Immune colloidal gold test paper strip for detecting yapamicin relict and preparation thereof
A technology of colloidal gold test paper and kanamycin, which is applied in the field of immunochemical rapid detection of veterinary drug residues, can solve the problems of unfavorable promotion and use, complicated operation process, and cumbersome measurement methods, and achieve short detection time, low temperature requirements, The effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Embodiment 1: the structure of immune colloidal gold test strip of the present invention
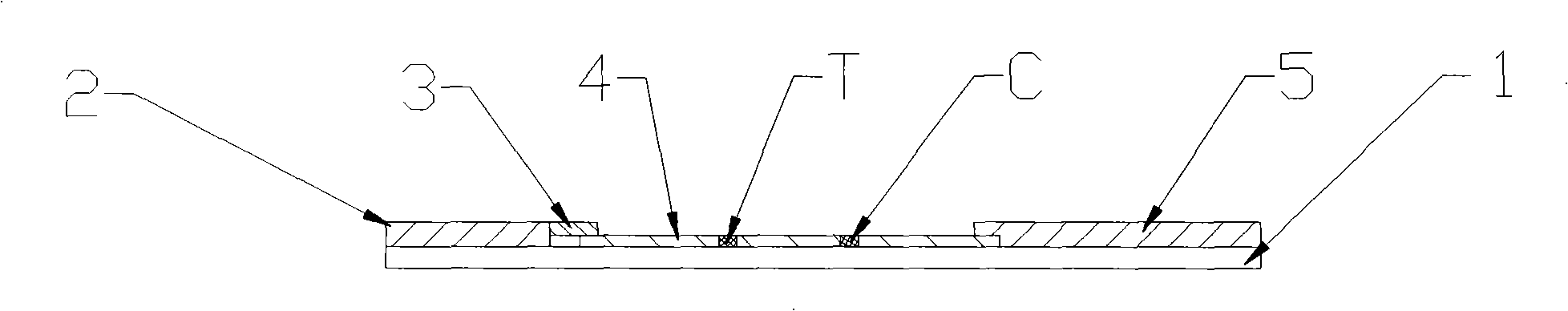
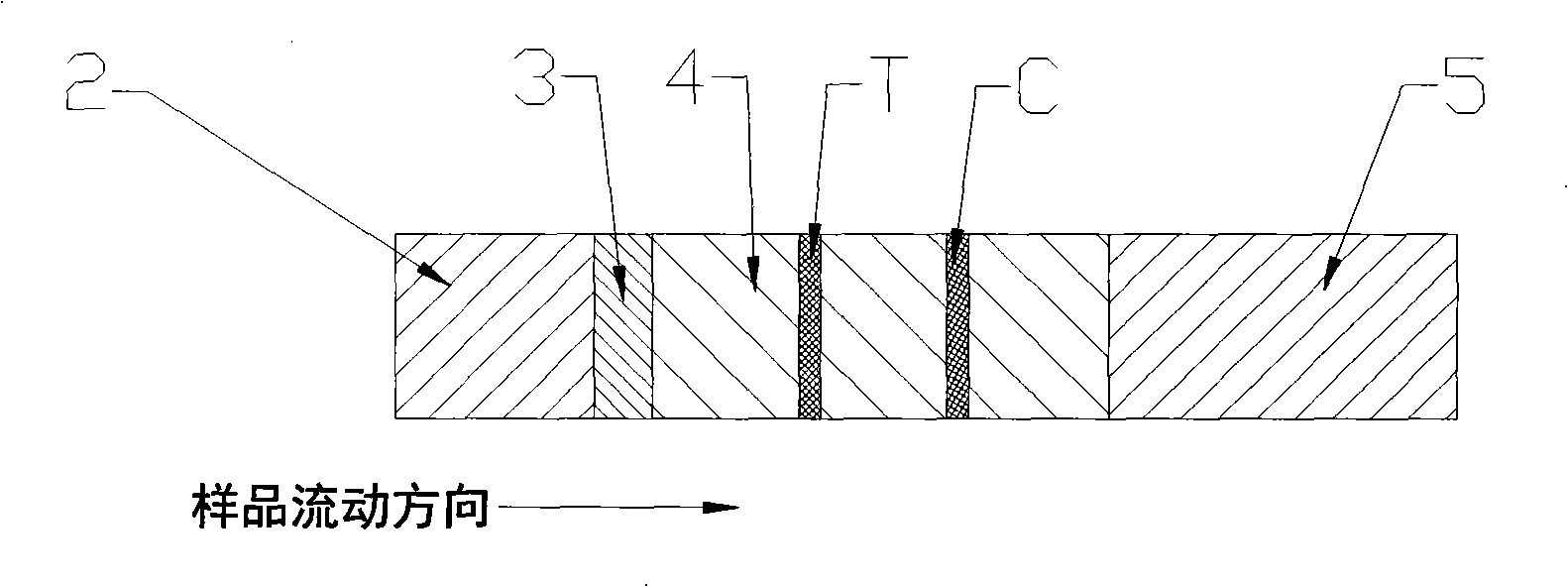
[0031] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, an immunocolloidal gold test strip for detecting kanamycin residues, including sample pad 2, binding pad 3, nitrocellulose membrane 4, absorbent pad 5 and PVC backing 1, on PVC backing 1 There are sample pad 2, binding pad 3, nitrocellulose membrane 4 and water-absorbing pad 5 successively adhered on it. There is overlap between binding pad 3 and nitrocellulose membrane 4, and between There is overlap; the binding pad 3 is coated with anti-kanamycin monoclonal antibody-colloidal gold marker, and the