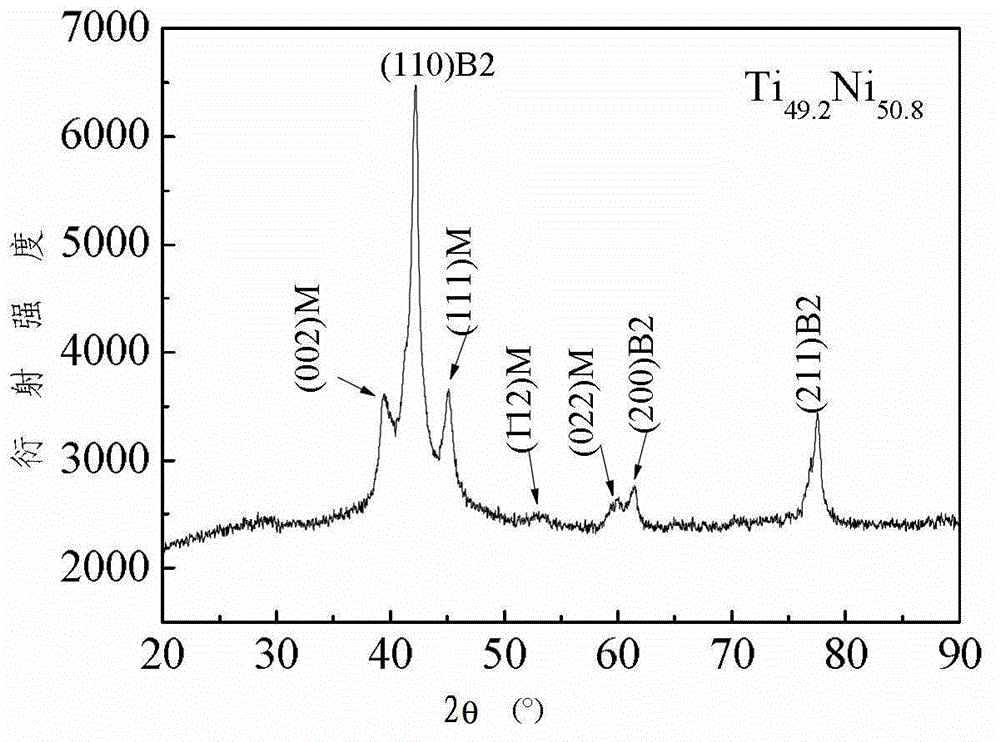
Patents
Literature
318 results about "Titanium nickelide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
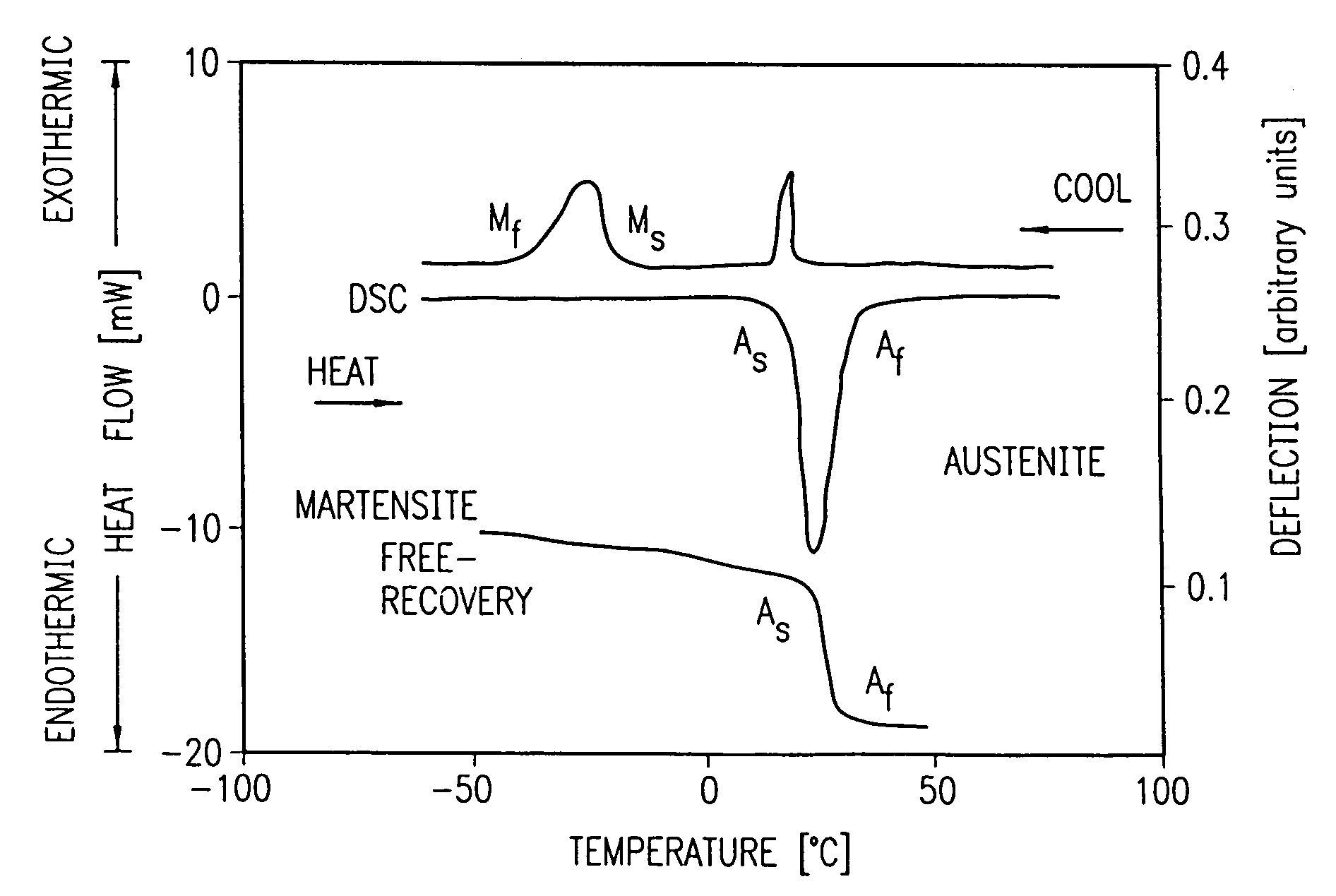
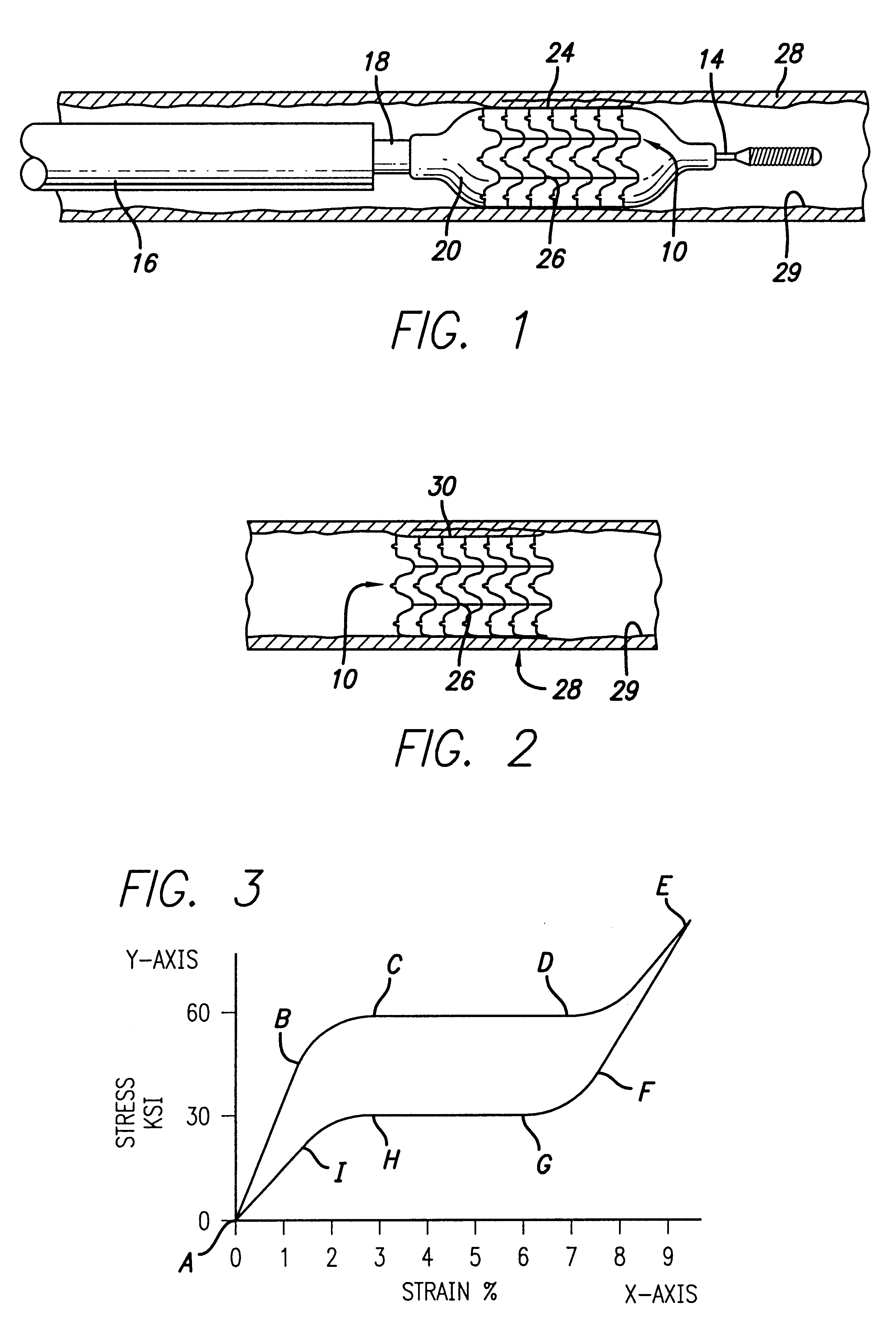
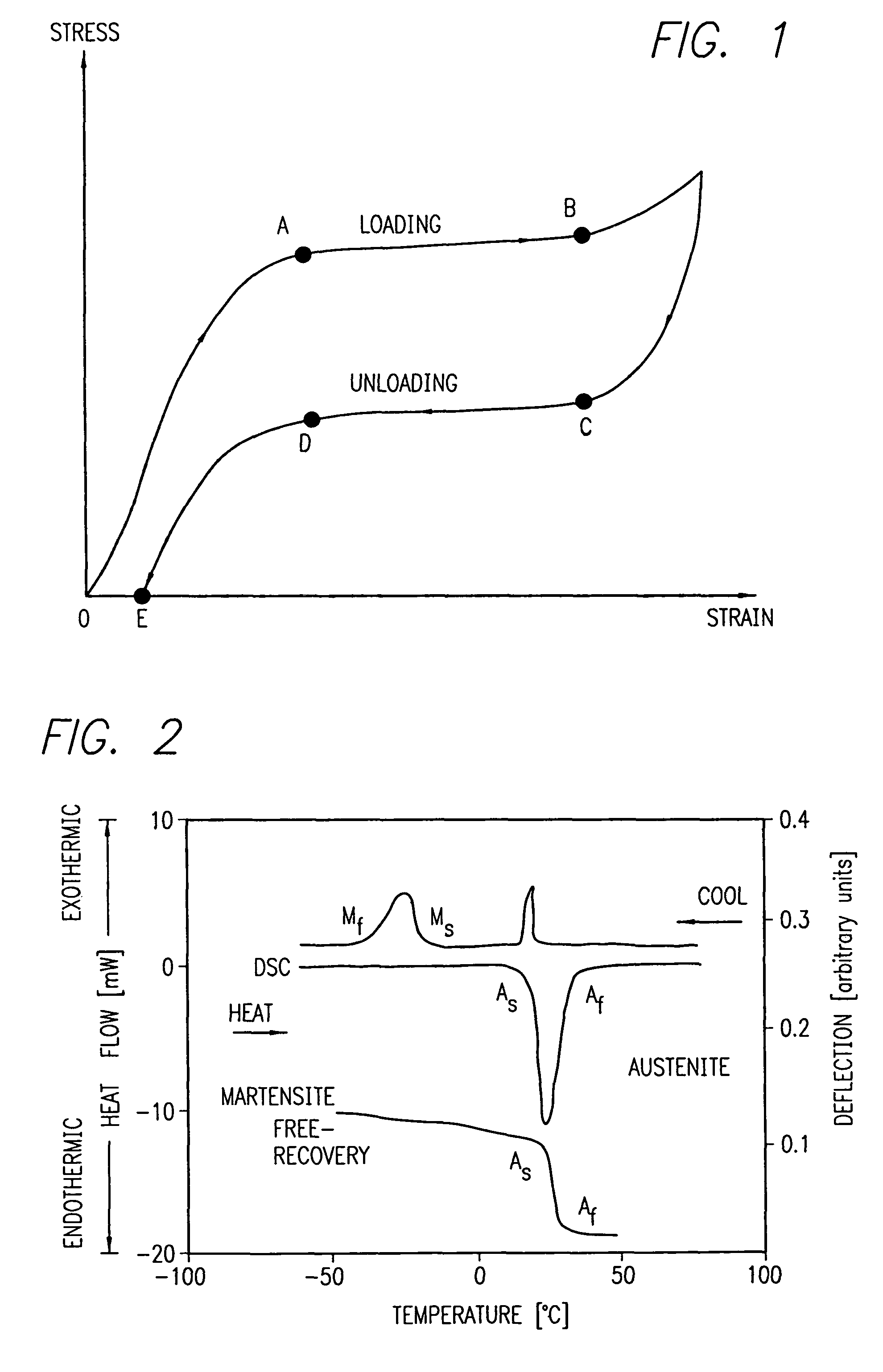
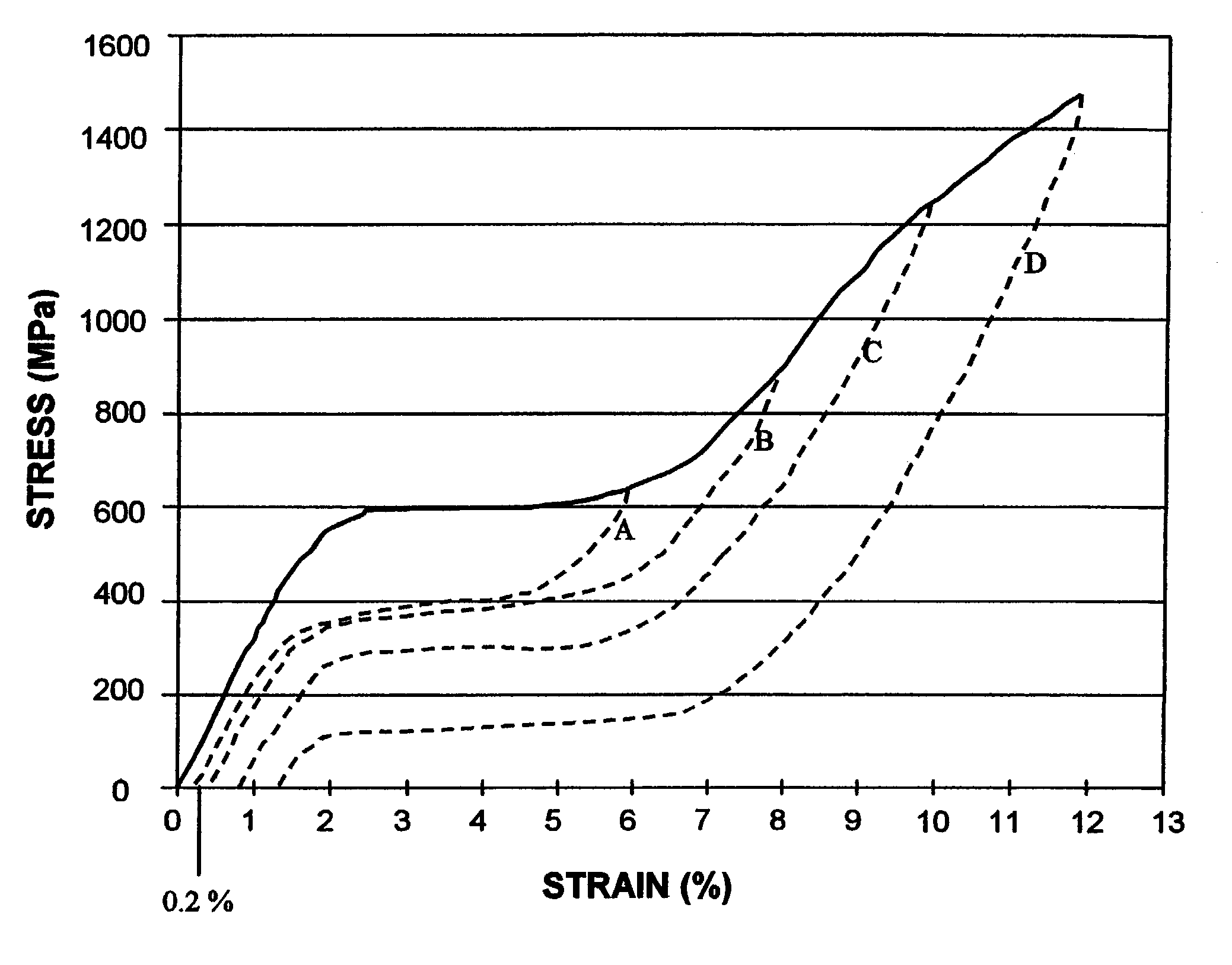
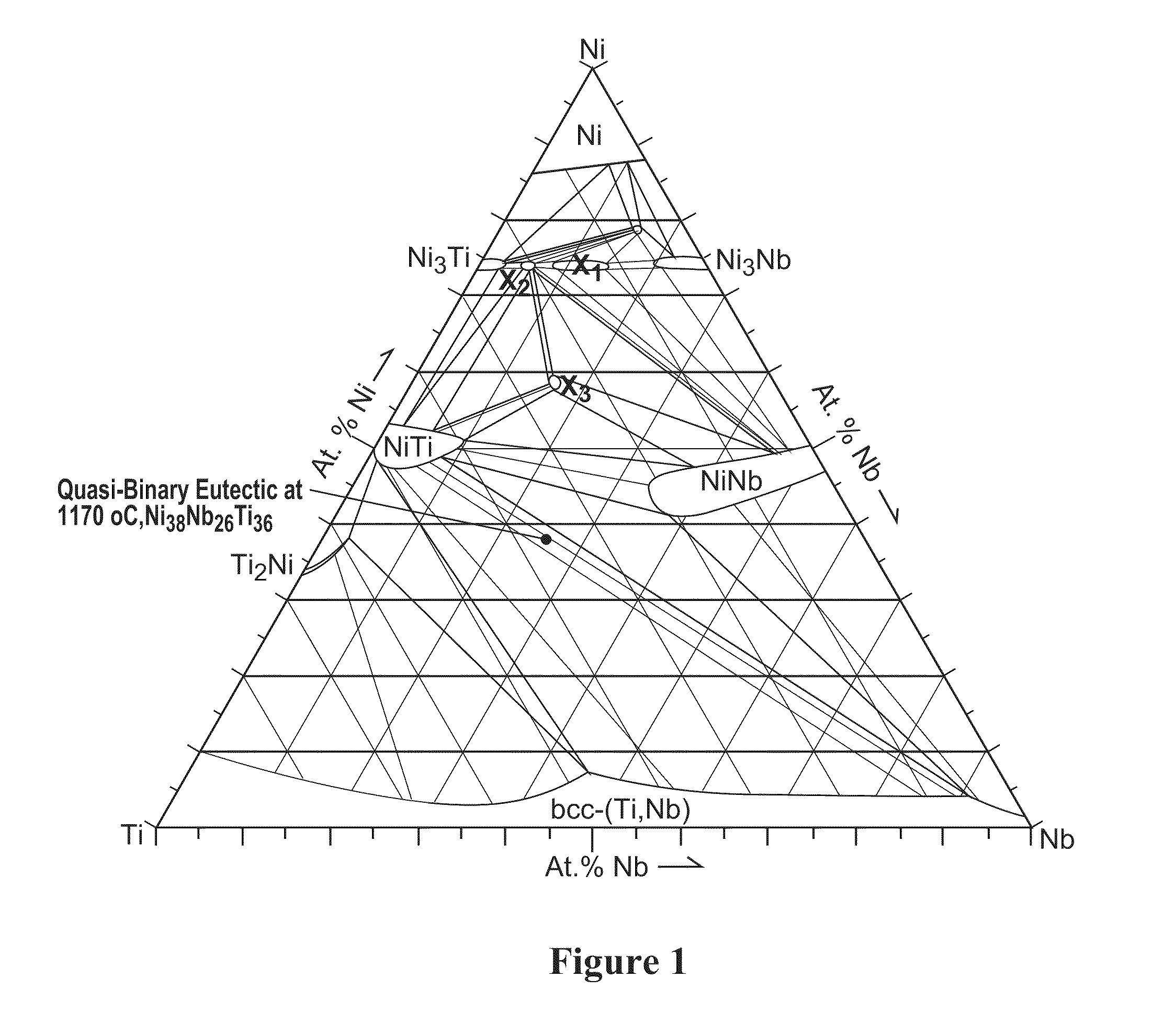
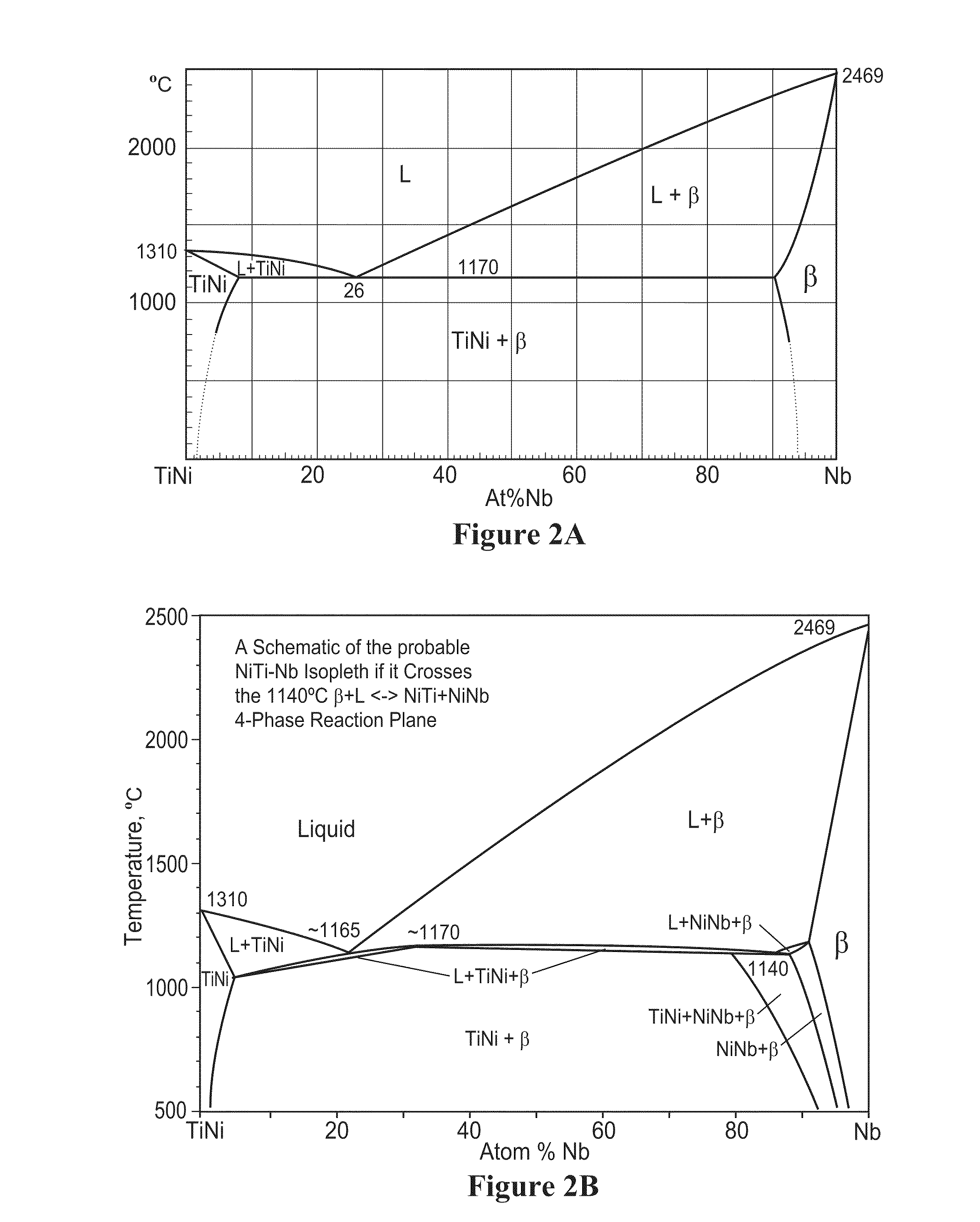
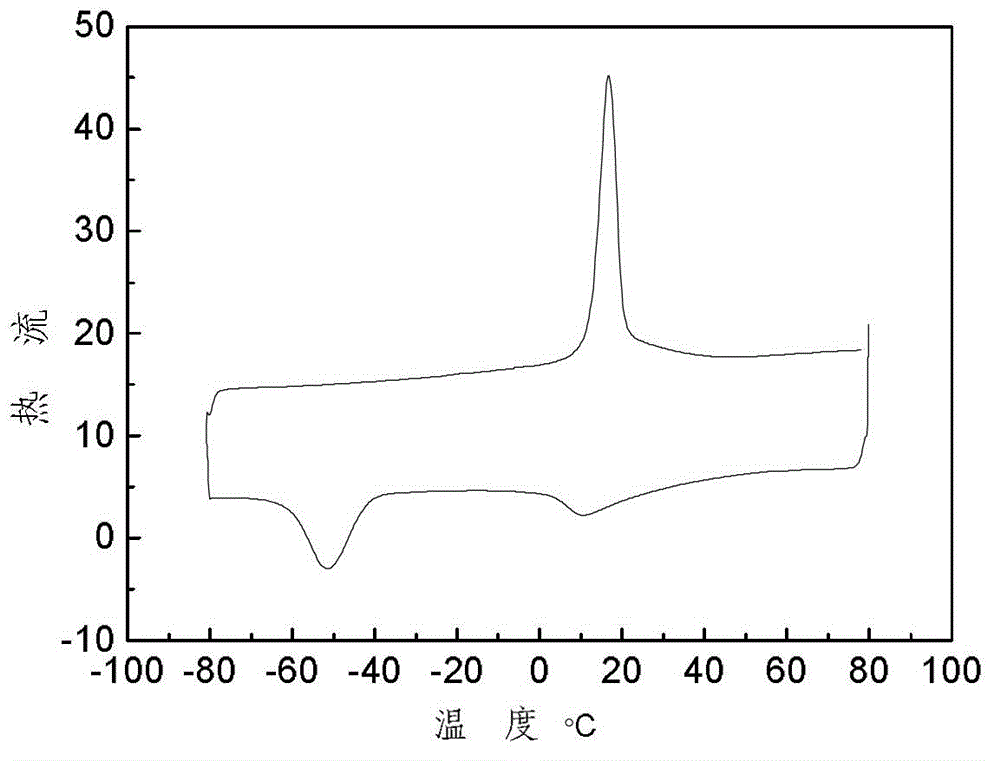
Therefore, the tasks of increasing the yield stress, as well as correct determination of yield stress in alloys with thermoelastic MT, including titanium nickelide alloys, are critical. Further expansion of the application scope for these alloys is associated with an increase of their yield stresses and strength.
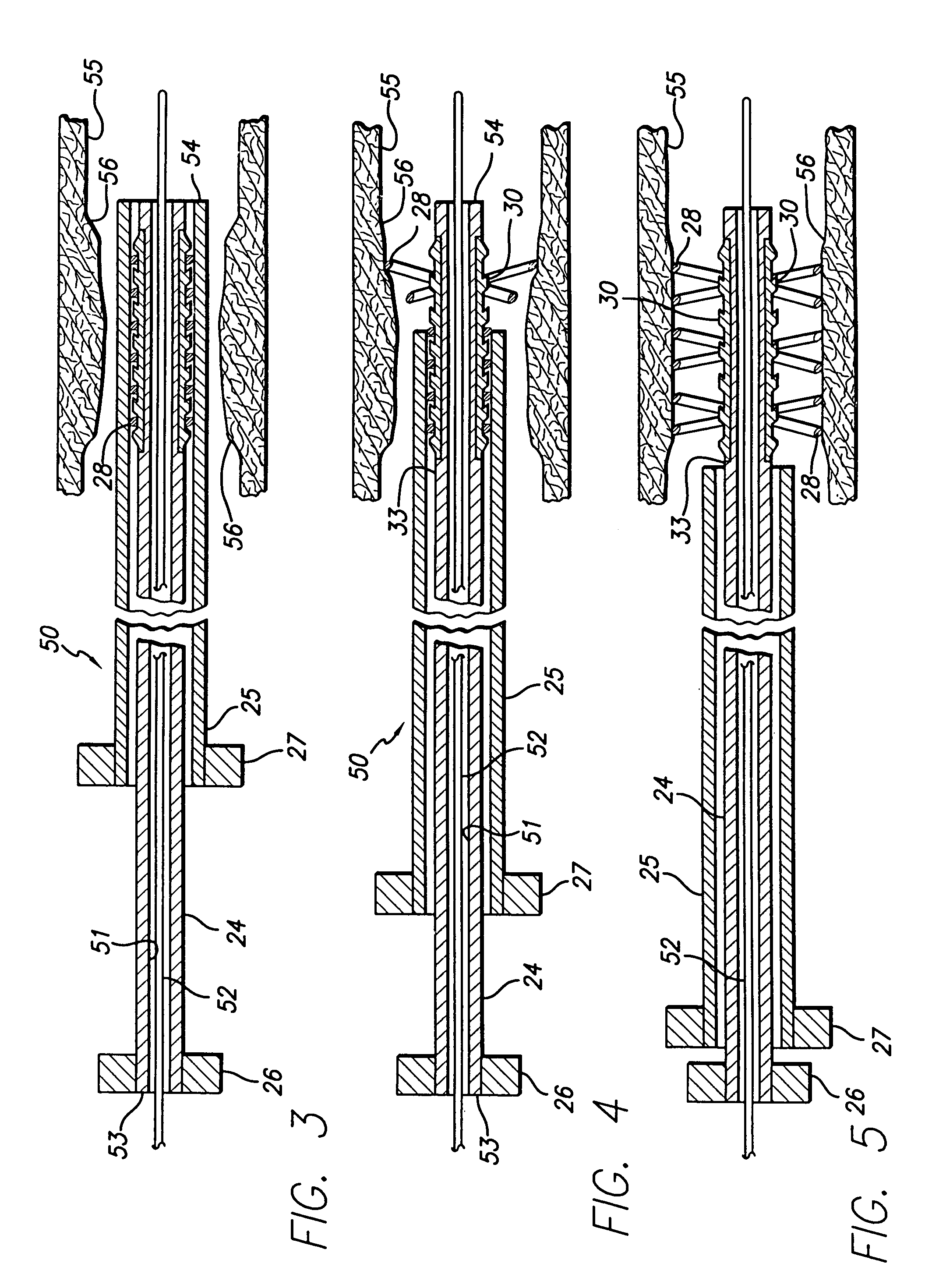
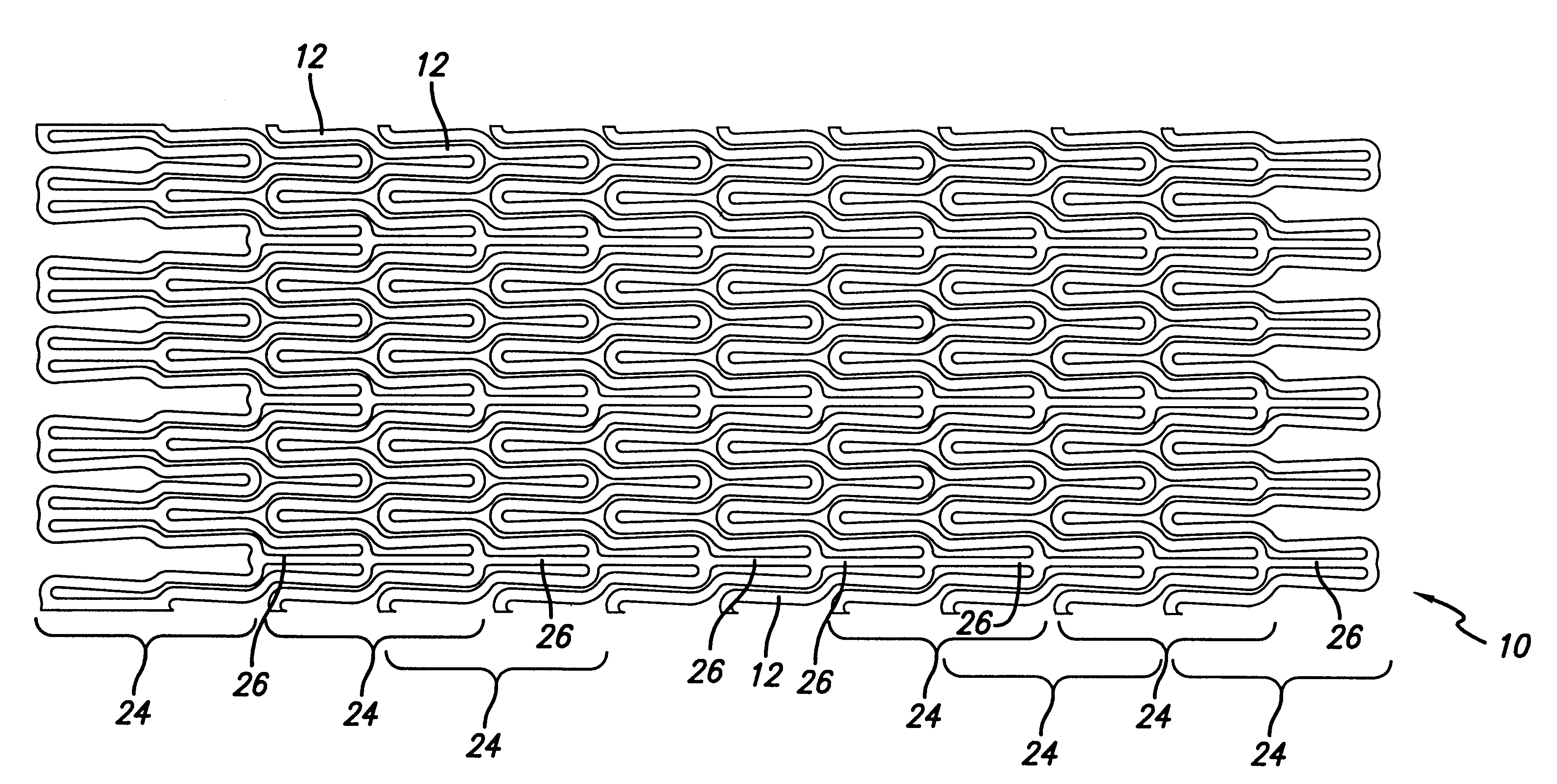
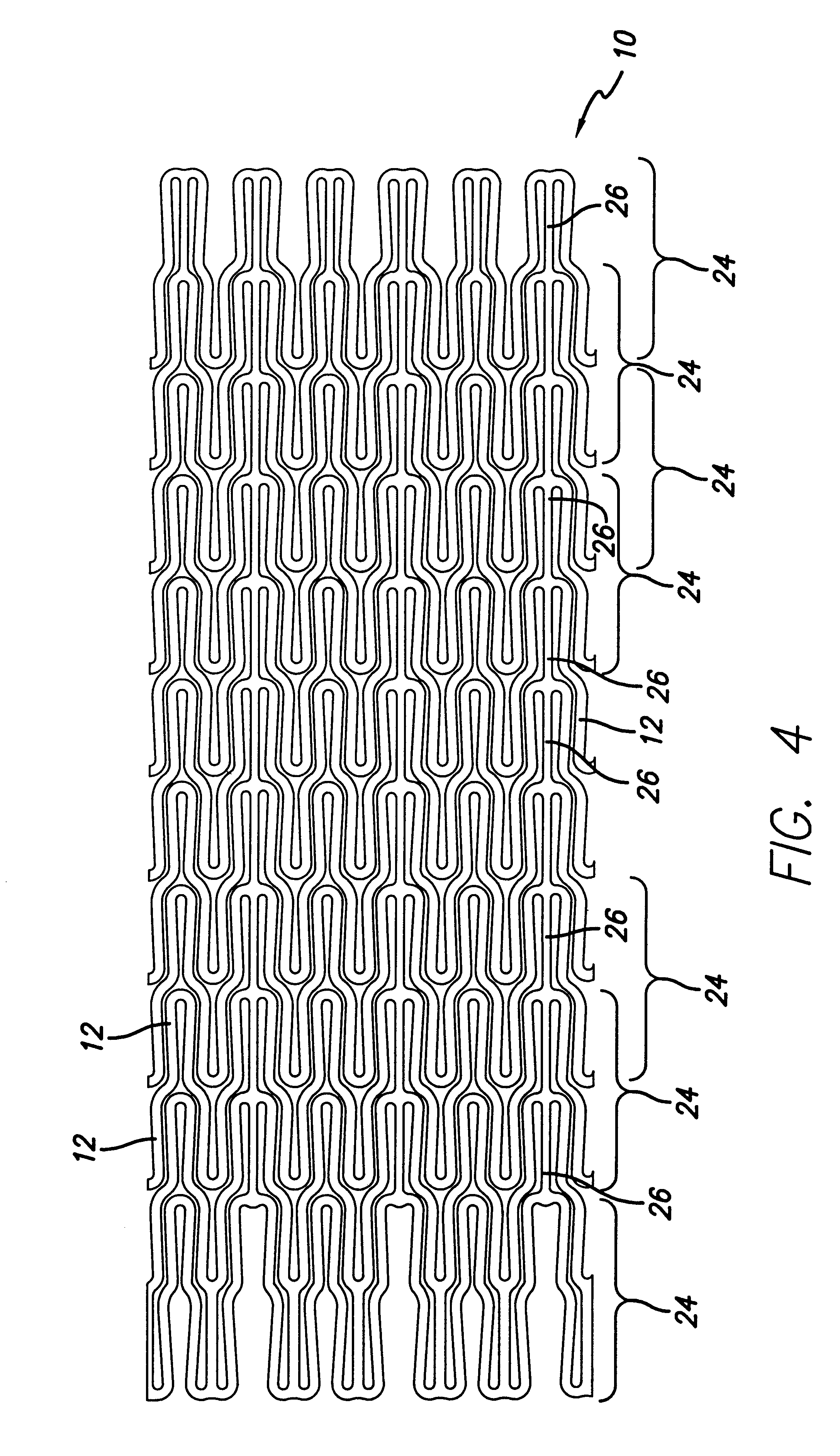
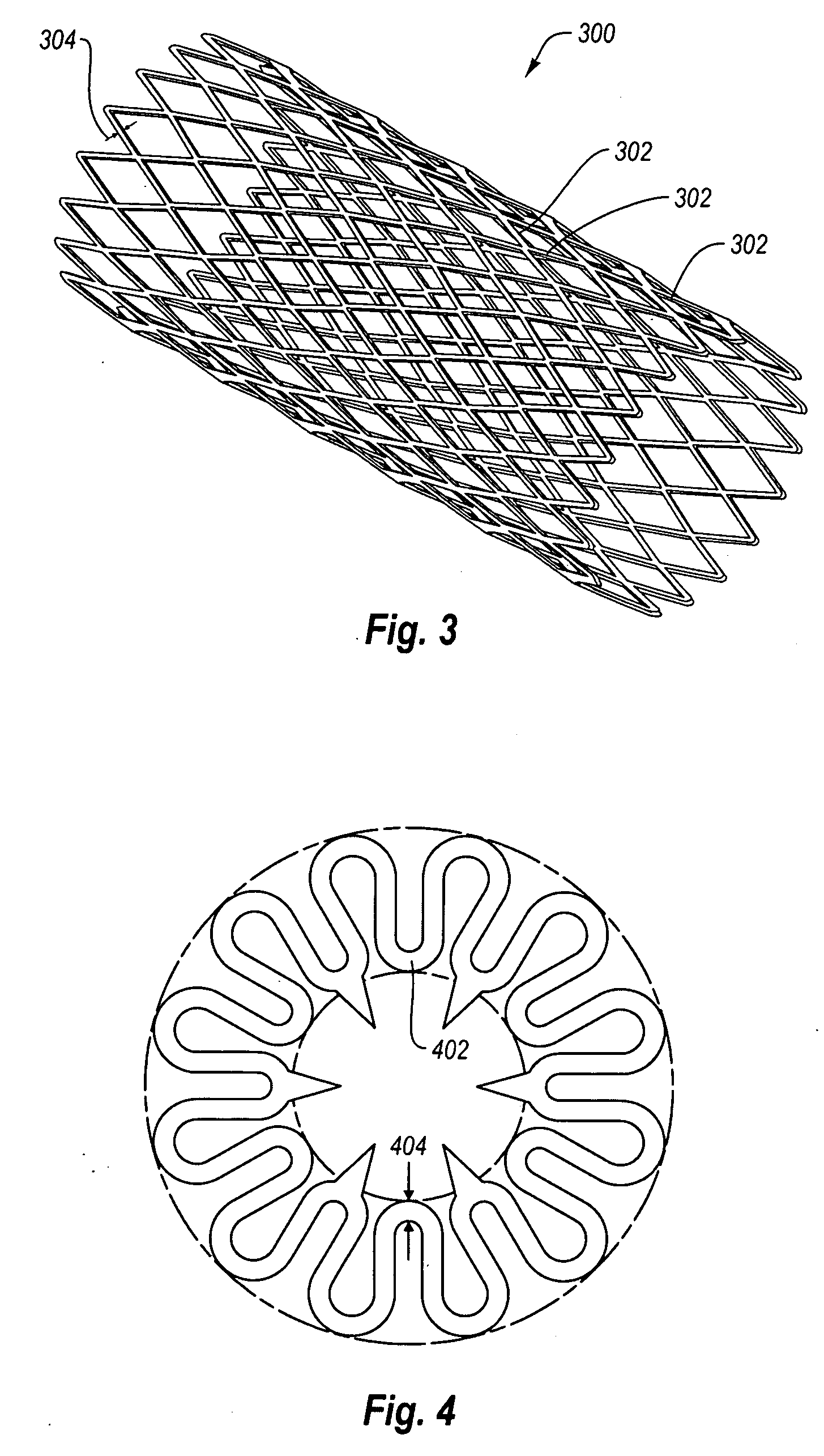
Coated implantable medical device
InactiveUS6918927B2Good worker safetyLow costOrganic active ingredientsSurgerySodium bicarbonateMedicine
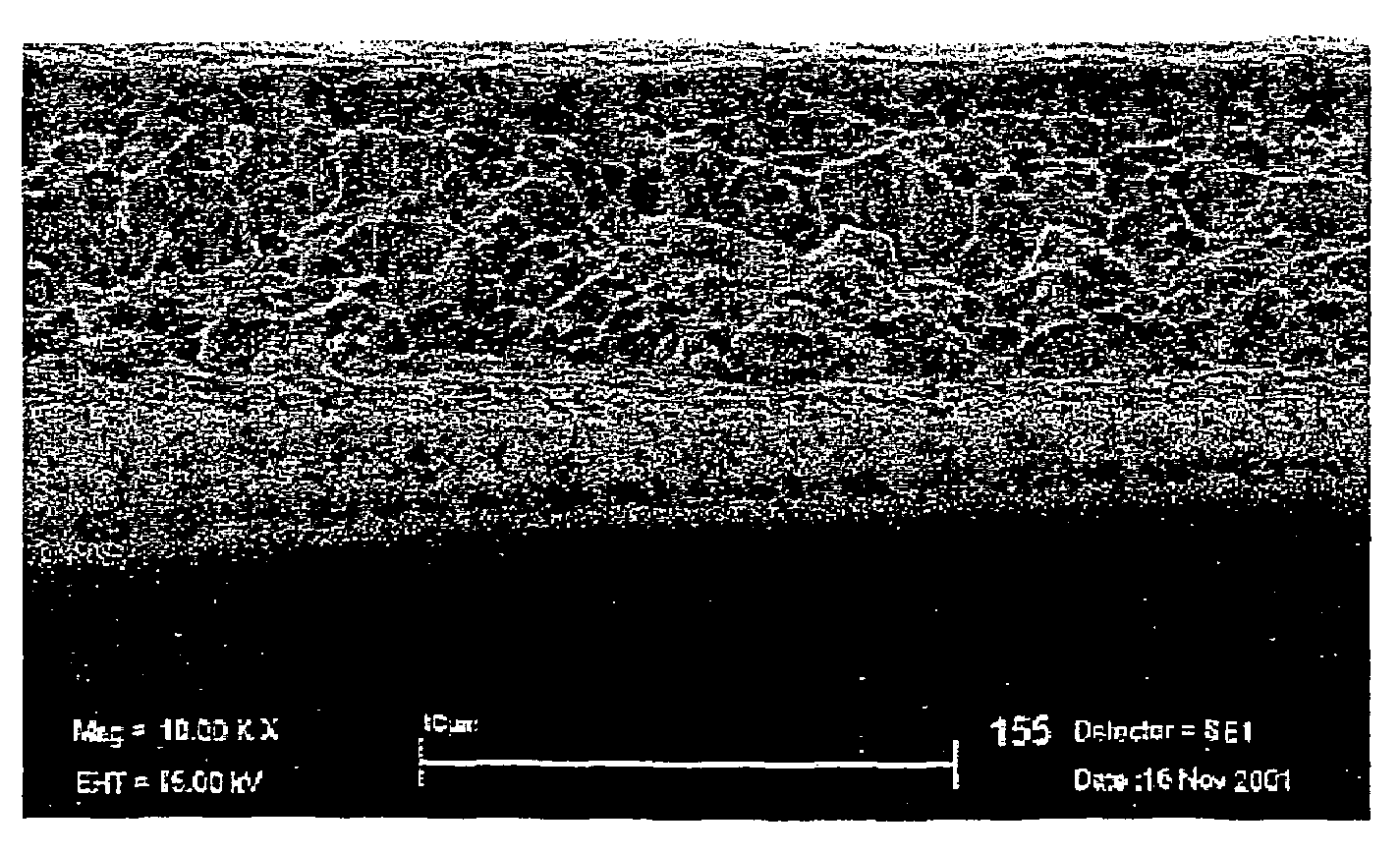
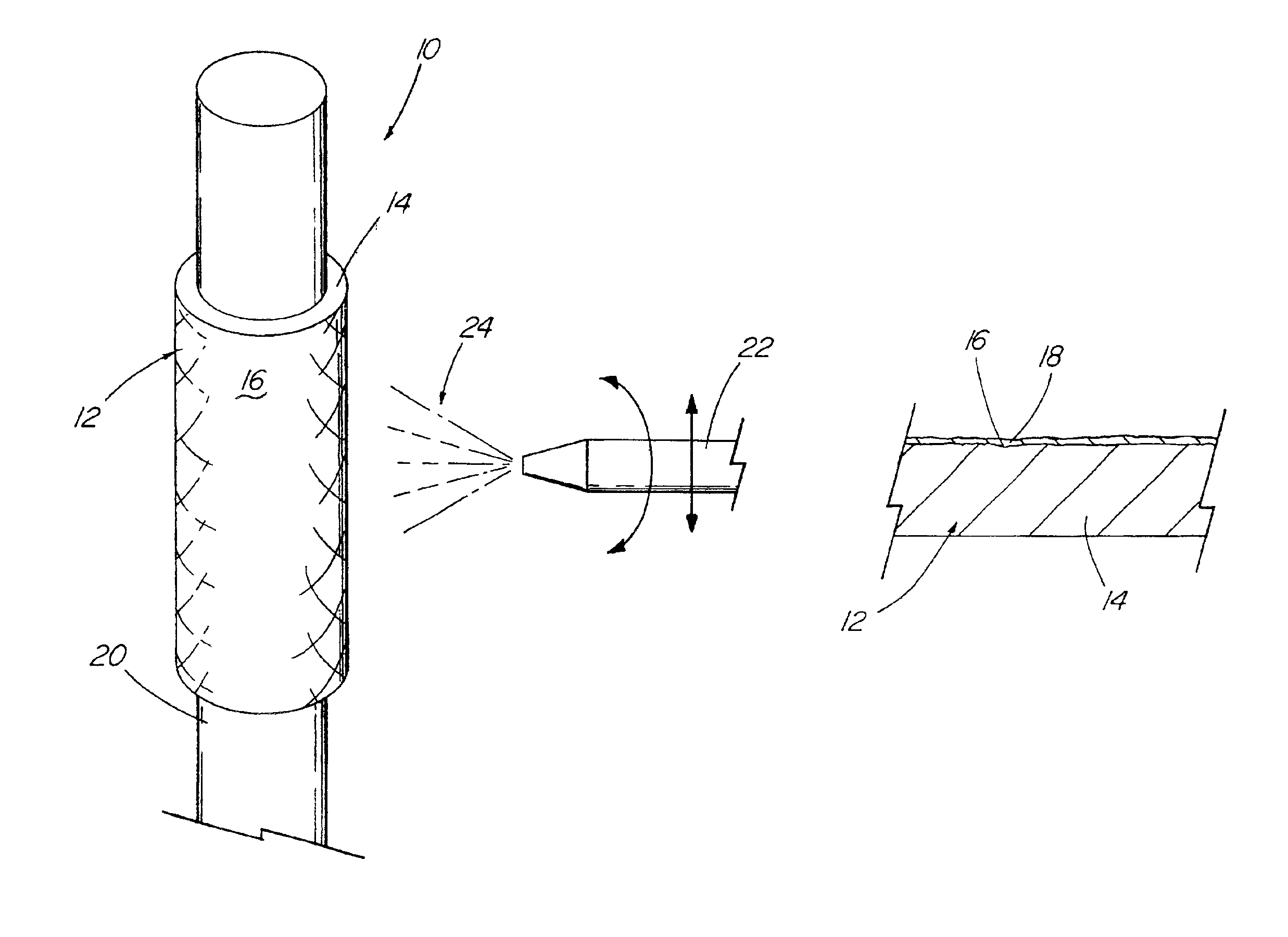
