Method for accelerating selective non-catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides
A nitrogen oxide, non-catalytic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, dispersed particle separation, etc., can solve the problems of low denitration efficiency of SNCR technology, limited residence time of reducing agent, narrow temperature range, etc. Shorter time, simple transformation, and the effect of widening the temperature range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
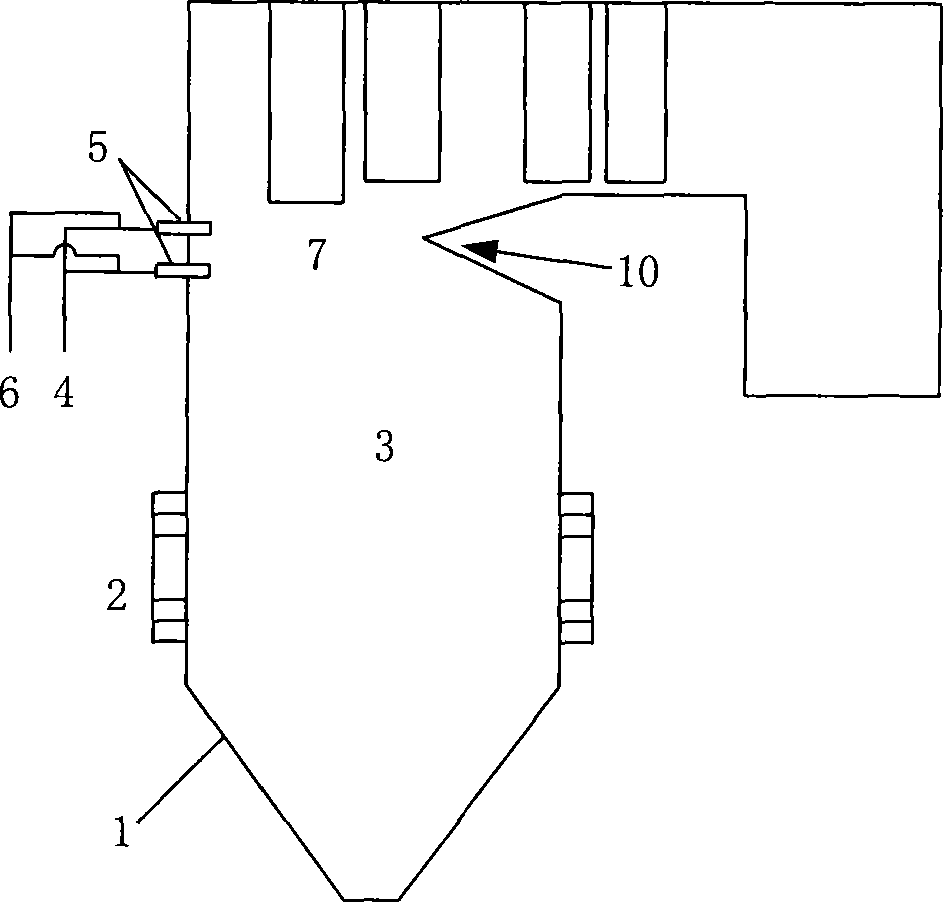
[0030] A method for promoting SNCR denitrification process by adding superfine coal powder additive, comprising SNCR reducing agent supply device 4, reducing agent nozzle 5, superfine coal powder additive supply device 6.
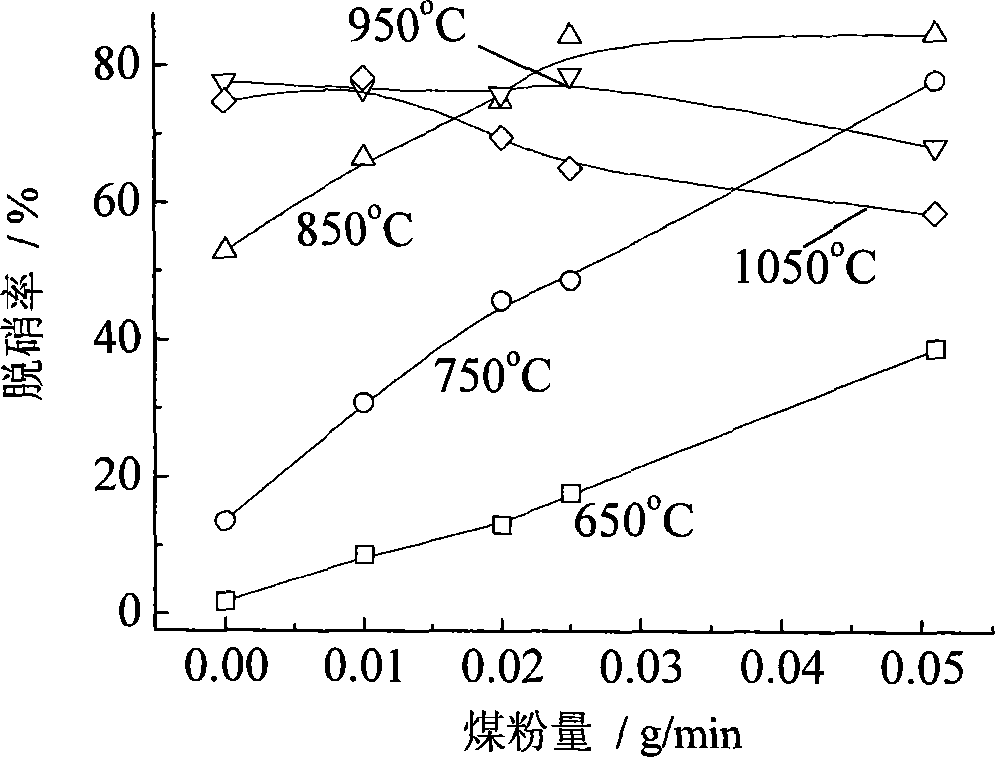
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the fuel burns inside the furnace 3 to generate flue gas containing NOx. The temperature of the flue gas drops to about 1000°C at the position of the folded flame angle 10, reaching a temperature suitable for the SNCR reaction. After that, the flue gas flows into the convective heat exchange zone. The temperature dropped rapidly and dropped to less than 900°C at the rear of the secondary superheater, leaving the optimum SNCR reaction temperature range. The reductant nozzle 5 is arranged at the position of the deflection angle 10, the reductant is supplied by the reductant supply device 4 and injected into the SNCR reaction zone 7 through the nozzle 5, and the injected amount of the SNCR reductant is expressed as NH 3 The m...
