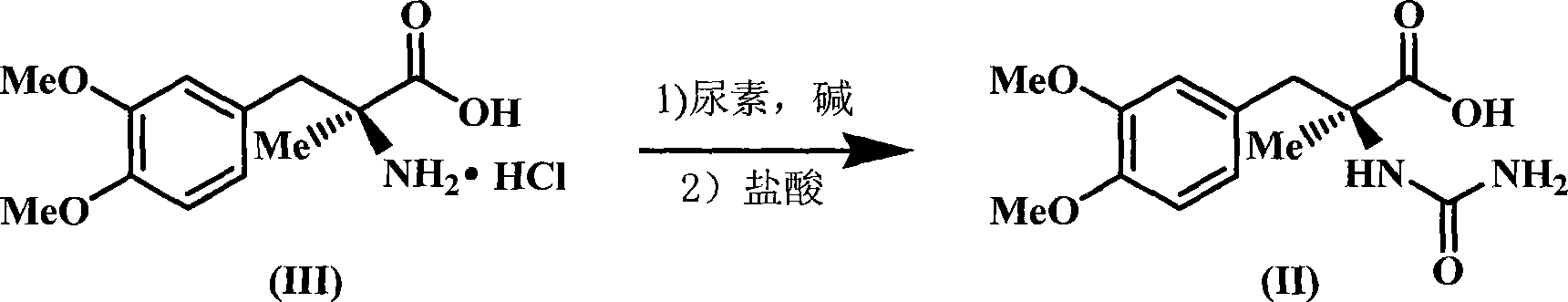
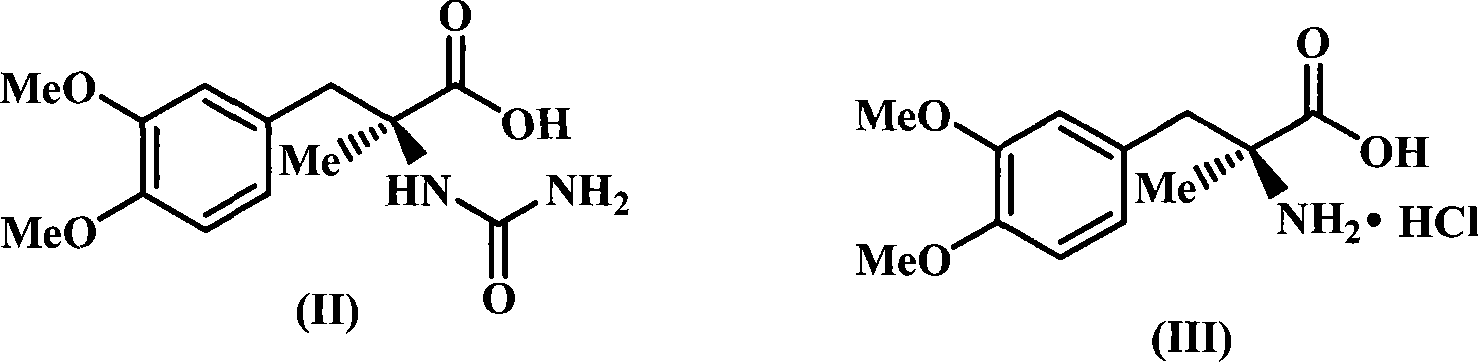Green synthesis of carbidopa midbody
A synthetic method, carbidopa technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of organic compounds, preparation of urea derivatives, etc., can solve the problems of high industrial production cost, troublesome handling, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve low production cost , raw materials are cheap, and the raw materials are easy to obtain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] The molar ratio of the feed material is (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride: urea: alkali=1: 1.5: 1.5, and the alkali is barium hydroxide, The solvent is water, and its dosage is 4 times the mass of (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride.
[0021] In a 500mL three-neck flask equipped with a thermometer, reflux condenser and mechanical stirring, add (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride (27.5g, 0.1 mol), urea (9.0g, 0.15mol), alkali (25.7g, 0.15mol), water (110g), start stirring and heating, control the temperature at 100°C, and stir for 3 hours. After cooling, it was acidified with 25% hydrochloric acid until the pH value was 2.5, a large amount of solids were precipitated, continued to stir for 30 minutes, filtered, and the solids were recrystallized with 80% ethanol to obtain a white solid, 14.1g, yield 50%, melting point: 205.0-205.4°C, HPLC purity 99.0%.
Embodiment 2
[0023] The molar ratio of the feed material is (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride: urea: alkali=1: 3.0: 2.0, and the alkali is barium hydroxide, The solvent is water, and its dosage is 6 times the mass of (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride.
[0024] In a 500mL three-neck flask equipped with a thermometer, reflux condenser and mechanical stirring, add (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride (27.5g, 0.1 mol), urea (18.0g, 0.3mol), alkali (34.2g, 0.2mol), water (110g), start stirring and heating, control the temperature at 100°C, and stir for 5 hours. After cooling, it was acidified with 20% hydrochloric acid until the pH value was 3, a large amount of solids were precipitated, continued to stir for 30 minutes, filtered, and the solids were recrystallized with 95% ethanol to obtain a white solid, 15.8g, yield 56%, melting point: 205.2-205.5°C, HPLC purity 99.1%.
Embodiment 3
[0026] The molar ratio of the feed material is (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride: urea: alkali=1: 6.0: 2.5, and the alkali is barium hydroxide, The solvent is water, and the amount used is 10 times the mass of (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride.
[0027] In a 500mL three-neck flask equipped with a thermometer, reflux condenser and mechanical stirring, add (S)-2-(3,4-dimethoxybenzyl)-2-aminopropionic acid hydrochloride (27.5g , 0.1mol), urea (36.0g, 0.6mol), alkali (42.75g, 0.25mol), water (275g), start stirring and heating, control the temperature at 100°C, and react for 4 hours. After cooling, it was acidified with 31% hydrochloric acid until the pH value was 2, a large amount of solids were precipitated, continued stirring for 30 minutes, filtered, and the solids were recrystallized with 50% ethanol to obtain a white solid, 18.33g, yield 65%, melting point: 205.0-205.4°C, HPLC purity 99.0%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com