Preparation of composite type light high-strength nickel-titanium memory alloy-based high damping material
A nickel-titanium memory alloy and composite technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of high damping materials, can solve the problems of difficulty in achieving damping effect and low volume fraction of nickel-titanium memory alloy, and achieve excellent damping capacity, good comprehensive mechanical properties, and bearing capacity. improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Use pure nickel powder (average particle size 57 μm) and pure titanium powder (average particle size 48 μm) according to nickel:titanium atomic ratio 50.8:49.2 and mix thoroughly for 24 hours to obtain raw material powder A. Add 10wt.% ammonium bicarbonate (particle size: 200-300, average particle size: 250 μm) to powder A, mix thoroughly to make powder B. Powder B was pressed at 200 MPa into a cylindrical green body with a diameter of 16 mm and a height of 12 mm. Put the billet into a tubular sintering furnace, raise the temperature to 200°C under the protection of argon with a purity higher than 99.99%, and keep it warm for 1.5 hours to remove the pore-forming agent ammonium bicarbonate and activate the billet. Then the temperature was raised to 700° C. at 15° C. / min and kept for 20 minutes. Finally, the temperature was raised to 1000° C. at 15° C. / min, kept for 3 hours, and a porous nickel-titanium memory alloy with a porosity of 36.1% was obtained after cooling.
...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Use pure nickel powder (average particle size of 57 μm) and pure titanium powder (average particle size of 48 μm) according to the atomic ratio of nickel and titanium of 51:49 and mix thoroughly for 24 hours to obtain raw material powder C. Add 20wt.