Preparation of strontium-barium titanate film material
A strontium barium titanate thin film and substrate technology, which is applied in metal material coating process, gaseous chemical plating, coating, etc., can solve the problems of slow growth rate, deviation of film composition, and large distance of process compatibility, etc. , to achieve excellent ferroelectric properties, uniform particle size, and eliminate the effect of crystal nucleus formation and diffusion process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] The cleaned (001)SrTiO 3 The substrate is placed in the reaction chamber, and argon gas is introduced to keep the pressure in the reaction chamber at 1 Torr, and the cooling water of the system is connected, and the water temperature is kept at 25°C. The temperature of the substrate was raised to 1000° C. and maintained for 1 minute, and the substrate was cleaned. Then the temperature of the substrate was lowered to 900° C., kept for 2 minutes and oxygen was introduced at the same time, the flow rate was 120 sccm, the pressure was stabilized at 2 Torr, and the substrate was oxidized under a mixed atmosphere of argon and oxygen.
[0026] One-stage growth of BST film: In situ, the oxidized substrate is lowered to 650°C for 50 minutes, and the precursor Ba(dfhd) is introduced at the same time 2 (tetraglyme), Sr (dfhd) 2 (tetraglyme) and TTIP-Ti(OC3H7) 4 , respectively as sources of Ba, Sr and Ti; the flow rates were 60 sccm, 60 sccm, and 20 sccm; the temperatures of the...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The rest of the growth conditions are the same as in Example 1, except that the growth of the film is a two-stage growth, that is, the nucleation stage is 650°C, and after holding for 20 minutes, the temperature is rapidly raised at a rate of 200°C / s, and the temperature is raised to 800°C. 30 minutes for film growth. Then the oxygen was turned off, and the BST film sample in the reaction chamber was lowered to room temperature in an argon atmosphere. Finally, the BST film samples were heat-treated according to the above method §6.
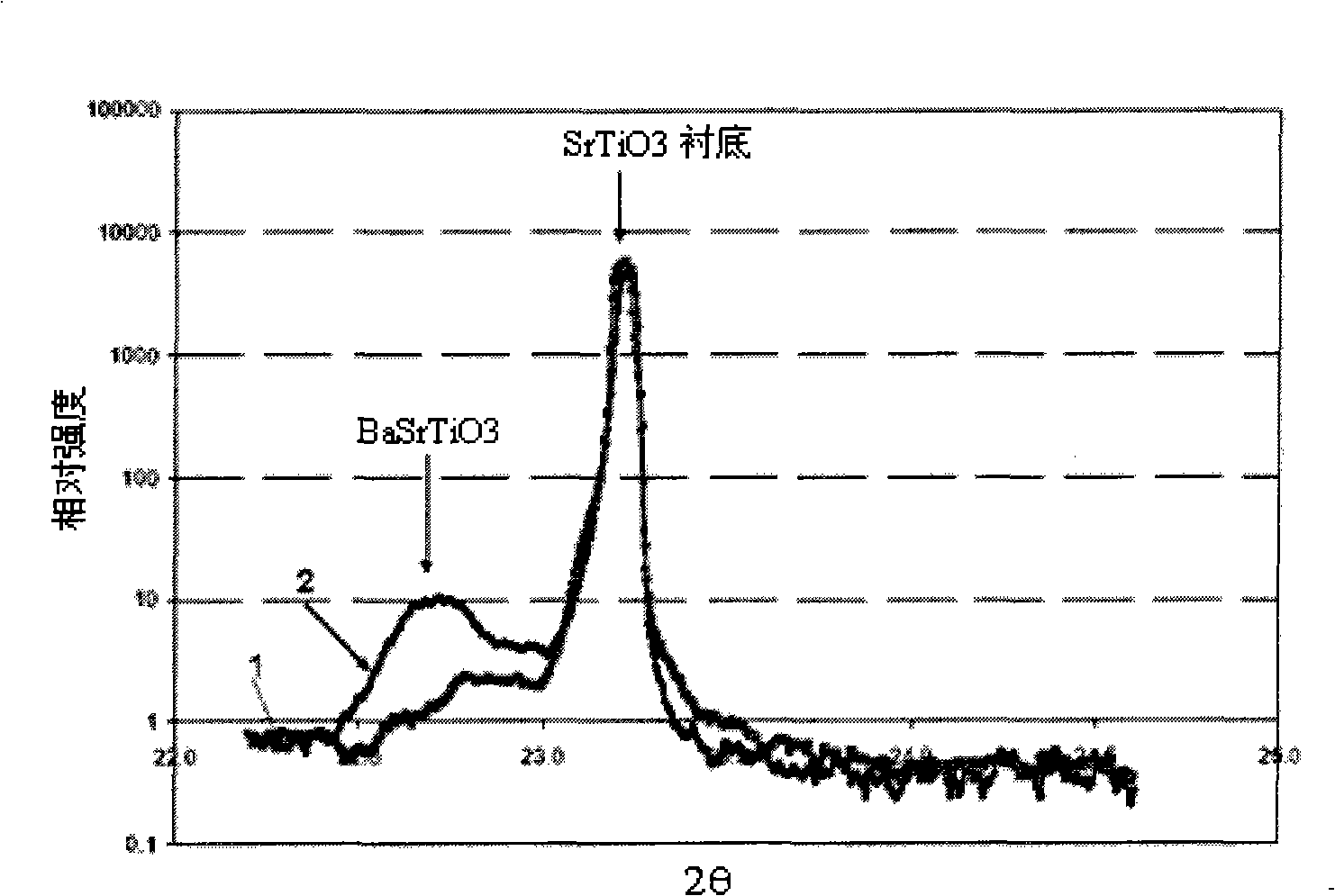
[0029] See figure 1 , it can be seen from the figure that the diffraction peak intensity (curve 1) of the BST film grown in one stage at 650°C is weaker than that of the BST film grown in two stages (curve 2), indicating that BST is in the growth stage at 650°C. The nuclear stage is in the growth stage at 800°C.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The cleaned (001)SrTiO3 The substrate is placed in the reaction chamber, and argon gas is introduced to keep the pressure in the reaction chamber at 3 Torr, and the cooling water of the system is connected to keep the water temperature at 25°C. The temperature of the substrate was raised to 1000° C. and maintained for 3 minutes, and the substrate was cleaned. Then the temperature of the substrate was lowered to 900° C., kept for 2 minutes and oxygen gas was introduced at the same time, the flow rate was 150 sccm, the pressure was stabilized at 4 Torr, and the substrate was oxidized under a mixed atmosphere of argon and oxygen.
[0032] Then lower the temperature to 650°C and keep it for 20 minutes while feeding the precursor Ba(dfhd) 2 (tetraglyme), Sr (dfhd) 2 (tetraglyme) and TTIP-Ti(OC3H7) 4 , respectively as sources of Ba, Sr and Ti; the flow rates were 60 sccm, 60 sccm, and 20 sccm; the temperatures of the sources were 125°C, 125°C, and 70°C, respectively. The t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com