Photochemical reduction method for treating chromium-containing waste water without additional reducing agent and sacrificial agent
A sacrificial agent and reducing agent technology, used in chemical instruments and methods, reduced water/sewage treatment, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc. Broad application prospects and the effect of improving utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
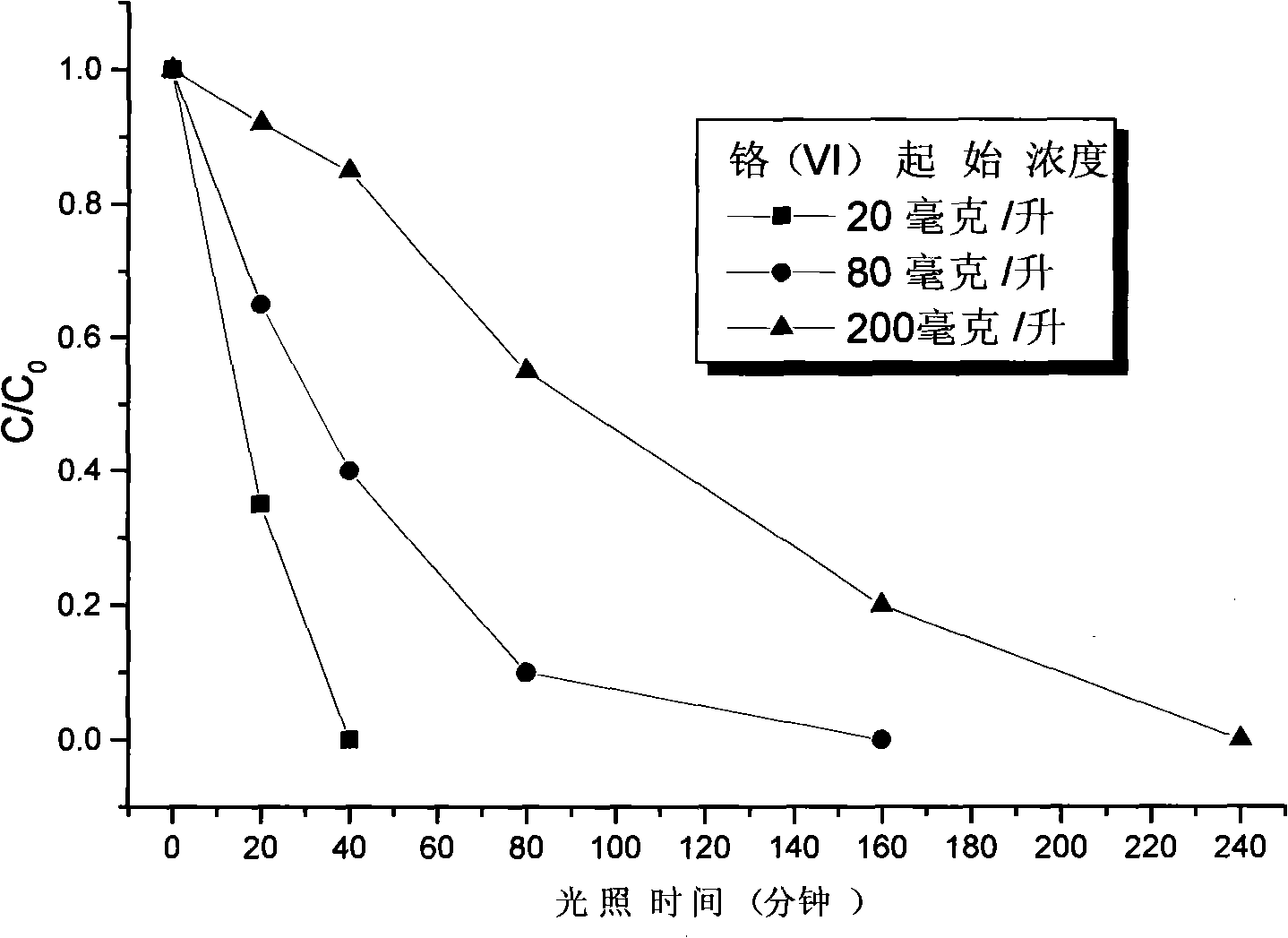
[0024] Add 50 ml of simulated hexavalent chromium-containing wastewater containing potassium dichromate at a concentration of 20, 80, and 200 mg / liter (calculated as chromium mass) into three glass reactors, and add nitrogen-fluorine co-doped titanium dioxide nanometer visible light Catalyst 50 milligrams (consumption amount 1 gram / liter contains hexavalent chromium wastewater), adjusts the pH value of simulated hexavalent chromium-containing wastewater with sulfuric acid to be 1.5, magnetically stirs and disperses the catalyst, the artificial light source used is a 500W xenon lamp, and a cut-off filter of 450nm is configured. Light sheet, turn on the light source and irradiate with visible light for 240 minutes, so that the nitrogen-fluorine co-doped titanium dioxide nano-visible light photocatalyst is excited by visible light to undergo charge separation, and the generated conduction band electrons are used to reduce the highly toxic hexavalent chromium in the water body to lo...
