Fusion metallurgy sample analysis fusing agent and its preparation and use method
A sample analysis and flux technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problems of poor melting decomposition effect, no metallurgical analysis samples, large consumption of drugs, etc., and achieve excellent melting decomposition effect and melting time. The effect of short, simple preparation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] Preparation method of the present invention comprises the steps:
[0029] A. Mix evenly: Mix anhydrous sodium carbonate and boric acid evenly according to the weight ratio of 2:1.
[0030] B. Drying procedure: Put the uniformly mixed main flux in an oven, dry at 105°C for 2h-3h, then take it out and cool it to room temperature.
[0031] C, milling procedure: grind the dried main flux into powder with a mortar or other milling equipment, and bottle it for subsequent use;
[0032] D, auxiliary flux: white crystalline powder auxiliary flux ammonium nitrate or potassium nitrate are bottled for subsequent use. Add appropriate amount of auxiliary flux according to the difficulty of sample decomposition during use.
[0033] The present invention adopts following steps when concrete use:
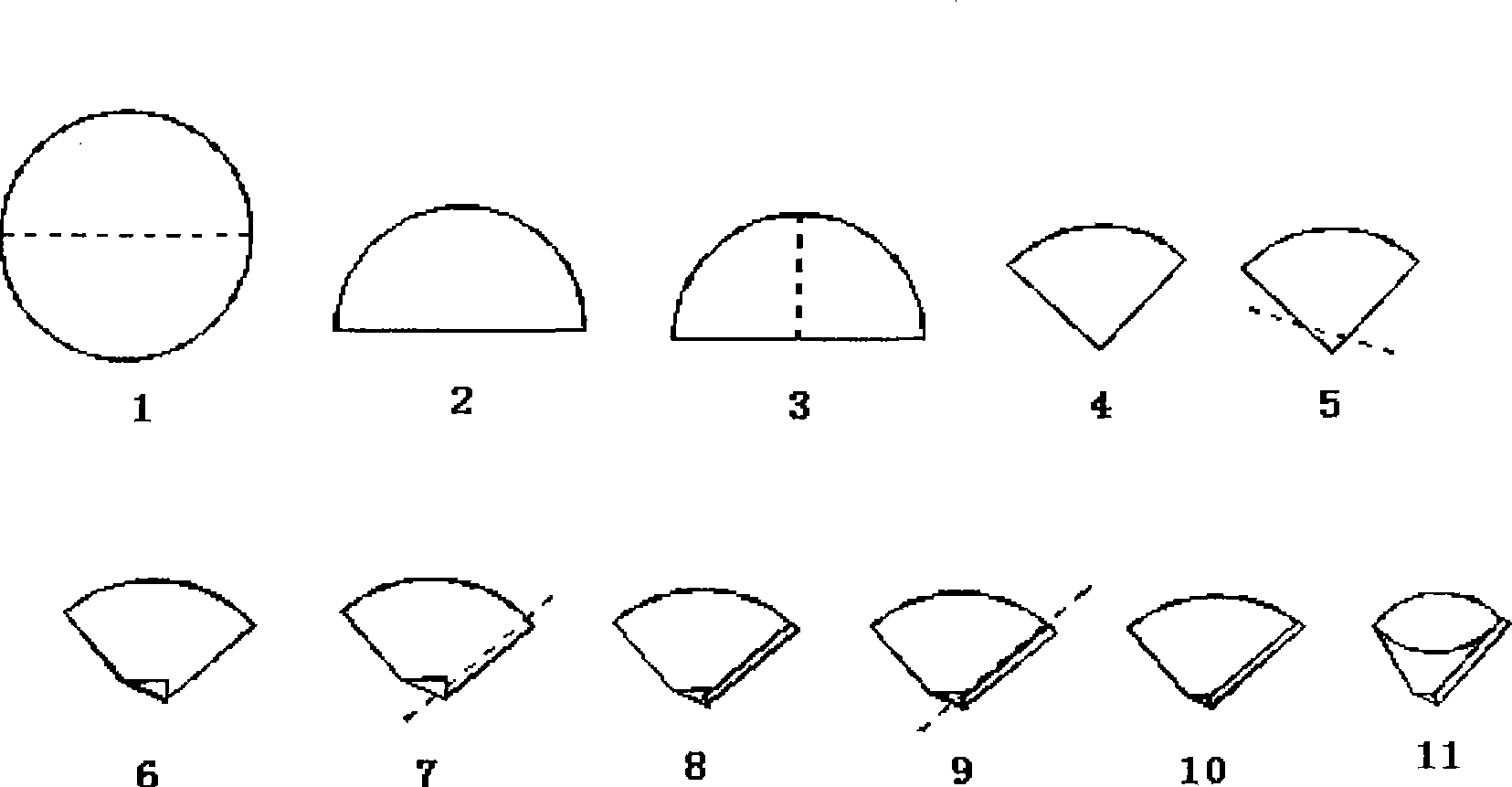
[0034] a. Put the Φ12.5cm or Φ15cm slow or medium-speed quantitative filter paper according to the attached figure 1 The folding procedure shown, folded along the dotted line, finally fol...