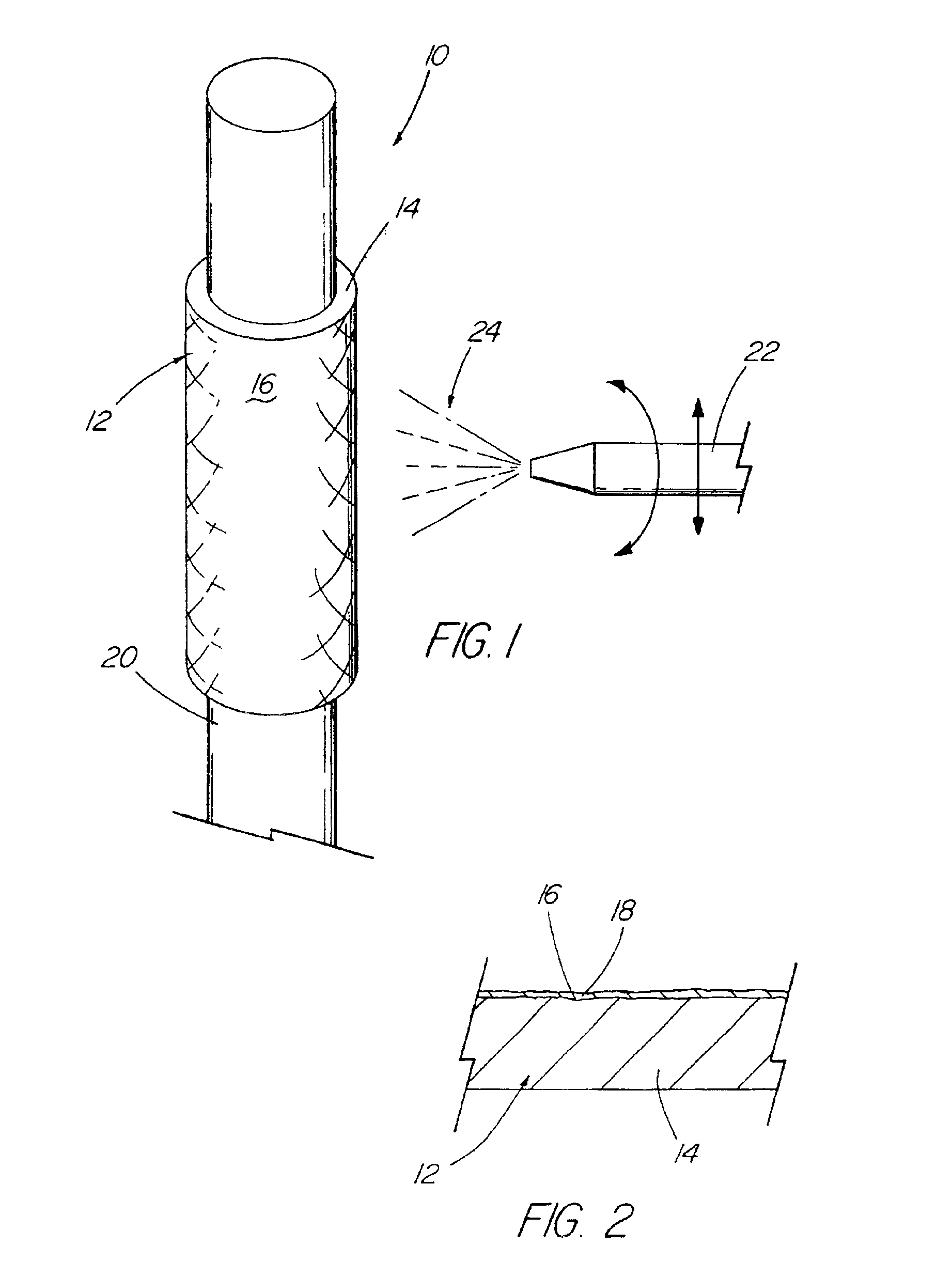
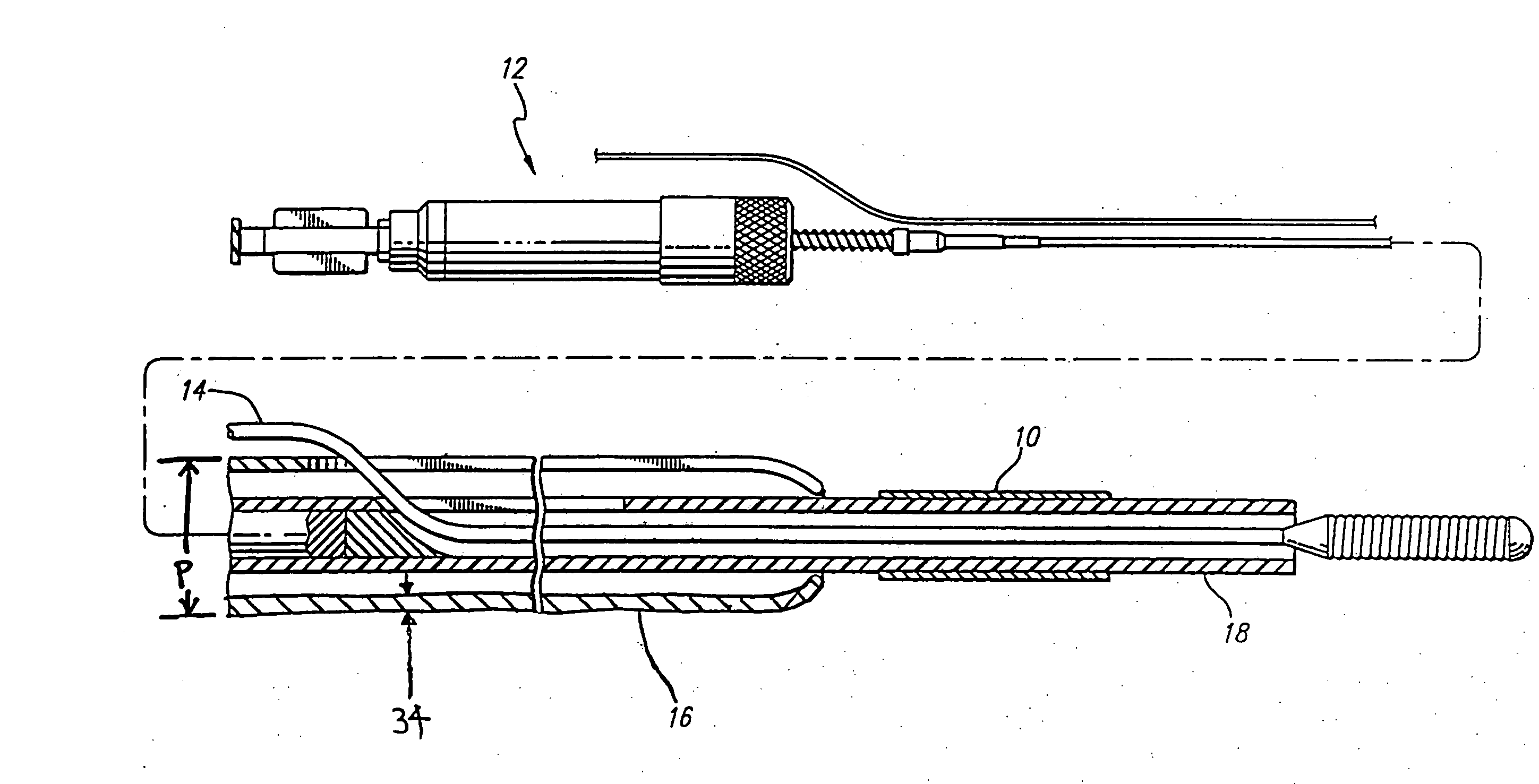
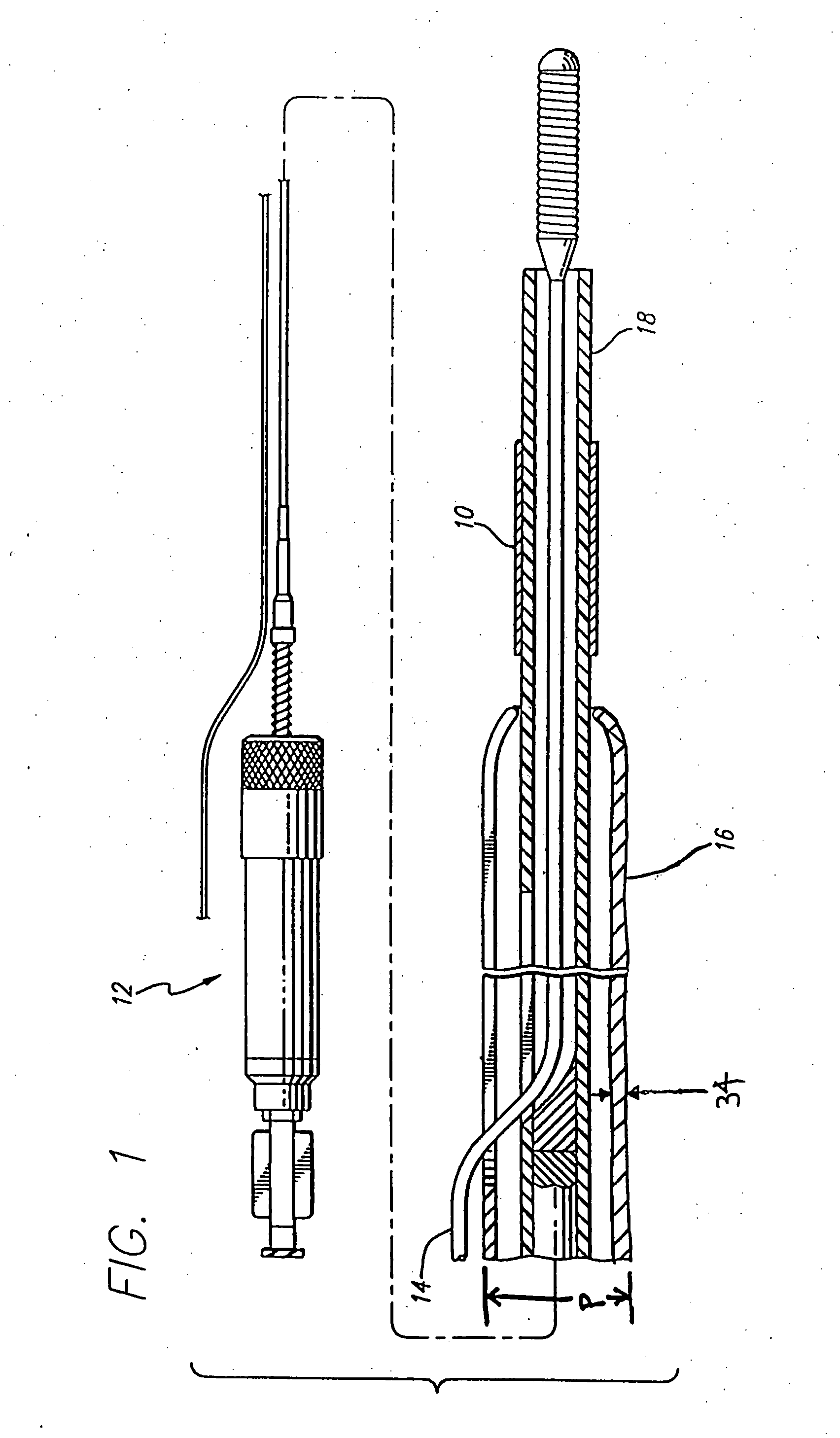
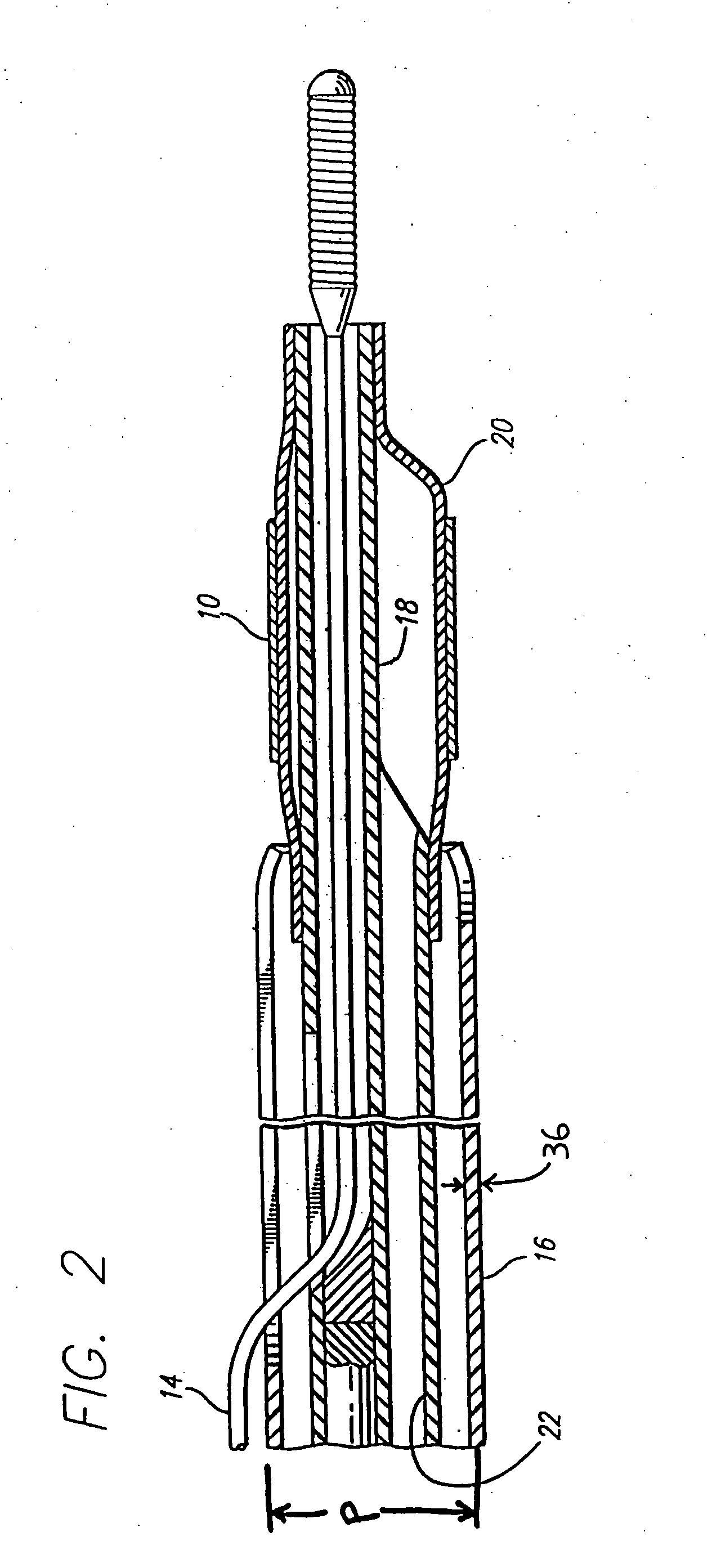
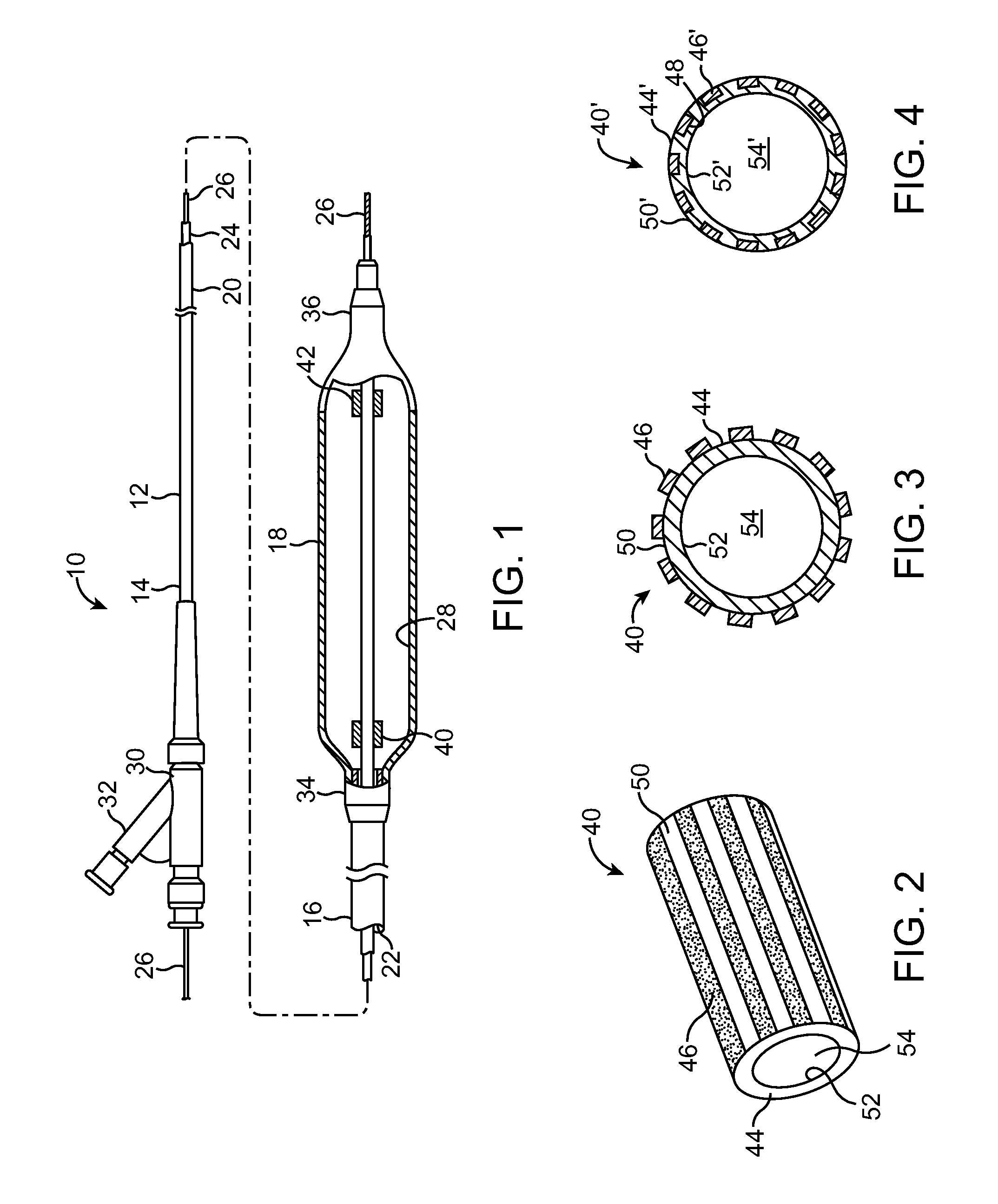
A medical device (10) includes a structure (12) adapted for introduction into a patient, the structure (12) being formed of a preferably non-porous base material (14) having a roughened or textured surface (16). The structure (12) is conveniently configured as a vascular stent with a base material (14) of stainless steel, nitinol or another suitable material. The medical device (10) also includes a layer (18) of a bioactive material posited directly upon the roughened or textured surface (16) of the base material (14) of the structure (12). The surface (16) of the base material (14) is roughened or textured by etching or by abrasion with sodium bicarbonate or another suitable grit. A preferred roughened or textured surface (16) is thought to have a mean surface roughness of about 10 μin. (about 250 nm) and a surface roughness range between about 1 μin. and about 100 μin. (about 25 nm and about 2.5 μm). The particularly preferred