Embodiment 2
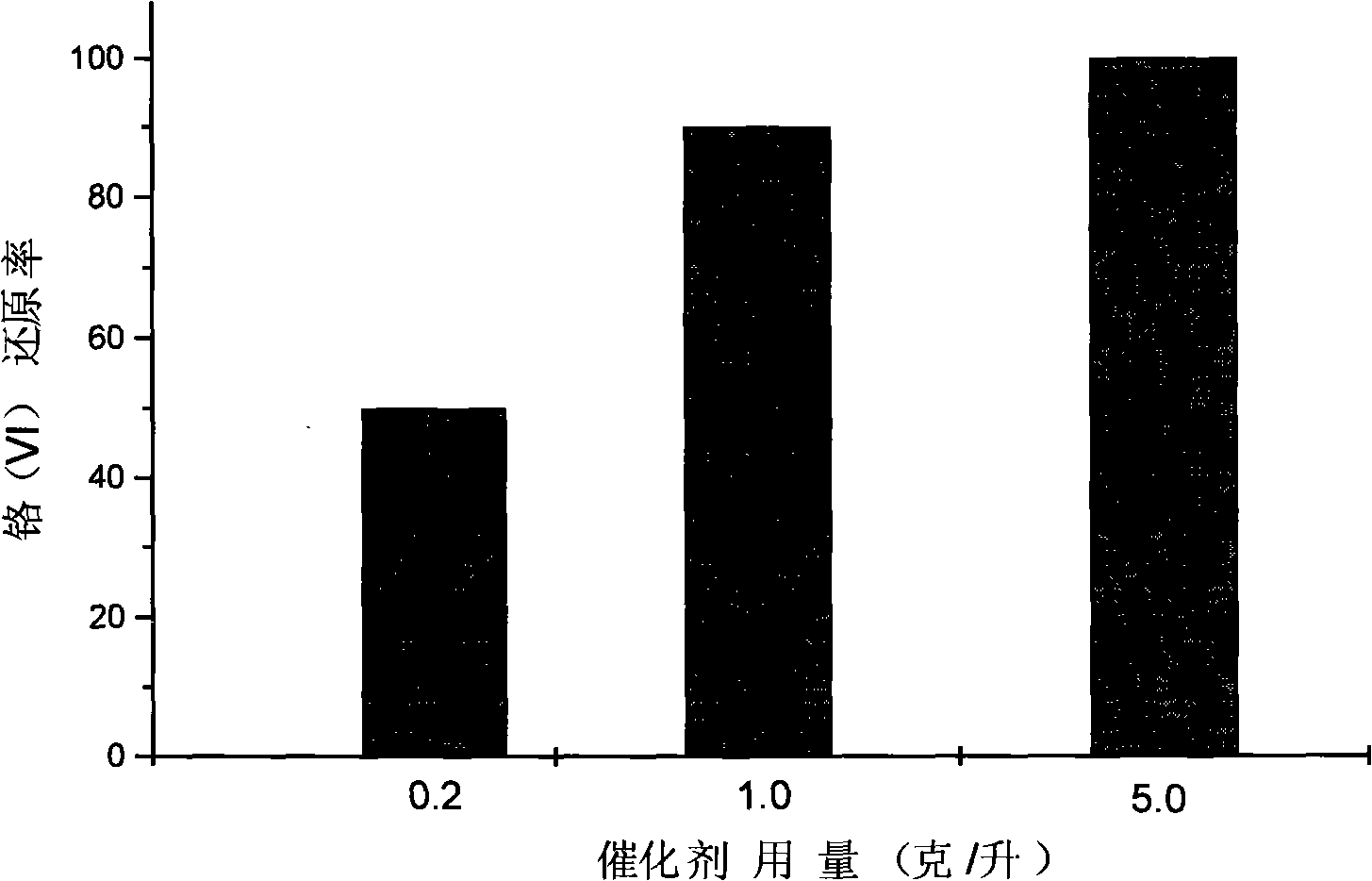
[0026] In three glass reactors, add respectively 50 milliliters of simulated waste water containing hexavalent chromium containing potassium dichromate concentration of 40 mg / liter (calculated in terms of chromium mass), and add respectively nitrogen-fluorine co-doped Titanium dioxide nano-visible light photocatalyst, the dosage is 0.2 g / L waste water containing hexavalent chromium, 1 g / L waste water containing hexavalent chromium, 5 g / L waste water containing hexavalent chromium, and sulfuric acid is used to adjust the pH of the simulated waste water containing hexavalent chromium The value is 2.0, and magnetic stirring is used to disperse the catalyst. The artificial light source used is a 500W xenon lamp, equipped with a 450nm cut-off filter, and the light source is turned on to irradiate with visible light for 60 minutes, so that the titanium dioxide nano-visible light photocatalyst co-doped with nitrogen and fluorine is excited by visible light and undergoes charge separati...