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1: the mensuration of total iron in iron ore.
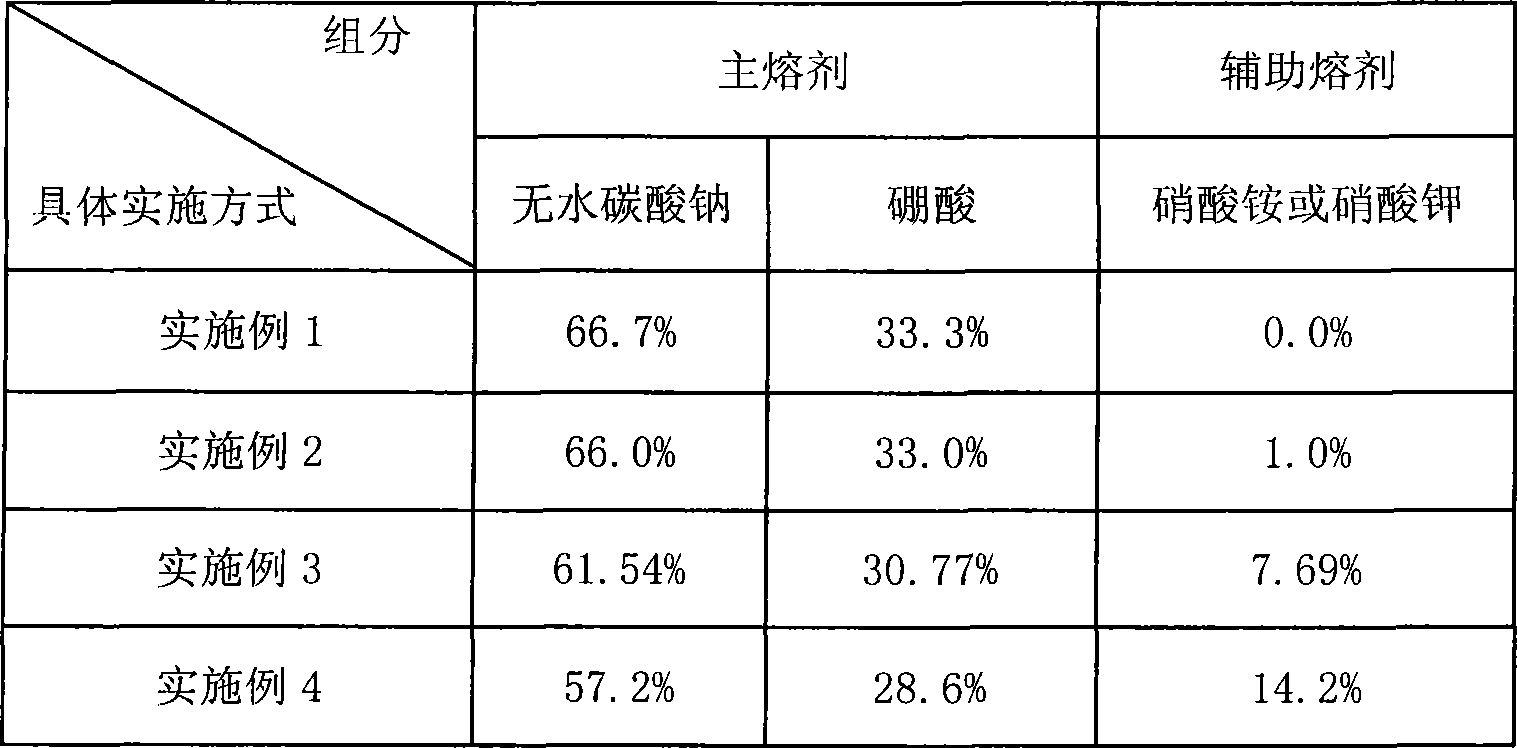
[0046] Take 66.67% of anhydrous sodium carbonate and 33.3% of boric acid. Pour the above ratio of anhydrous sodium carbonate and boric acid into a porcelain plate, mix evenly, put it in an oven, and dry it at 105°C until it does not agglomerate, then keep it warm for 2 hours; take out the dried main flux and cool it until At room temperature, grind it into powder with a mortar or other grinding equipment, and bottle it for later use.