use of sodium bicarbonate as the abrasive to provide roughness or texture to the surface (16) of the base material (14) of the structure (12) is additionally advantageous in the low toxicity of the sodium bicarbonate to production workers, the ease of product and waste cleanup, and the biocompatibility of any residual sodium bicarbonate.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickel titanium alloys used in medical devices
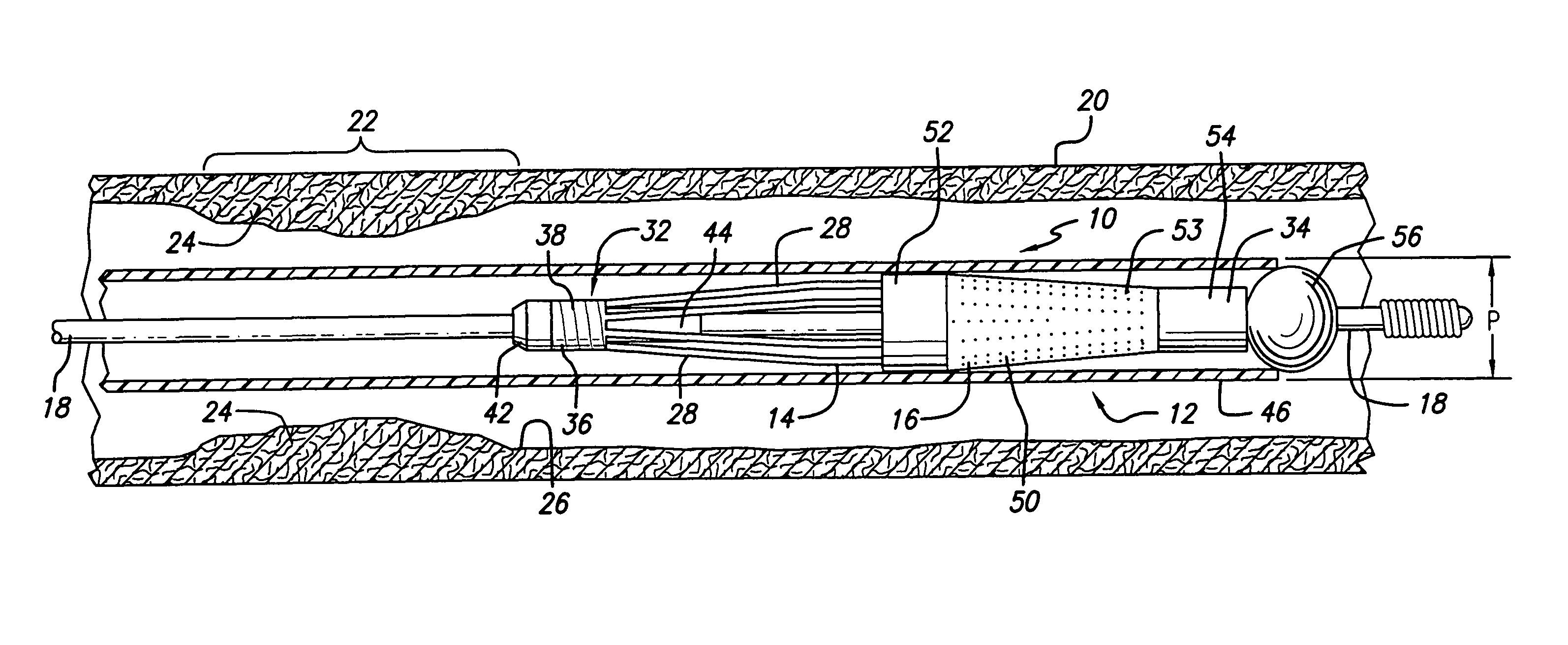
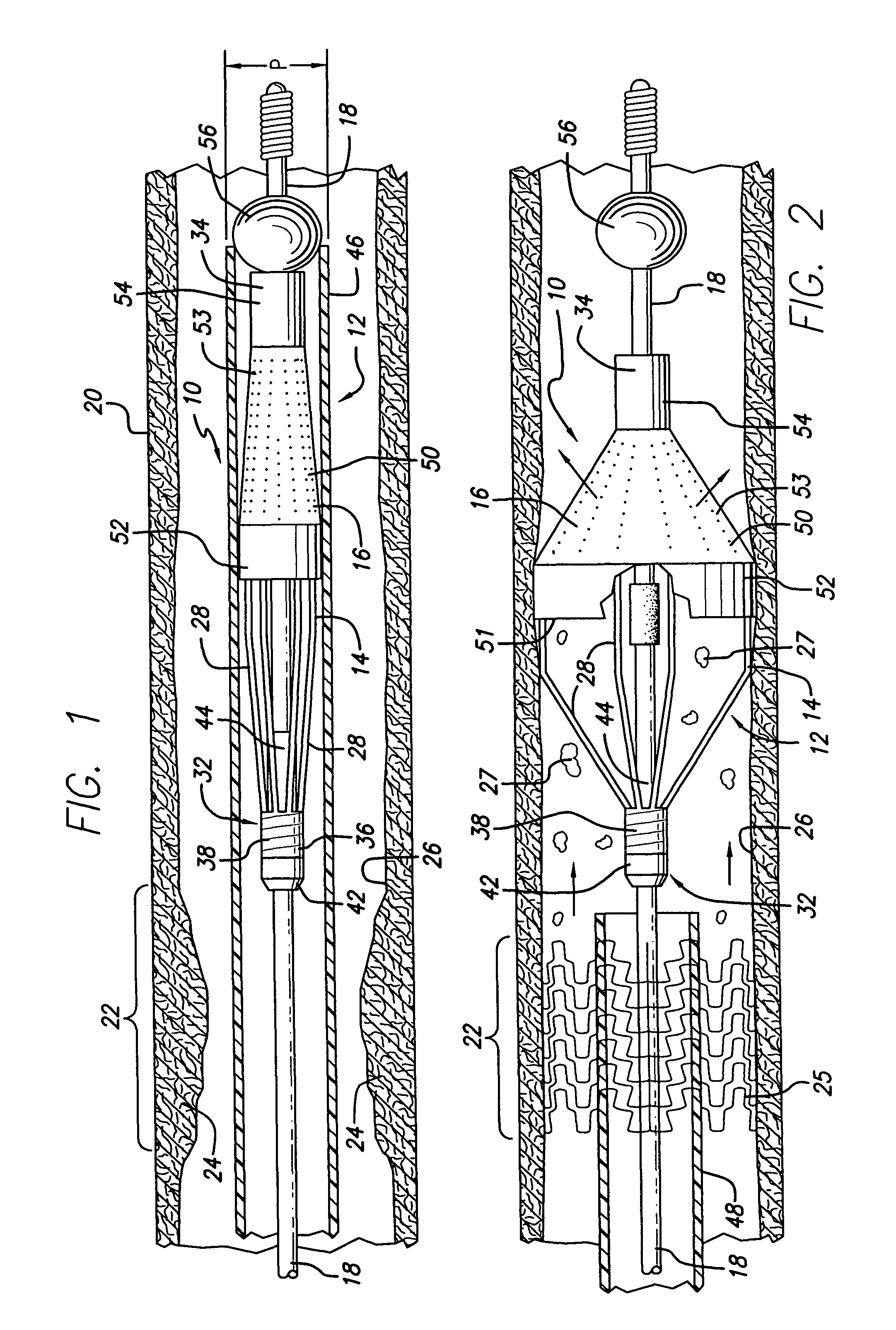
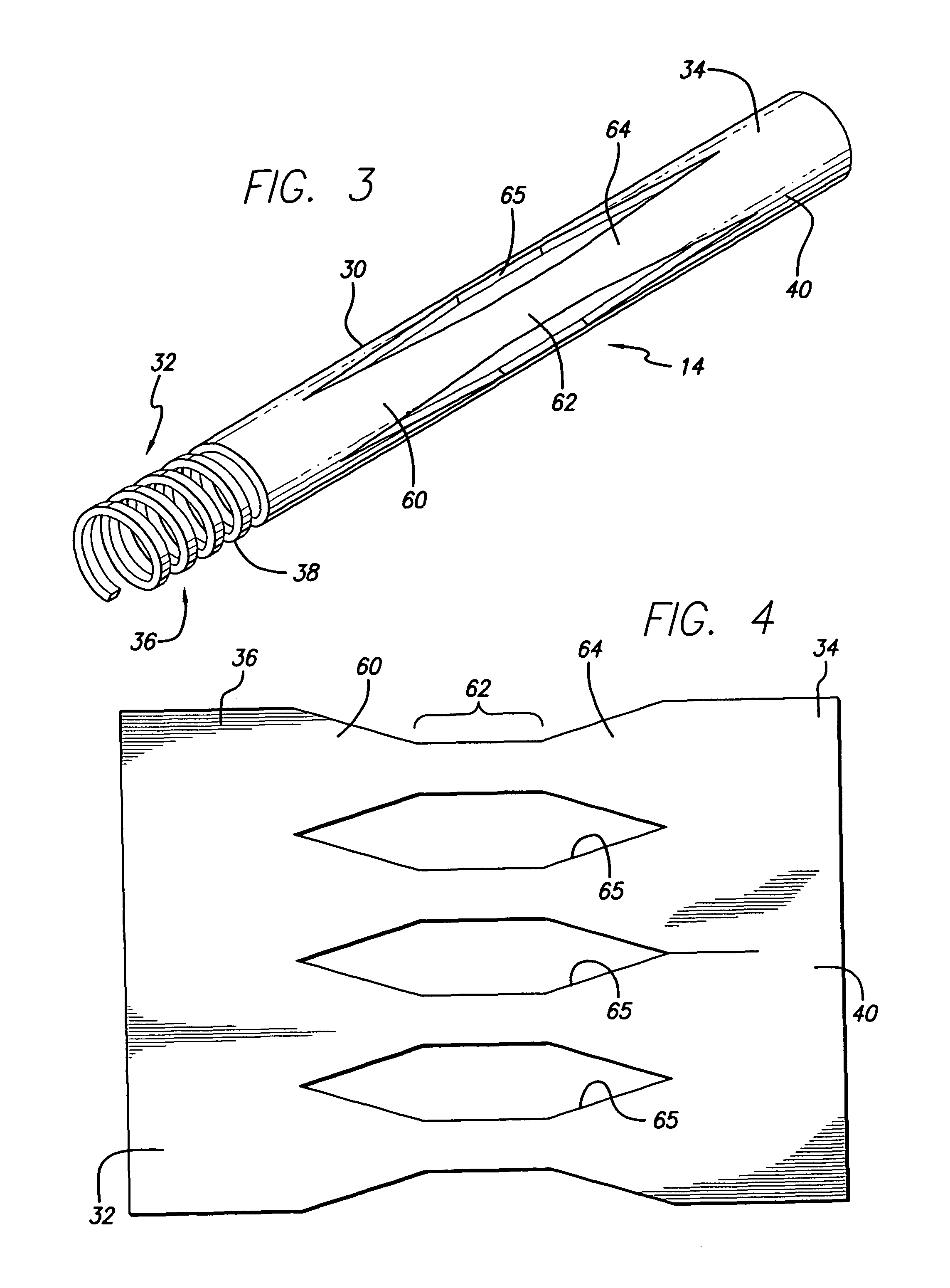
A process for assembling a medical device made from a nickel-titanium alloy for use in a mammalian body while avoiding the formation of stress-induced martensite and a medical device used in combination with a delivery system for deployment into the mammalian body are disclosed. By heating the nickel-titanium alloy of the medical device to a temperature above Md, and deforming and installing the device into a delivery system or holding capsule, it is possible to avoid the formation of stress-induced martensite in the stent, which stays in the austenitic phase throughout.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Radiopaque nitinol alloys for medical devices