Embodiment 2
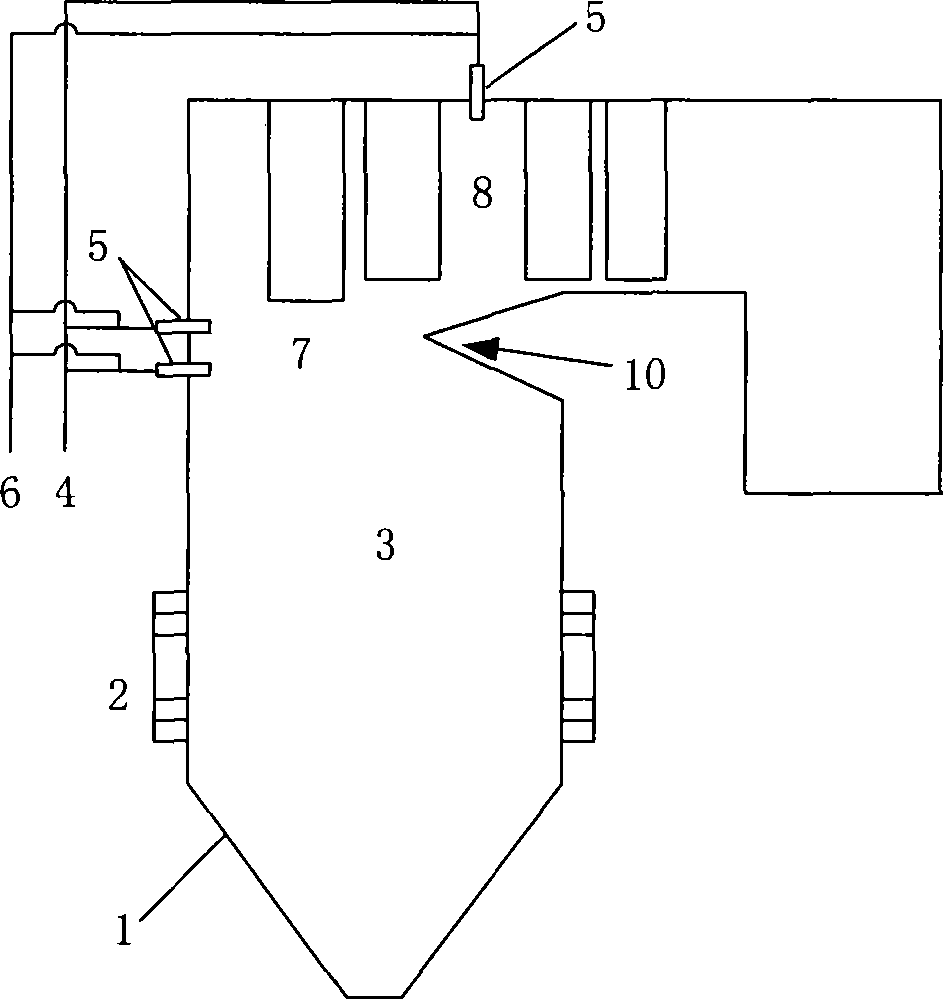
[0034] A process for adding natural gas additives to promote SNCR denitrification process, comprising SNCR reducing agent supply device 4, reducing agent nozzle 5, and natural gas additive supply device 6.
[0035] Such as image 3 As shown, the fuel burns inside the furnace 3 to generate flue gas containing NOx. The temperature of the flue gas drops to about 1000°C at the position of the folded flame angle 10 and reaches a temperature suitable for the SNCR reaction. After that, the flue gas flows into the rear part of the reaction zone 8 , the temperature drops rapidly, and drops to less than 900°C at the rear of the secondary superheater, leaving the optimum SNCR reaction temperature range. A multi-layer reducing agent nozzle 5 is arranged at the position of the deflection angle 10 and between the superheater and the reheater. The reducing agent is supplied by the reducing agent supply device 4 and injected into the SNCR reaction zone 7 and the rear part of the reaction zone...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A process for adding syngas additives to promote SNCR denitrification process, comprising SNCR reducing agent supply device 4 and reducing agent nozzle 5, syngas additive supply device 6 and additive nozzle 9.
[0039] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the fuel burns inside the furnace 3 to generate flue gas containing NOx. The temperature of the flue gas drops to about 1000°C at the position of the folded flame angle 10 and reaches a temperature suitable for the SNCR reaction. After that, the flue gas flows into the rear part of the reaction zone 8 , the temperature drops rapidly, and drops to less than 900°C at the rear of the secondary superheater, leaving the optimum SNCR reaction temperature range. The reducing agent nozzle 5 is arranged at the position of the deflection angle 10. The reducing agent is supplied by the reducing agent supply device 4 and sprayed into the SNCR reaction zone 7 through the reducing agent nozzle 5. The injection amount of the SNCR reducing age...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com