nitrocellulose membrane 4 is coated with kanamycin-carrier protein (bovine serum albumin) coupling The detection line T composed of substances and the quality control line C composed of rabbit anti-mouse IgG. Finally cut into strips with a width of 3mm and vacuum package.
[0032] When in use, after a certain treatment of the sample, ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 (preparation embodiment)
[0035] Preparation method of immunocolloidal gold test strip for detecting kanamycin
[0036] l. Preparation of kanamycin-carrier protein conjugates
[0037] Synthesis of immunogen: Weigh 45 mg of kanamycin sulfate and 10 mg of hemocyanin (KLH) into 1.5 mL of PBS, and stir on a magnetic stirrer. Dissolve 300 mg of EDC·HCl in 1 mL of PBS, adjust the pH value to 7.4, and then add it dropwise to the above mixed solution, stir at room temperature for 1 hour, and then place it at 4°C for 3 days. Dialyze with PBS for 3 days, change the dialysate 2 to 3 times a day, pass through Sephadex G-25 for further purification, subpackage, and store at -20°C.
[0038] Synthesis of coating agent: Weigh 45 mg of kanamycin sulfate and 10 mg of BSA, dissolve in 1.5 mL of PBS, and stir on a magnetic stirrer. 300 mg of EDC·HCl was dissolved in 1 mL of PBS, and then added dropwise to the above mixed solution, and stirred and reacted at room temperatur...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3 (application embodiment)
[0058] Application Evaluation of Immunocolloidal Gold Test Strip for Detection of Kanamycin
[0059] 1. Specificity test
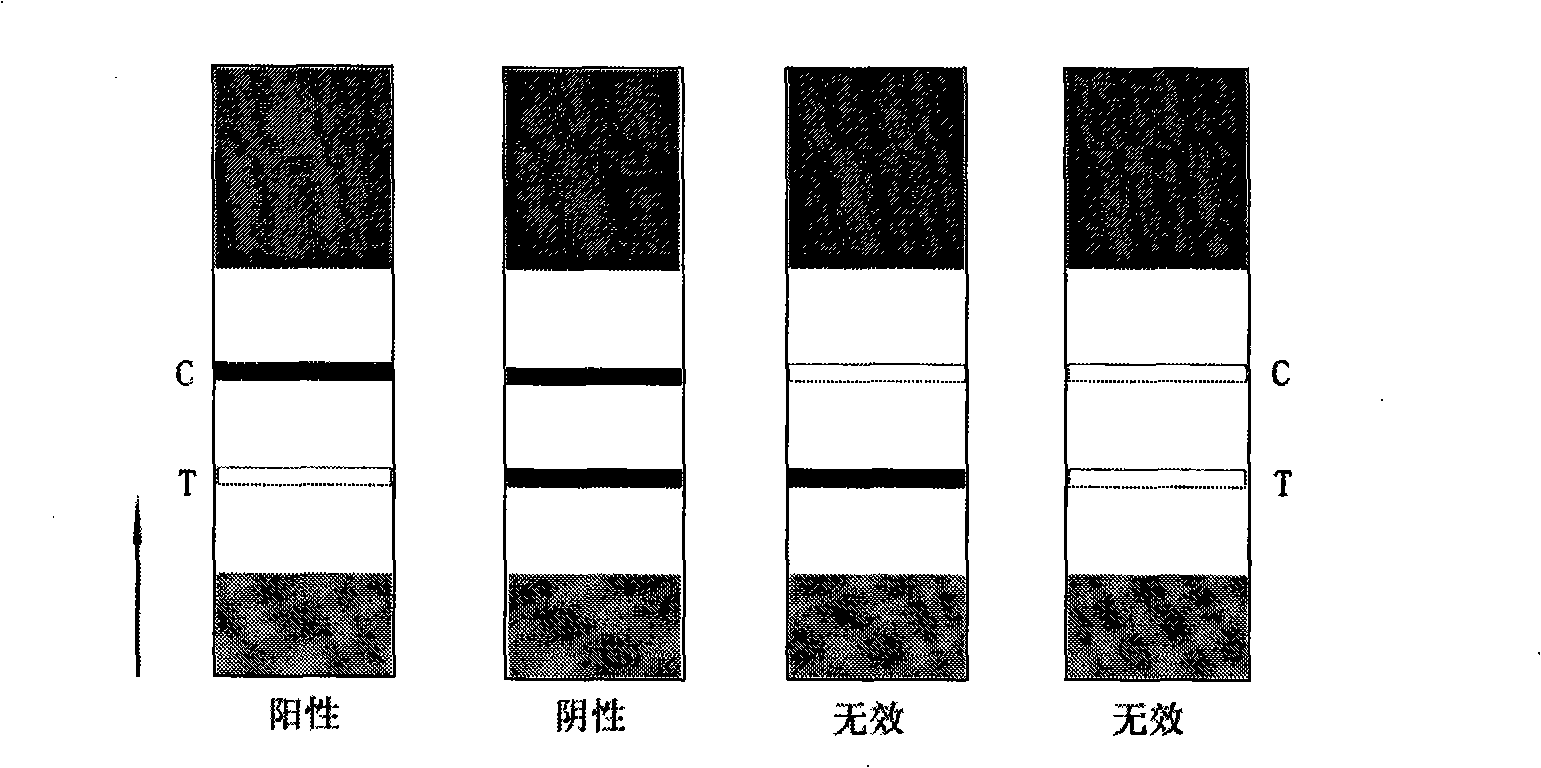
[0060] Prepare kanamycin, gentamicin, neomycin, streptomycin, chloramphenicol, cephalexin, sulfadimethoxine, and enrofloxacin into samples with a concentration of 10 ng / mL, and drop them on Test on the sample pad or on the sample well. Result of the test (seeing table 1) shows that the kanamycin sample detection line has no color, and a red band appears on the quality control line simultaneously, while gentamicin, neomycin, streptomycin, chloramphenicol, cephalexin , sulfadimethoxine, enrofloxacin sample test strip test line and quality control line all appear red bands, which indicates that gentamicin, neomycin, streptomycin, chloramphenicol, cephalexin, sulfa Dimethoxine and enrofloxacin have no cross-reaction with the test strip of the present invention, showing that the test strip of the present inventi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com