InactiveUS6855161B2Enhance alloy 's formabilityEnhance thermomechanical propertyStentsSurgeryIridiumRhenium
A radiopaque nitinol medical device such as a stent for use with or implantation in a body lumen is disclosed. The stent is made from a superelastic alloy such as nickel-titanium or nitinol, and includes a ternary element selected from the group of chemical elements consisting of iridium, platinum, gold, rhenium, tungsten, palladium, rhodium, tantalum, silver, ruthenium, or hafnium. The added ternary element improves the radiopacity of the nitinol stent comparable to that of a stainless steel stent of the same size and strut pattern coated with a thin layer of gold. The nitinol stent has improved radiopacity yet retains its superelastic and shape memory behavior and further maintains a thin strut / wall thickness for high flexibility.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Vasoocclusive coil
InactiveUS7070608B2Provide bending stiffnessDesired bendingDilatorsDiagnostic markersEngineeringAlloy
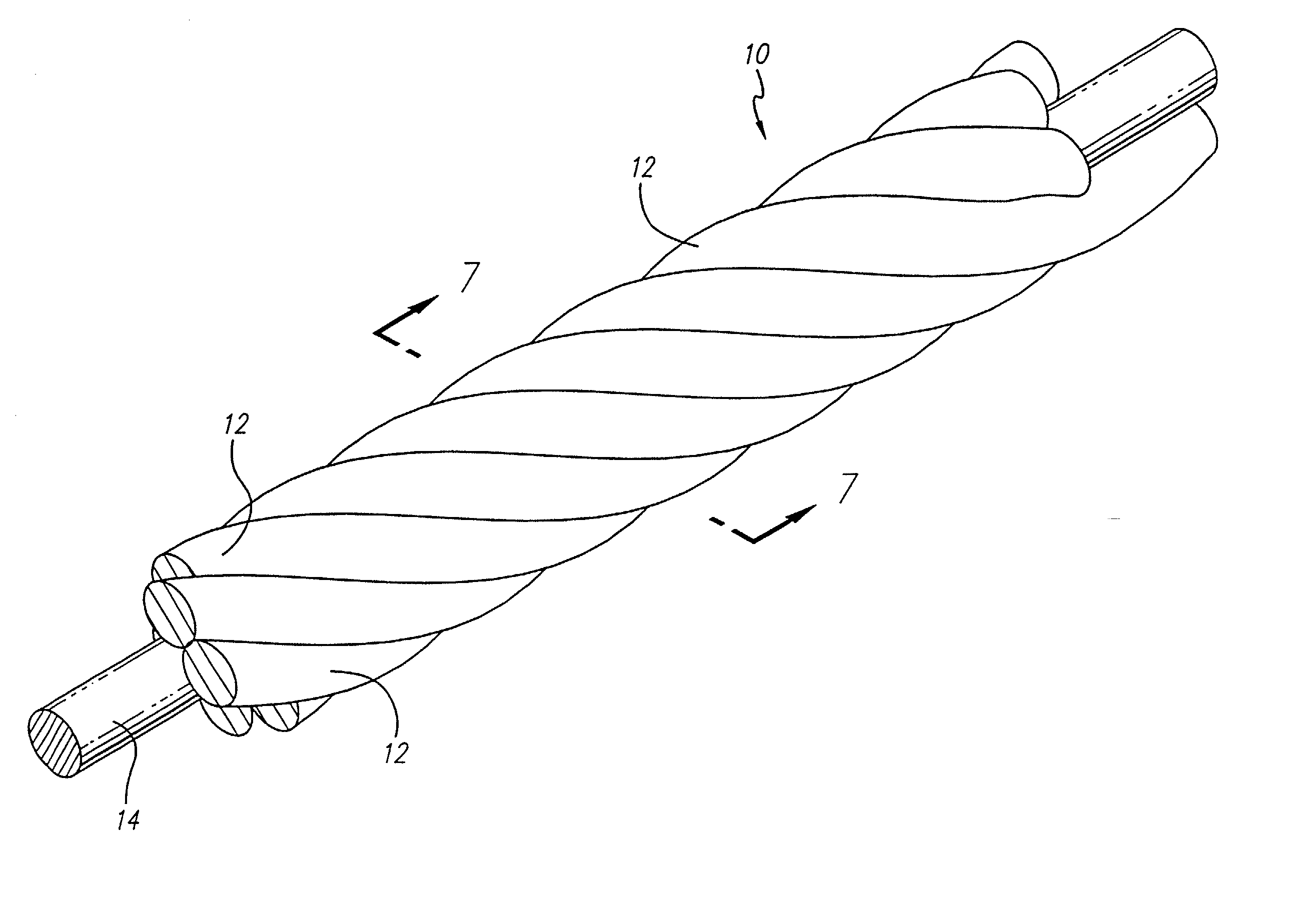
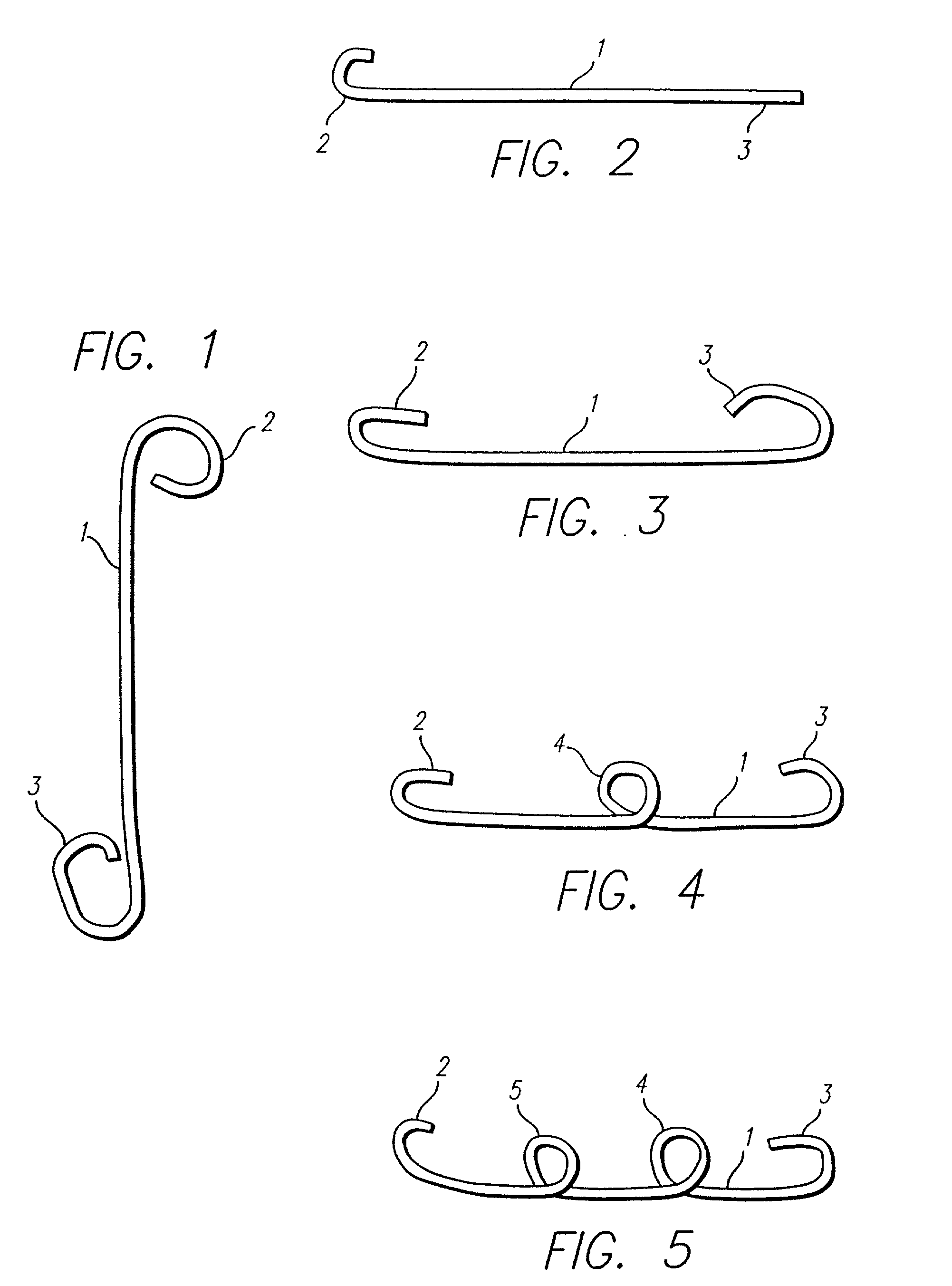
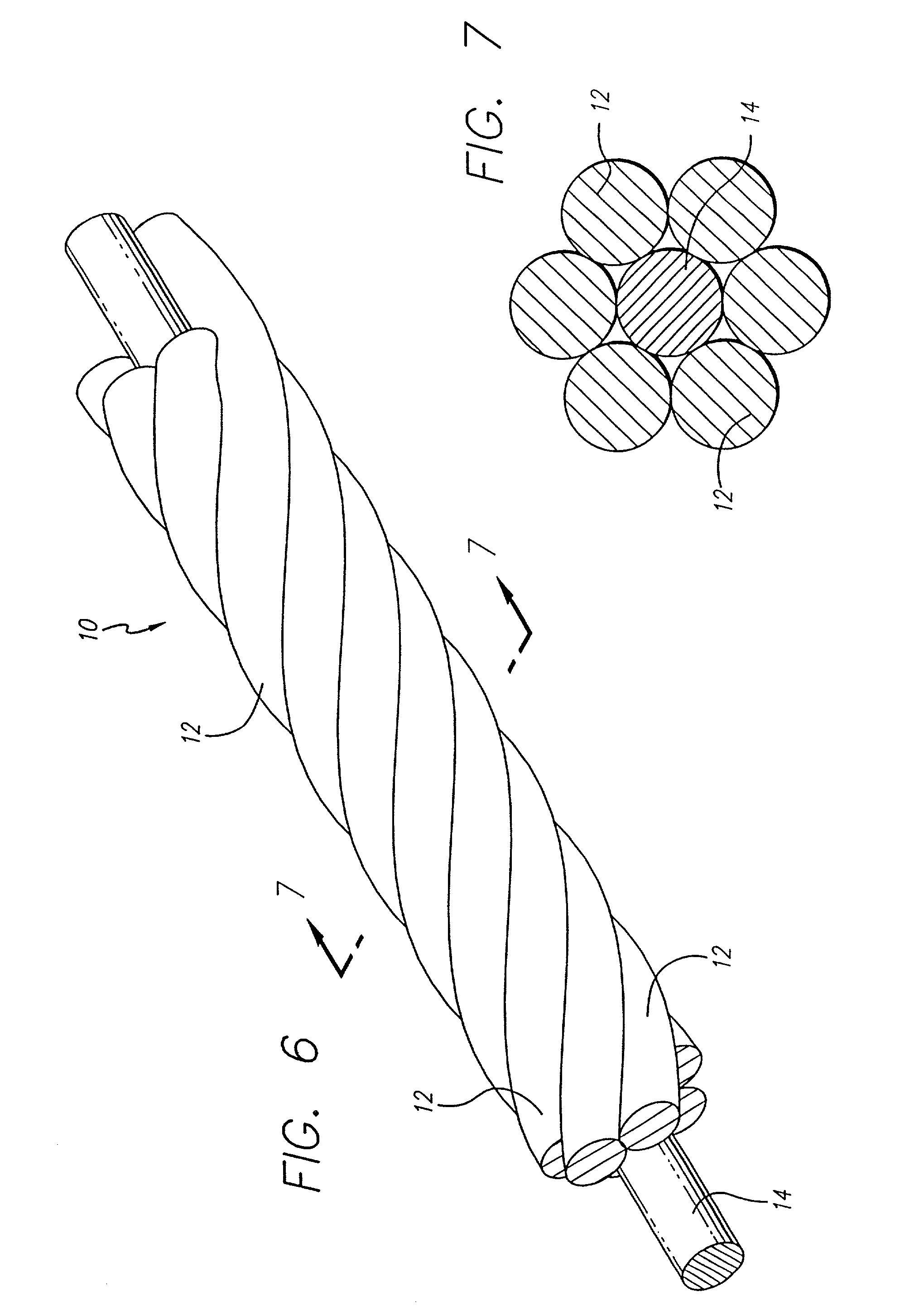
The vasoocclusive coil has a primary coil configuration with a helical loop at at least one end. The terminal helical loop can have a J-shaped configuration, preferably with a loop diameter of about 2 mm. The coil is preferably provided with helical loops at both ends, with helical loop at the proximal and distal ends of the coil acting as an anchor to prevent the coil from coming free from the location being treated and escaping into the vasculature. In a presently preferred embodiment both ends of the coil have a J-shape. In another presently preferred aspect, the vasoocclusive coil includes one or more loops intermediate the ends of the coil. The device is formed from a multi-stranded micro-cable having a plurality of flexible strands of a shape memory material and at least one radiopaque strand. The strands can be made of a shape memory nickel titanium alloy, that is highly flexible at a temperature appropriate for introduction into the body via a catheter, and that after placement will take on the therapeutic shape.