[0047] Take Φ12.5cm quantitative filter paper, according to the attached figure 1 Fold in the order of folding, put into the mixed flux of 4g-5g according to the ratio above into the folded packaging filter paper, put the 0.2000g vanadium-titanium magnetite powder sample taken out into the flux and stir evenly, Then packed into metallurgical balls;
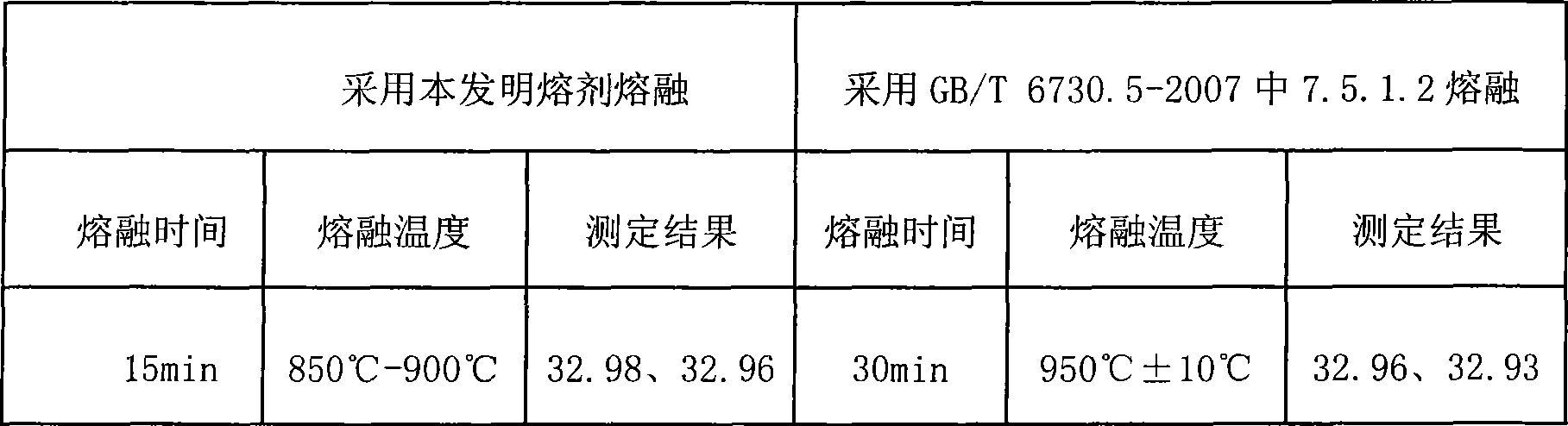
[0048] Fill a 50mL porcelain crucible with graphite powder, place it in a high-temperature muffle furnace, burn it at 800°C-900°C...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Embodiment 2: the mensuration of calcium and magnesium in high titanium slag.
[0054] Anhydrous sodium carbonate 66.0%, boric acid 33.0%, ammonium nitrate 1.0%. Pour the proportion of anhydrous sodium carbonate and boric acid into a porcelain plate, mix evenly, put it in an oven, and dry it at 105°C until it does not agglomerate, and then keep it warm for 3 hours; take out the dried main flux and cool it until At room temperature, use a mortar or other grinding equipment to grind into powder, bottle for later use;
[0055] Take Φ15cm quantitative filter paper, according to the attached figure 1 Fold in order, put 4.95g of main flux in the above ratio into the folded packaging filter paper, and weigh out 0.2000g~0.5000g of metallurgical auxiliary materials (including high titanium slag, composite slagging agent, desulfurizer , semi-steel, deoxidizer, etc.) powder sample into the main flux, add 0.05g of ammonium nitrate, stir evenly, and then pack into metallurgical sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com