Preparation of antibacterial nano filter membrance
A nanofiltration membrane and antibacterial technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of antibacterial nanofiltration membranes, can solve the problems of complex preparation process, and achieve the effects of simple process, excellent performance and excellent antibacterial performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] 1. After cleaning the polyethersulfone-based membrane with pure water, soak it in pure water for 10 hours, and change the water every 2 hours in between.
[0023] 2. Immerse the base film treated in step 1 in a solution of sodium polystyrene sulfonate with a concentration of 0.05mol / L for 20min, wash with pure water, and soak it for 20min; the immersion concentration is 0.05mol / L polydiallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride solution for 20min, washed with pure water, soaked for 20min. The above steps are repeated until a polyelectrolyte primary layer consisting of three layers of sodium polystyrene sulfonate film layers and three layers of polydiallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride film layers alternately is obtained, respectively.
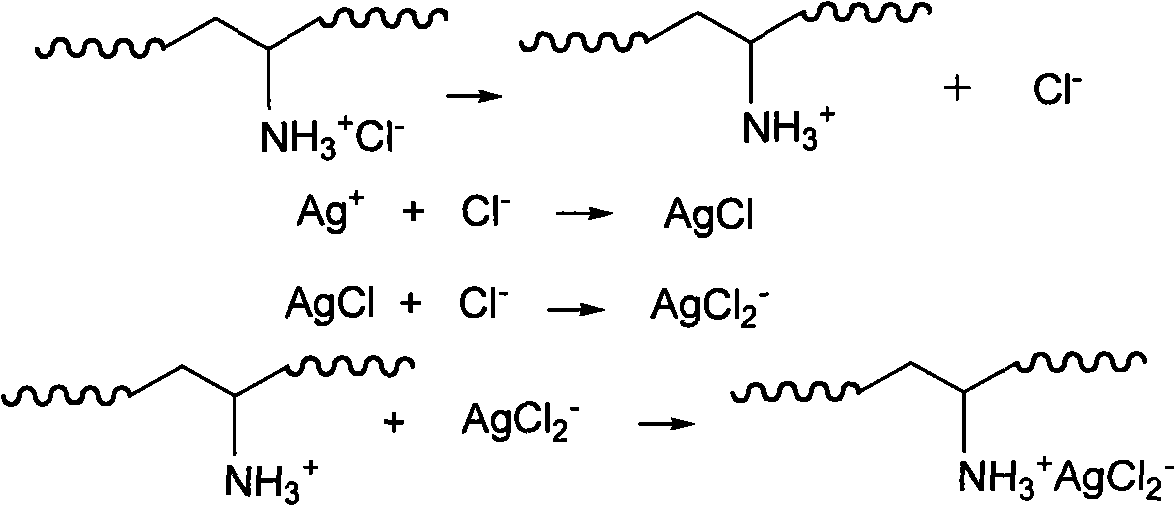
[0024] 3. Immerse the film treated in step 2 in a sodium polyacrylate solution with a concentration of 0.002mol / L for 20min, wash with pure water, and soak it for 20min; then immerse it in polyallyl ammonium chloride-silver chloride (10mmol / LPAH+ 0....
Embodiment 2
[0029] 1. After cleaning the polyethersulfone-based membrane with pure water, soak it in pure water for 10 hours, and change the water every 2 hours in between.
[0030] 2. Immerse the base film treated in step 1 in a solution of sodium polystyrene sulfonate with a concentration of 0.05mol / L for 20min, wash with pure water, and soak it for 20min; the immersion concentration is 0.05mol / L polydiallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride solution for 20min, washed with pure water, soaked for 20min. The above steps are repeated until a polyelectrolyte primary layer consisting of three layers of sodium polystyrene sulfonate film layers and three layers of polydiallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride film layers alternately is obtained, respectively.
[0031] 3. Immerse the film treated in step 2 in a sodium polyacrylate solution with a concentration of 0.002mol / L for 20min, wash with pure water, and soak it for 20min; then immerse it in polyallyl ammonium chloride-silver chloride (10mmol / LPAH+ 0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com