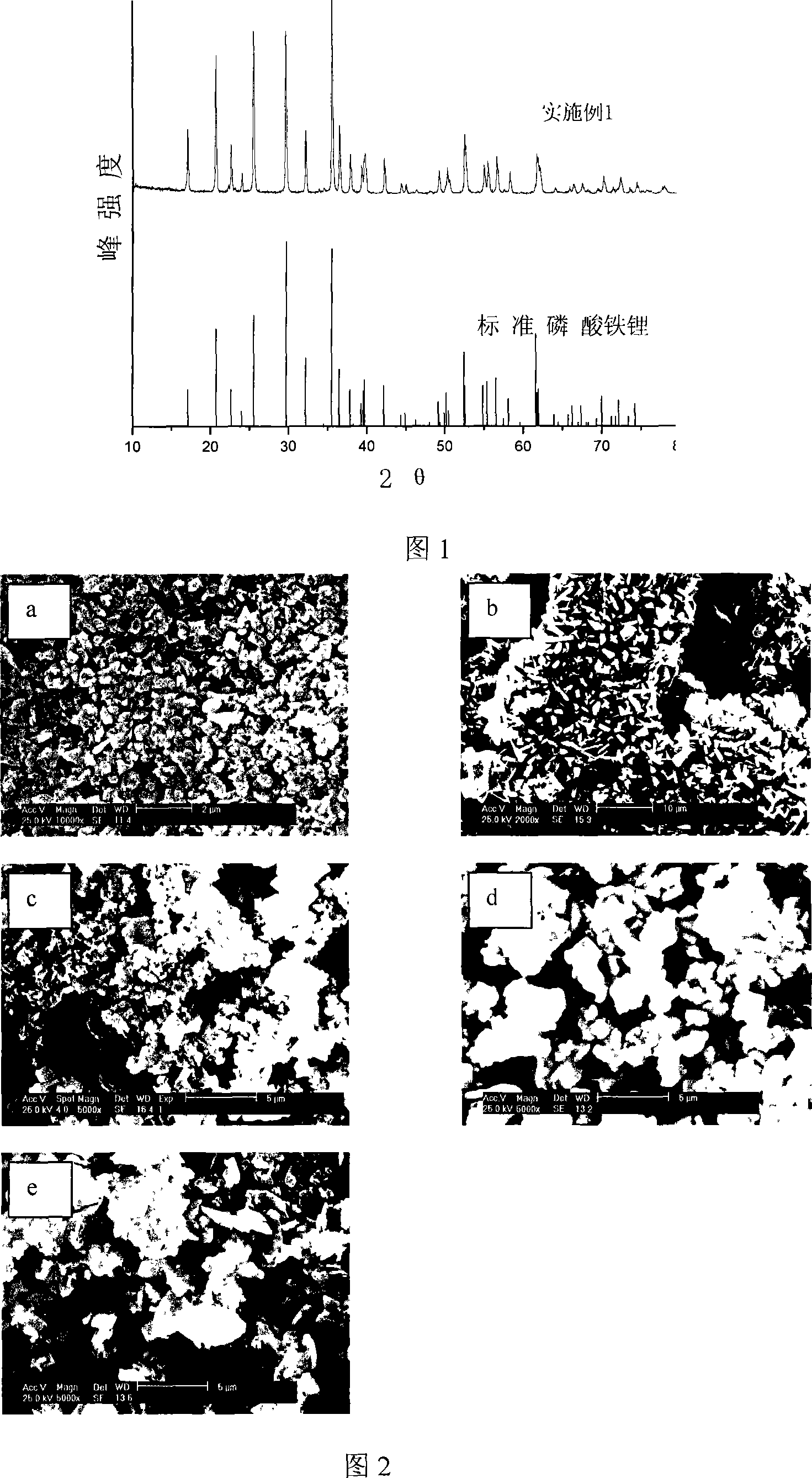
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The first step, hydrothermal synthesis reaction
[0033] 973g or 3.5mol of FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in water and diluted to 3.5L. After standing for 12 hours, filtered to remove a small amount of precipitate; 408g of 85% phosphoric acid containing 3.5mol of pure phosphoric acid was dissolved in water and diluted to 0.5L; 442g That is, 10.5mol of LiOH·H 2 O was dissolved in water and diluted to 3L.
[0034]Add the above-mentioned phosphoric acid solution and lithium hydroxide solution into a 10L autoclave, then add 2g of cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and 0.5g of nonionic surfactant octylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, and use an inert After the air in the dead volume in the autoclave is purged by gas, the autoclave is sealed, heated to 45 ° C under stirring at 200 rpm, the feed valve and the exhaust valve are opened, and pure ferrous salt solution is added, then the autoclave is sealed, and the 150°C, react for 300 minutes, at this time, the co...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Except that the reaction temperature in the first step of Example 1 was changed to 180° C., the corresponding autogenous pressure was 1.0 Mpa, and the reaction time was changed to 30 minutes, the others were the same as in Example 1.
[0045] The morphology of the product obtained in this embodiment is the same as that in Example 1. The electrochemical performance test method of the product of this embodiment is the same as that of Example 1, and the test results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0060] The first step, hydrothermal synthesis reaction
[0061] 795g or 4mol of FeCl 2 4H 2 O dissolved in water and diluted to 4L, after standing for 12 hours, filtered; 484g of 85% phosphoric acid was dissolved in water and diluted to 1.5L, wherein the pure phosphoric acid was 4.2mol; 2 O was dissolved in water and diluted to 2.5 L.
[0062] Add above-mentioned phosphoric acid solution and lithium hydroxide solution in the autoclave of 10L, then add 1.6g cationic surfactant bis-octyl dimethyl ammonium bromide and 0.8g nonionic surfactant nonylphenol polyoxyethylene ether, After purging the air in the dead volume of the autoclave with an inert gas, seal the autoclave, heat it to 40°C under stirring at 200rpm, open the feed valve and exhaust valve, then add pure ferrous salt solution, and then seal the autoclave , at 140°C, reacted for 480 minutes, the corresponding autogenous pressure was 0.36Mpa, and the Li:Fe:P molar ratio was 3.15:1:1.06. When the reaction was started, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com