Owner:MICRUS CORP
Fixation device
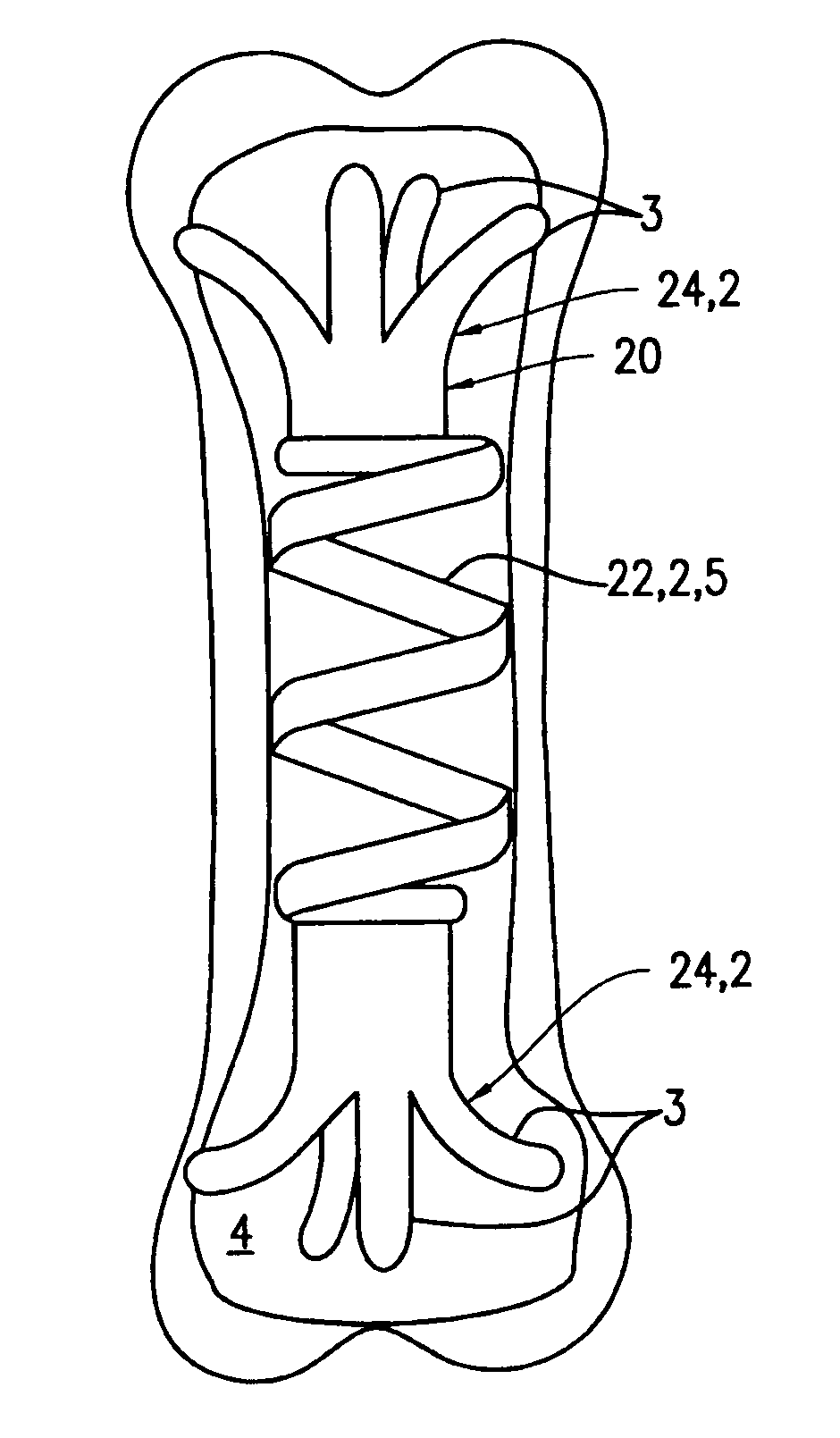
The present invention relates to a bone fixation device having a fixation member using a shape memory effect to secure bone fractures, including but not limited to, femur, tibia and humerus fractures. The fixation member can be malleable at a room temperature, but become rigid at a body temperature because of the shape memory effect, such as derived from a super-elastic property found in such as a nickel titanium alloy. The fixation member can be formed on one or more of the shaft portion and the two end portions of a nail member for securing bone fractures, such as by providing translational and rotational stabilities. The fixation member is also capable of providing a continuous and controllable compression force over the fractured bone, if needed.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
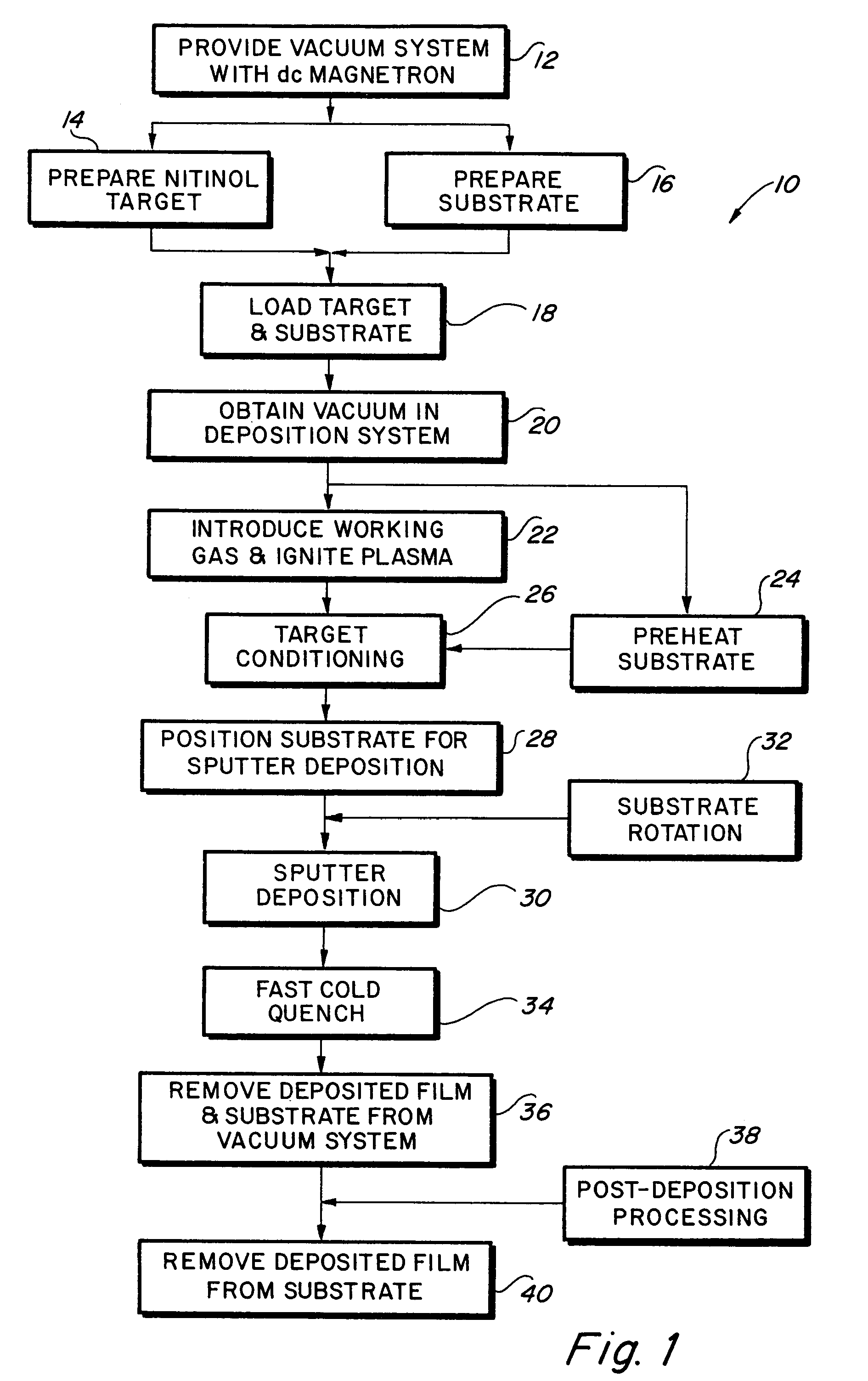
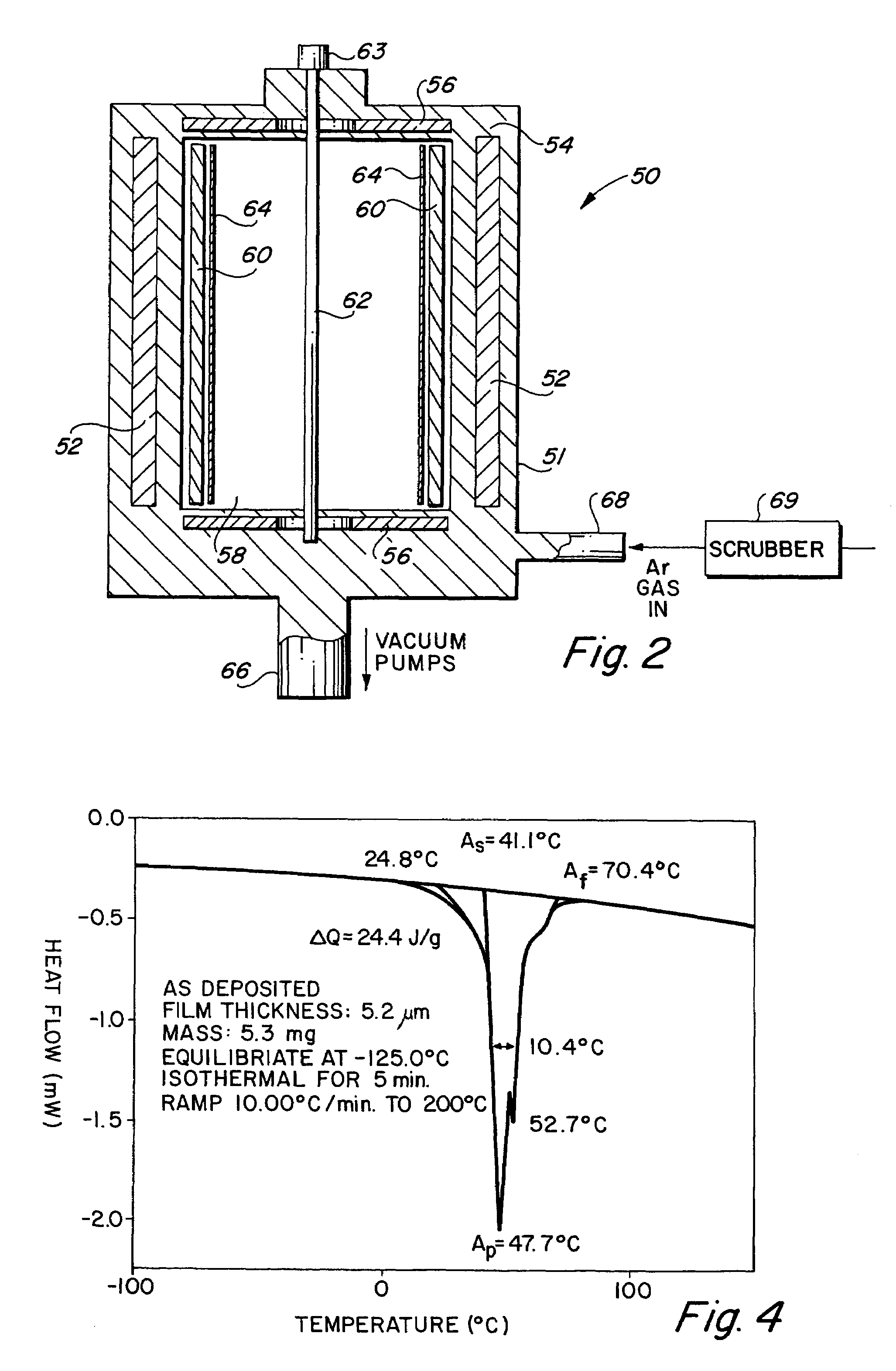
High strength vacuum deposited nitinol alloy films and method of making same
InactiveUS7335426B2Minimise scatteringControlled surface roughnessPig casting plantsThermometers using material expansion/contactionThin membraneTitanium
A vacuum deposition method for fabricating high-strength nitinol films by sputter depositing nickel and titanium from a heated sputtering target, and controlling the sputter deposition process parameters in order to create high-strength nitinol films that exhibit shape memory and / or superelastic properties without the need for precipitation annealing to attenuate the transition conditions of the deposited material. A vacuum deposited nitinol film having high-strength properties equal to or better than wrought nitinol films and which are characterized by having non-columnar crystal grain structures.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
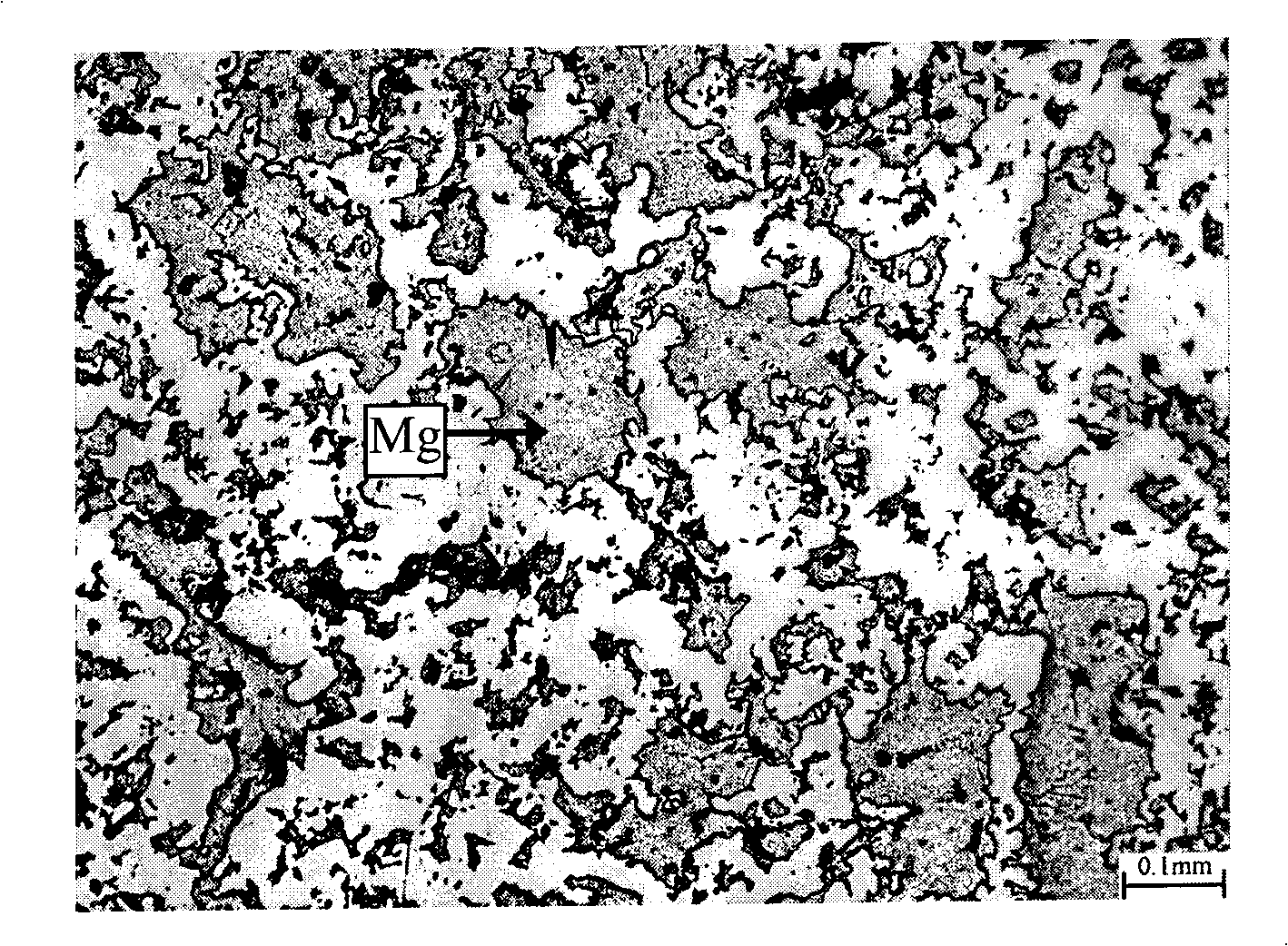
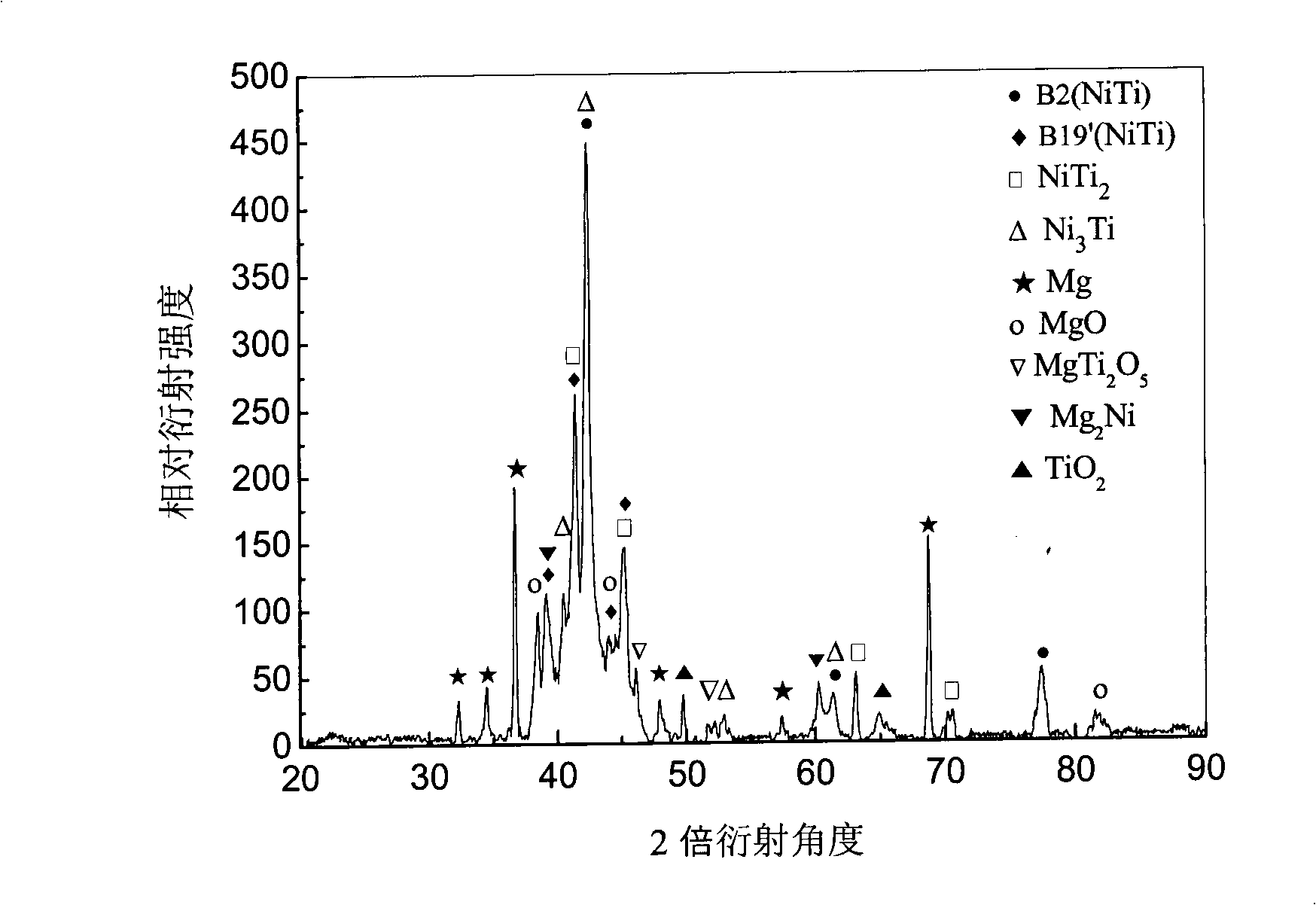
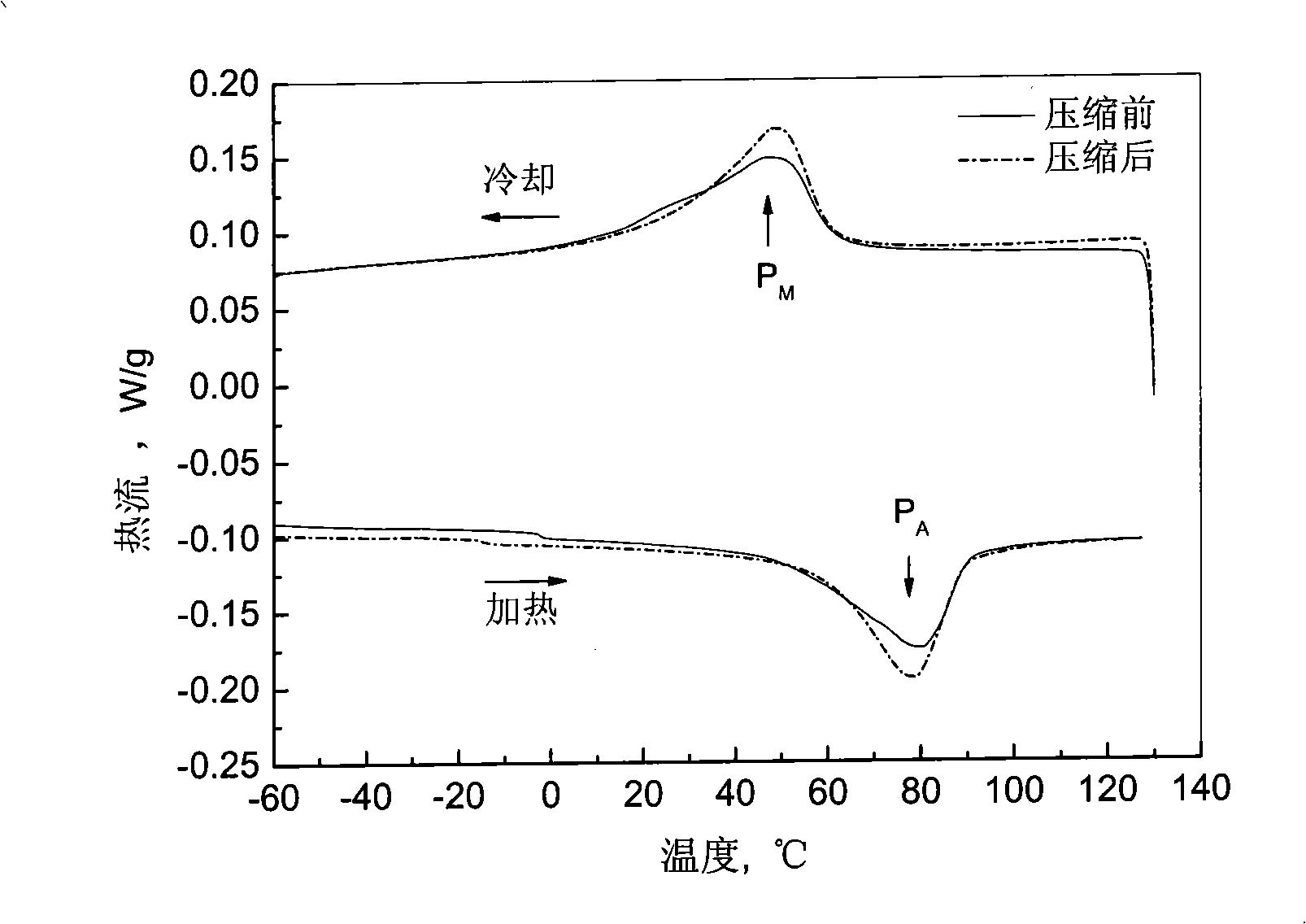
Preparation of composite type light high-strength nickel-titanium memory alloy-based high damping material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a compound type light-weight high-intensity nickel-titanium memorial alloy base high damping material. In the method, a powder sintering method is mainly used as a foundation and a pressureless infiltration technology is used as assistance; a pore-creating technology is firstly adopted; and a unit metal powder cascade sintering method is used for preparing a porous nickel-titanium alloy the holes of which are uniformly distributed; and then the pressureless infiltration technology is adopted for inducing the pure magnesium or magnesium alloy phase with high intrinsic damping, low density and micron scale into the porous nickel-titanium alloy, thereby preparing the high-damping magnesium(or magnesium alloy) / nickel-titanium memorial alloy base compound material the damping control phase of which is magnesium or the magnesium alloy. The compound nickel-titanium memorial alloy prepared by the invention still has the shape memory effect and the superelasticity action as well as has weight lighter than that of the compact nickel-titanium memorial alloy and intensity and damping capacity more excellent than that of the common porous nickel-titanium memorial alloy. The preparation method has good technical suitability, simple preparation process and low cost, and can be used for manufacturing the light-weight high-intensity compound damping materials, damping structures and apparatuses.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Device for correcting spinal deformities
InactiveCN1697630AConstant and controllable correction forceInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention relates generally to a device of and a method for correcting spinal deformities, such as scoliosis and kyphosis. The invention employs the superelasticity or pseudoelasticity, such as found in a nickel-titanium alloy, to provide a continuous, predictable, and controllable correction force and to achieve a gradual and full correction. The correction force can be exerted on the deformed spine either at the time of the spine surgery or after the surgery or both, to afford a full or substantially full correction. The continuous and controllable correction force of the present invention is safer than an instantaneous and large correction force applied only at the time of surgery. Additionally, the continuous and controllable correction force is capable of gradually and fully correcting the spinal deformities without any post-operative manipulation of the correction device or re-operation.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD +1
Fatigue-Resistant Nitinol Instrument
InactiveUS20120231414A1Improve the immunityFew stepsMetal-working drilling toolsFurnace typesWire rodTitanium
A fatigue-resistant Nitinol instrument has a working portion in the deformed monoclinic martensitic state and an austenite finish temperature in the range of 40° to 60° C. Because the operating environment of the instrument is about 37° C., the working portion remains in the monoclinic martensitic state during its use. The relatively high austenite finish temperature and fatigue resistance is achieved by subjecting the nickel-titanium alloy to a final thermal heat treat in a temperature range of about 410° to 440° C. while the nickel-titanium alloy is under constant strain of about 3 to 15 kg. Further, the high austenite finish temperature is achieved without subjecting the alloy to thermal cycling to produce shape memory. Additionally, there are no intermediate processing steps occurring between obtaining a finished diameter of the wire or blank through cold working and the final thermal heat treat under constant strain.
Owner:DENTSPLY SIRONA INC
Manufacture of fine-grained material for use in medical devices
Medical devices are manufactured from fine grained materials, processed from of a variety of metals and alloys, such as stainless steel, cobalt-chromium and nickel-titanium alloys. A fine grained metal or alloy is formed from a specimen rapidly heated to its recrystallization temperature, and then subjected to high temperature, multi-axial deformation, for example, by heavy cross-forging or swaging. The deformed specimen may be cooled and reheated to a second recrystallization temperature. The metal or alloy in the specimen is then allowed to recrystallize, such that the grain size is controlled by quenching the specimen to room temperature. A desired medical device is then configured from the fine grained material. Decreasing the average grain size of a substrate material and increasing the number of grains across a thickness of a strut or similar component of the medical device increases the strength of the device and imparts other beneficial properties into the device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
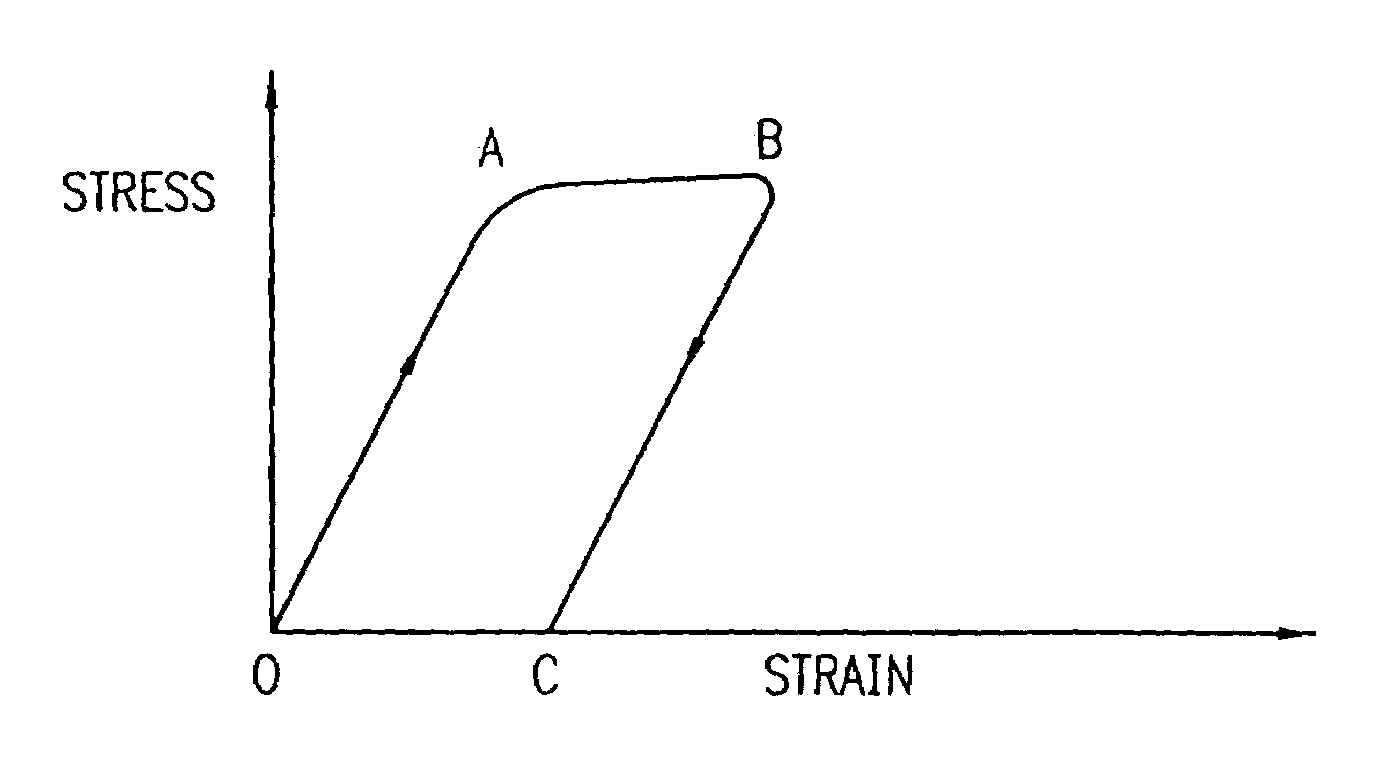
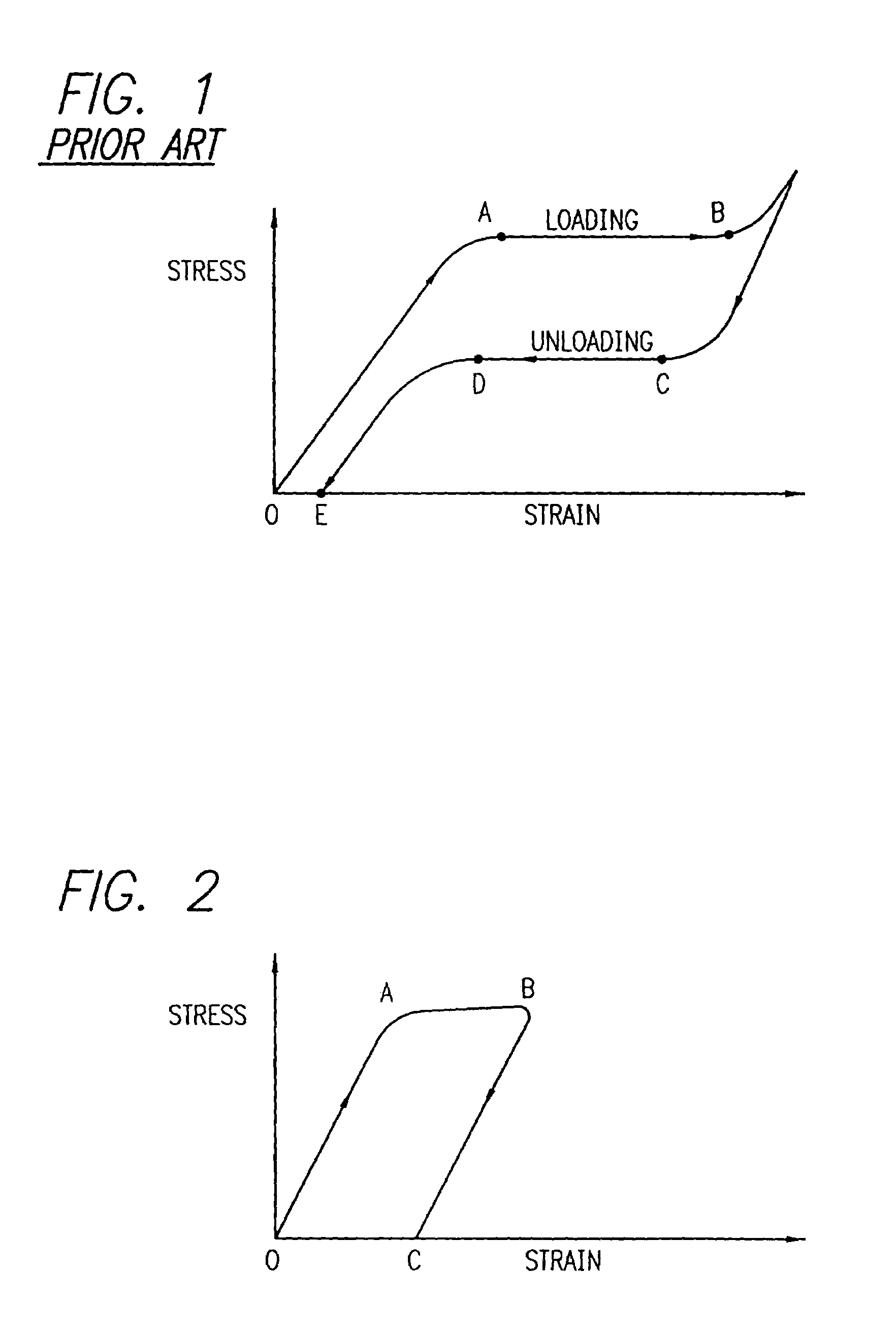
Nitinol alloy design and composition for medical devices
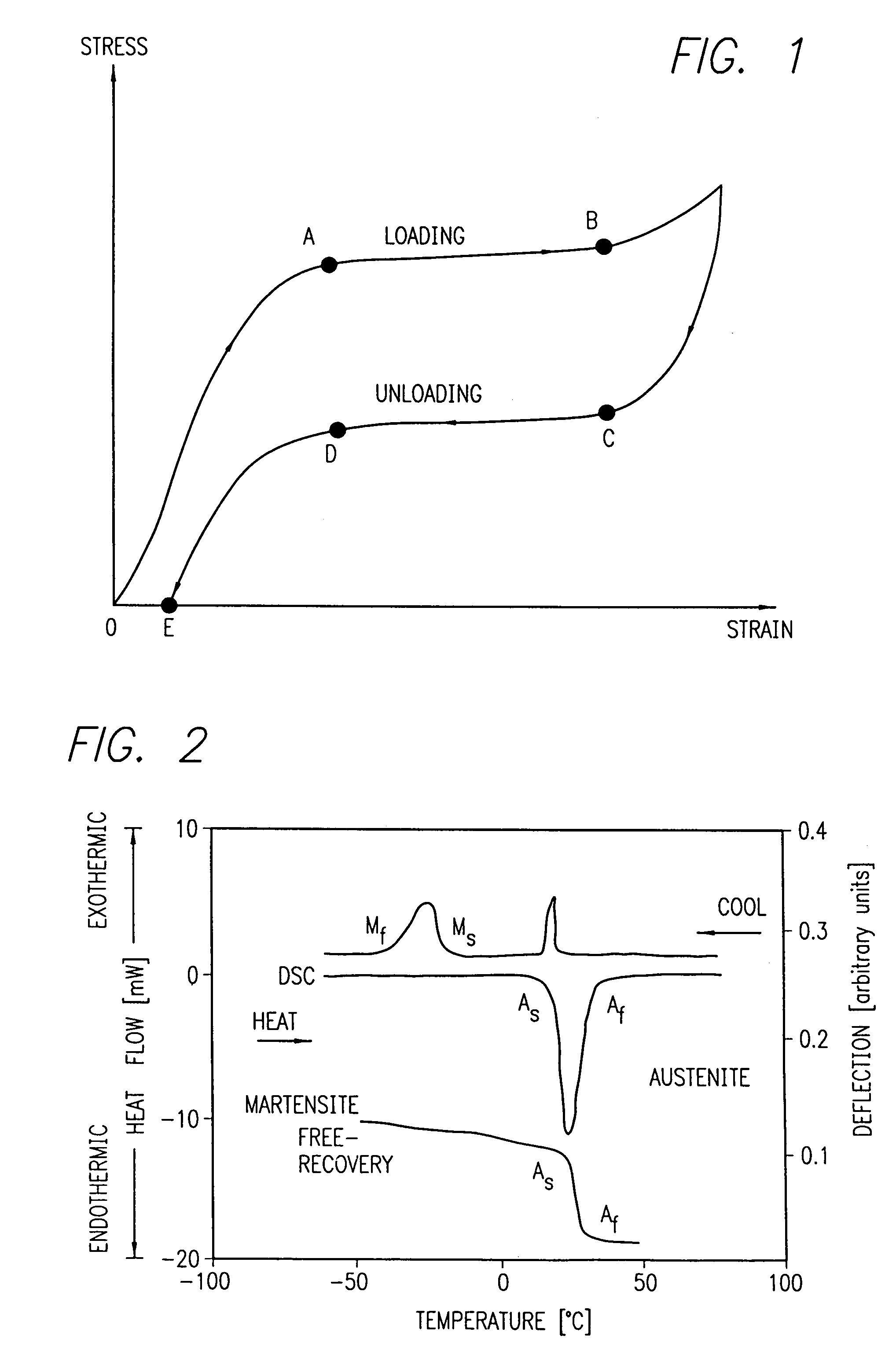
A stent and a delivery system for implanting the stent in a body lumen is disclosed. The stent is made from a superelastic alloy such as nickel-titanium or nitinol, and includes a ternary element in order to minimize the stress hysteresis of the superelastic material. The stress hysteresis is defined by the difference between the loading plateau stress and the unloading plateau stress of the superelastic material. The resulting delivery system has a small profile and includes a sheath covering the stent that has a thin wall. A guide wire core can also be made from the small stress hysteresis superelastic material.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
4D printing method of in-situ regulation of functional characteristics of nickel-titanium alloy and application
ActiveCN110465662ANickel content controlUniform compositionAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransportation and packagingManufacturing technology4d printing