Embodiment 3
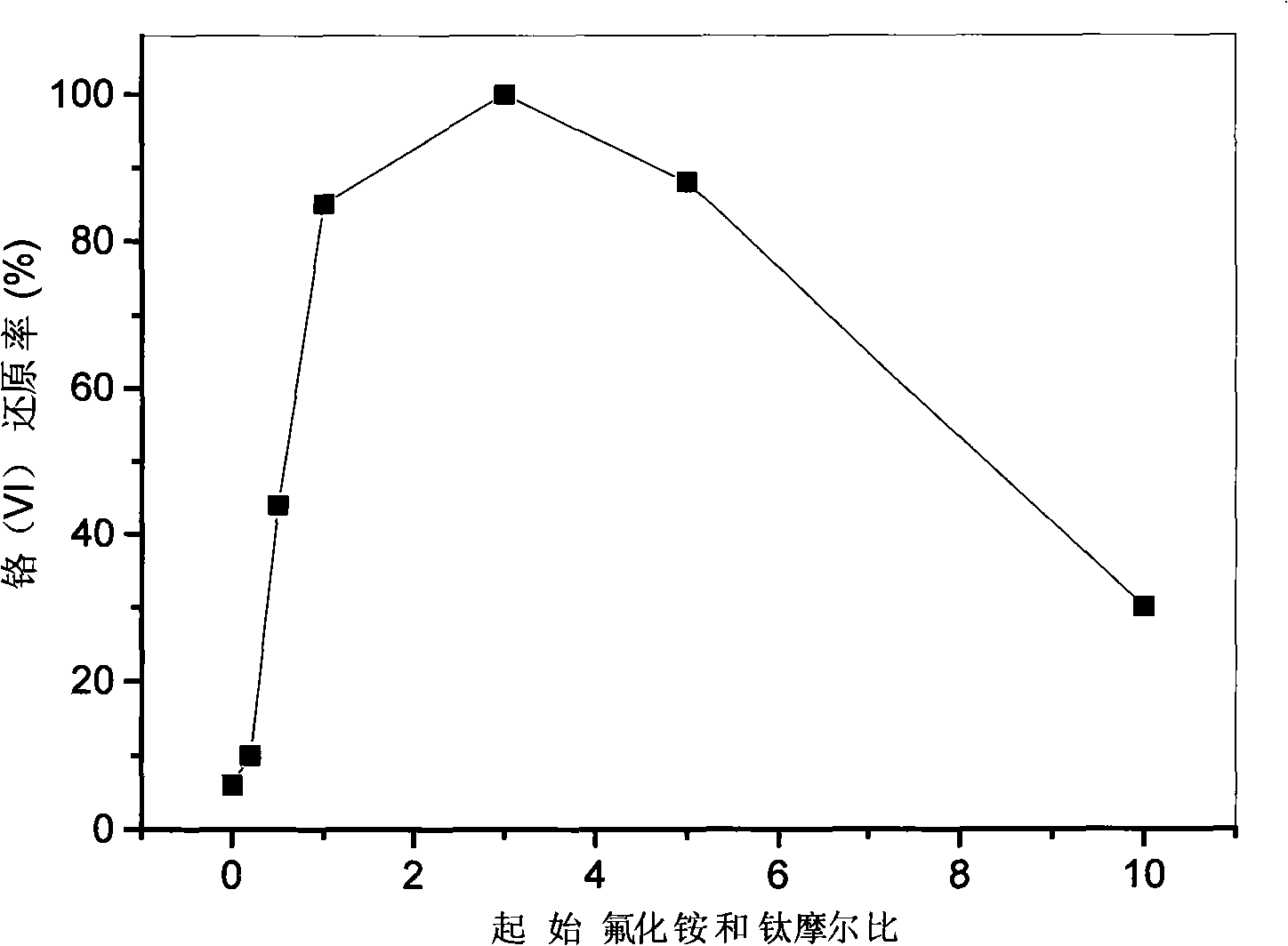
[0028] In a glass reactor, add 50 milligrams of simulated waste water containing hexavalent chromium containing potassium dichromate concentration of 20 mg / liter (calculated in terms of chromium quality), and add 50 milligrams of titanium dioxide nanometer visible light photocatalysts mixed with nitrogen and fluorine (amount of 1 g / L waste water containing hexavalent chromium), use hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value of the simulated waste water containing hexavalent chromium to 1.0, and magnetically stir to disperse the catalyst. The light source is irradiated with visible light for 100 minutes, so that the nitrogen-fluorine co-doped titanium dioxide nano-visible light photocatalyst is excited by visible light to undergo charge separation, and the generated conduction band electrons are used to reduce the highly toxic hexavalent chromium in the water body to low-toxic trivalent chromium, while the valence band is empty. The holes were trapped by the hole scavenger water, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com