% ammonium bicarbonate (with a particle size of 50-200 and an average particle size of 100 μm) to powder C, and mix thoroughly to make powder D. Powder D was pressed at 100 MPa into a cylindrical green body with a diameter of 16 mm and a height of 12 mm. The billet is put into a tube sintering furnace, heated to 250° C. under the protection of argon with a purity higher than 99.99%, and kept for 1 hour to remove the pore-forming agent. Then heat at 20°C / min to 750°C and keep warm for 15 minutes. Finally, it was heated to 1050°C at 10°C / min, kept for 2 hours, and cooled to room temperature to obtain a porous nickel-titanium memory alloy with a porosity of 43.6%.
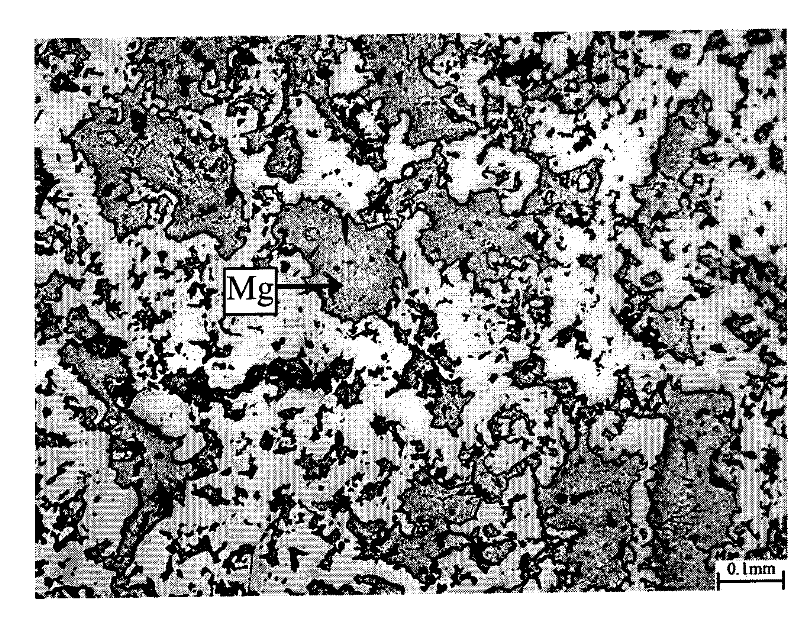
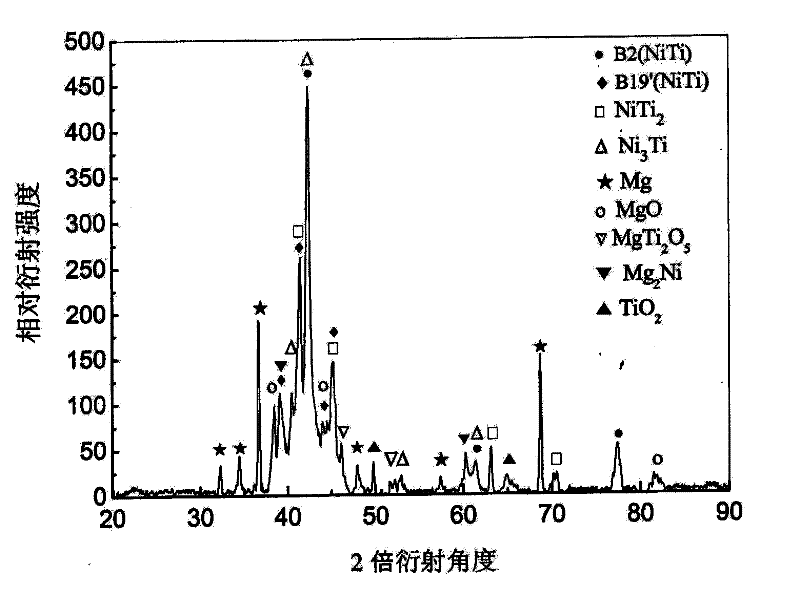
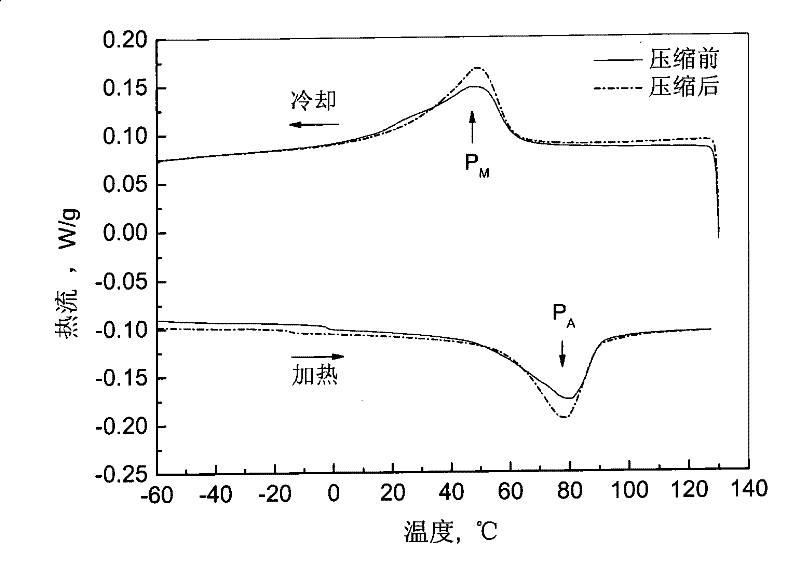
[0058] Metal magnesium and porous nickel-titanium memory all...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Use pure nickel powder (average particle size of 57 μm) and pure titanium powder (average particle size of 48 μm) according to the atomic ratio of nickel and titanium of 50:50 and mix thoroughly for 24 hours to obtain raw material powder E. Add 30wt.% urea (particle size: 300-450, average particle size: 400 μm) to powder E, and mix for 8 hours to make powder F. Powder F was pressed at 100 MPa into a cylindrical green body with a diameter of 16 mm and a length of 12 mm. The billet is put into a tube-type sintering furnace, heated to 300° C. under the protection of argon with a purity higher than 99.99%, and kept for 0.5 hours to remove the pore-forming agent. Then heat at 10°C / min to 800°C and keep warm for 10 minutes. Finally, it was heated to 1000° C. at a heating rate of 20° C. / min, kept for 3 hours, and cooled to room temperature to obtain a porous nickel-titanium memory alloy with a porosity of 60%.
[0062] AZ91D magnesium alloy and porous nickel-titanium memory ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com