The invention belongs to the technical field of additive manufacturing, and discloses a 4D printing method of in-situ regulation of the functional characteristics of a nickel-titanium alloy and application. A nickel-titanium alloy rod material is powdered by atomization to obtain nickel-titanium alloy powder with a particle size of 15-53 [mu]m, then the nickel-titanium alloy powder is placed in adischarge plasma-assisted ball mill for discharge treatment to promote the activity activation of the powder, and then nano-scale nickel powder with the particle size being 100-800nm is added to obtain mixed powder; the discharge treatment is continued to realize metallurgical bonding between the nickel-titanium alloy powder and the nano-nickel powder to obtain modified powder; and finally the modified powder is prepared and formed by an additive manufacturing technology to obtain the functionalized nickel-titanium alloy. The metallurgical bonding is realized by adding the nano-scale nickel powder and the large-sized spherical nickel-titanium alloy powder during the discharge treatment process, so that a bulk alloy and parts thereof with uniform composition, microstructure and performanceare prepared.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Shape memory material and method of making the same
The present invention relates generally to a shape memory and / or super-elastic material, such as a nickel titanium alloy. Additionally or alternatively, the present invention relates to a super-elastic or pseudo-elastic material that has an initial transition temperature Af above a body temperature. The shape memory material can have a super-elasticity or pseudo-elasticity property at a temperature below the initial transition temperature Af of the material. For example, the shape memory material can have its workable temperature for producing super-elasticity or pseudo-elasticity of about 0° C. to 15° C. below the initial transition temperature Af. The shape memory material can be malleable at a room temperature, and become super-elastic or pseudo-elastic at a body temperature. In addition, the present invention relates to a method of making a shape memory or a super-elastic material. The treatment protocols can include but not limited to thermo-mechanical, thermo-mechanical, radiation, and ternary alloying treatments.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD +2
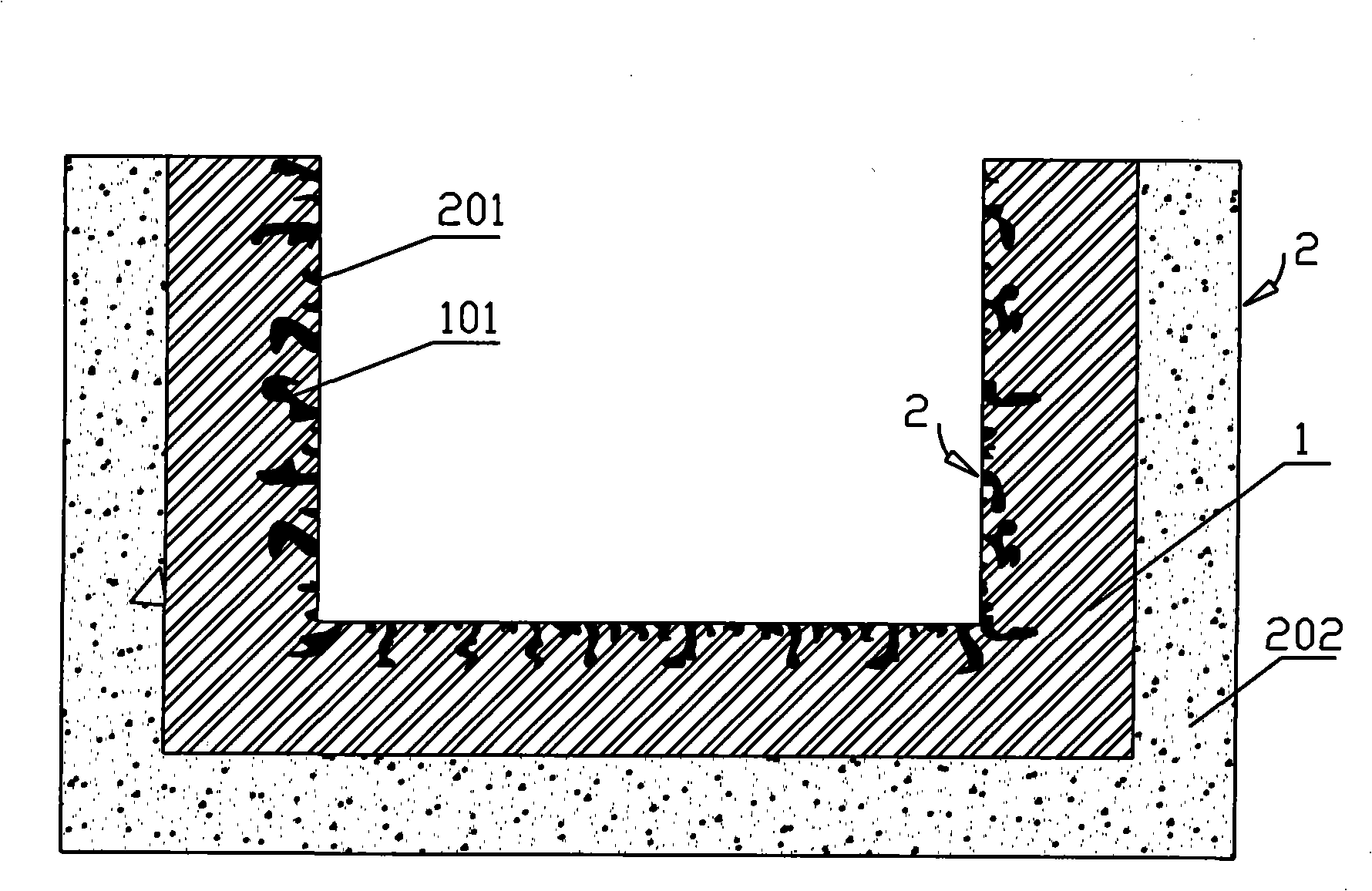
Method for differential arc oxidation treatment of Nickel-titanium alloy for medical purpose
InactiveCN101063221ANo reduction in mechanical propertiesSmall mechanical propertiesSurgerySurface reaction electrolytic coatingPlasma electrolytic oxidationMicro arc oxidation
The invention discloses a method of medical nickel titanium alloy differential arc oxidation treatment, which comprises the following steps: (1) pre-treating surface; (2) putting into hydraulic fluid; choosing NiTi ally as positive pole and loading trough as negative pole; treating; (3)washing; drying; getting the product. This invention possesses simple method, which can inhibit discharging of Ni ion in nickel titanium alloy and reinforce safety.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Austenitic nitinol medical devices
InactiveUS7128758B2StrongHoop strength of was so lowStentsSurgeryStress induced martensiteTitanium alloy
A medical device for use within a body lumen that is made from a binary nickel-titanium alloy that remains in its austenitic phase throughout its operational range is disclosed. The medical device, such as an intraluminal stent, is made from superelastic nickel-titanium and may optionally be alloyed with a ternary element. By adding the ternary element and / or through heat treatment, it is possible to lower the phase transformation temperature between the austenitic phase and the martensitic phase of the nickel-titanium alloy. By lowering the phase transformation temperature, the martensite deformation temperature is likewise depressed. It is possible then to depress the martensite deformation temperature below body temperature such that when the device is used in a body lumen for medical treatment, the nickel-titanium device remains completely in the austenitic phase without appearance of stress-induced martensite even if the device is placed under stress.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Avoiding stress-induced martensitic transformation in nickel titanium alloys used in medical devices
A process for assembling a medical device made from a nickel-titanium alloy for use in a mammalian body while avoiding the formation of stress-induced martensite and a medical device used in combination with a delivery system for deployment into the mammalian body are disclosed. By heating the nickel-titanium alloy of the medical device to a temperature above Md, and deforming and installing the device into a delivery system or holding capsule, it is possible to avoid the formation of stress-induced martensite in the stent, which stays in the austenitic phase throughout.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Laparoscopic surgical retractor, retractor head for laparoscopic surgery, retractor head main body and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102499730AStrong reset functionTurn easilySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTitaniumAlloy
The invention discloses a laparoscopic surgical retractor, a retractor head for laparoscopic surgery, a retractor head main body and a manufacturing method thereof. The laparoscopic surgical retractor is provided with a handle, a handle seat, a wire thread insert, a stem, a fixed sleeve, a screw rod, a connection sleeve, a seal ring, a fixed plate, a retractor rod, a pull tube, a retractor seat and a retractor head, wherein a retractor head main body is made from shape memory hyperelastic nickel-titanium alloy. The retractor head comprises the retractor head main body and the front part of the retractor head. The invention further comprises the retractor head main body for the laparoscopic surgery and the manufacturing method thereof, the manufacturing method of the retractor head main body comprises the steps that: nickel and titanium raw materials are placed in a copper crucible to seal and vaccumize, and are smelted at 1800 DEG C for 2h; a plate is rolled after four times of rolling and annealing; the plate is cut into strips through electric sparks; the strip-shaped plates undergo finish machining to form blanks; and the blanks are placed in a shaper to be thermally treated for 20min at 480-500 DEG C, are cooled and demoulded. The laparoscopic surgical retractor and the retractor head main body have reasonable structures, and the retractor head has the superstrong reset function, and can be flexible in an instrument, so the surgery is facilitated.
Owner:HANGZHOU KANGJI MEDICAL INSTR
Shape memory alloy articles with improved fatigue performance and methods therefor
InactiveUS7789979B2Improve fatigue performanceImprove fatigue lifeStentsSurgeryPre strainControl manner
Articles made of shape memory alloys having improved fatigue performance and to methods of treating articles formed from shape memory alloy materials by pre-straining the articles (or desired portions of the articles) in a controlled manner so that the resultant articles exhibit improved fatigue performance. The shape memory articles are preferably medical devices, more preferably implantable medical devices. They are most preferably devices of nitinol shape memory alloy, most particularly that is superelastic at normal body temperature. The pre-straining method of the present invention as performed on such articles includes the controlled introduction of non-recoverable tensile strains greater than about 0.20% at the surface of a desired portion of a shape memory alloy article. Controlled pre-straining operations are performed on the shape-set nitinol metal to achieve nonrecoverable tensile strain greater than about 0.20% at or near the surface of selected regions in the nitinol metal article. The pre-straining operations result in a significant increase in fatigue life of the selectively treated regions and an overall improvement in the fatigue performance of the device.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Manufacture of fine-grained material for use in medical devices
Medical devices are manufactured from fine grained materials, processed from of a variety of metals and alloys, such as stainless steel, cobalt-chromium and nickel-titanium alloys. A fine grained metal or alloy is formed from a specimen rapidly heated to its recrystallization temperature, and then subjected to high temperature, multi-axial deformation, for example, by heavy cross-forging or swaging. The deformed specimen may be cooled and reheated to a second recrystallization temperature. The metal or alloy in the specimen is then allowed to recrystallize, such that the grain size is controlled by quenching the specimen to room temperature. A desired medical device is then configured from the fine grained material. Decreasing the average grain size of a substrate material and increasing the number of grains across a thickness of a strut or similar component of the medical device increases the strength of the device and imparts other beneficial properties into the device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Self-Crimping Radiopaque marker
A radiopaque marker band includes a tube having an inner surface and an outer surface. The tube is made from a shape-memory material, such as a nickel-titanium alloy. A coating is disposed on at least a portion of the outer surface of the tube. The coating has a greater radiopacity that said shape-memory material. The coating may be applied in a plurality of bands on the outer surface of the tube.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Fatigue-resistant nickel-titanium alloys and medical devices using same
Superelastic and / or shape memory nickel-titanium alloys having an increased fatigue life that is superior to known nickel-titanium alloys are disclosed. The nickel-titanium alloys have a minimum fatigue life that may be at least about 10 million strain cycles at a strain of at least about 0.75. The minimum fatigue life may be due, at least in part, to the nickel-titanium alloy having at least one of an oxygen concentration of less than about 200 ppm, a carbon concentration of less than about 200 ppm, the absence of oxide-based and / or carbide-based inclusions having a size greater than about 5 microns (μm), the presence of an R-phase, or combinations of the foregoing. Articles manufactured from such fatigue-resistant nickel-titanium alloys can be more durable because they are more resistant to repetitive strain and crack propagation.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Manufacture of Shape-Memory Alloy Cellular Materials and Structures by Transient-Liquid Reactive Joining
ActiveUS20110008643A1Constant gainFine surfaceThermometers using material expansion/contactionSoldering apparatusNiobiumHoneycomb structure
This invention discloses a method, using pure niobium as a transient liquid reactive braze material, for fabrication of cellular or honeycomb structures, wire space-frames or other sparse builtup structures or discrete articles using Nitinol (near-equiatomic titanium-nickel alloy) and related shape-memory and superelastic alloys. Nitinol shape memory alloys (SMAs), acquired in a form such as corrugated sheet, discrete tubes or wires, may be joined together using the newly discovered joining technique. Pure niobium when brought into contact with nitinol at elevated temperature, liquefies at temperatures below the melting point and flows readily into capillary spaces between the elements to be joined, thus forming a strong joint.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
Biology polypeptide medicament blood vessel bracket and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101313873ANo effect on mechanical propertiesEffect on mechanical propertiesStentsOrganic active ingredientsProgenitorBiopolymer
The invention relates to a biologic polypeptide medicine blood vessel support and a preparation method thereof. The biologic polypeptide medicine blood vessel support comprises a support body and active medicines. The support body which is medical material with pores and good biocompatibility is made from stainless steel, cobalt-base alloy, titanium alloy, nickel-titanium alloy or polylactic acid biopolymer; the active medicines comprise a biologic polypeptide medicine and a smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibition medicine. The support is characterized in that: the support body with the pores has the biologic polypeptide medicine fixed on the internal surface of the body and the smooth muscle cell proliferation inhibition medicine coated on the external surface of the body. The preparation me(3) carrying out the after-treatment of the surface of the support body; (4) preparing the medicines; (5) coating the external surface; (6) fixing the medicine onto the internal surface; (7) carrying out the process step of low temperature drying. The support can selectively absorb endothelium progenitor cells which quickly differentiate into endothelium cells to promote the restoration of the endothelium after the support is built in; the support can also effectively inhibit the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells, persistently and effectively reduce the formation of a new inner membrane, effectively prevent restenosis inside the support, and avoid the risk of potentially fatal late thrombosis.
Owner:乐普(深圳)国际发展中心有限公司
Heat treatment for cold worked nitinol to impart a shape setting capability without eventually developing stress-induced martensite
InactiveUS7976648B1High mechanical strengthMore storage capacityGuide wiresSurgeryEmbolic Protection DevicesStress induced martensite
Cold worked nickel-titanium alloys that have linear pseudoelastic behavior without a phase transformation or onset of stress-induced martensite as applied to a medical device having a strut formed body deployed from a sheath. In one application, an embolic protection device that employs a linear pseudoelastic nitinol self-expanding strut assembly with a small profile delivery system for use with interventional procedures. The expandable strut assembly is covered with a filter element and both are compressed into a restraining sheath for delivery to a deployment site downstream and distal to an interventional procedure. Once at the desired site, the restraining sheath is retracted to deploy the embolic protection device, which captures flowing emboli generated during the interventional procedure. Linear pseudoelastic nitinol is used in the medical device as distinct from non-linear pseudoelastic (i.e., superelastic) nitinol.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
4D printing based temperature control self-deformation device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111842887AStress reliefAlleviate bindingAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyTemperature controlTitanium zirconium
The invention belongs to the field of 4D printing additive manufacturing, and discloses a 4D printing based temperature control self-deformation device and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps that S1, a three-dimensional model of a self-deformation device is set up, and areas obtained through division at least comprise a low-temperature deformation area, a transition area and a high-temperature deformation area; S2, laser printing parameters of the three areas are set, nickel and titanium based memory alloy powder is used for carrying out divisionforming on the three areas through the laser selective melting technology, an intelligent deformation part is obtained, and nickel-titanium-zirconium ternary alloy powder serves as the nickel and titanium based memory alloy powder correspondingly adopted by the transition area and the high-temperature deformation area; and S3, the intelligent deformation part is folded, and the temperature control self-deformation device is obtained. Zr is introduced into a nickel and titanium alloy to serve as a third component, and compared with the manner that in the prior art, manufacturing of function gradient NiTi materials can be achieved only by changing process parameters, the excitation temperature point of the NiTi based self-deformation device can be flexibly adjusted and controlled accordingto requirements.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
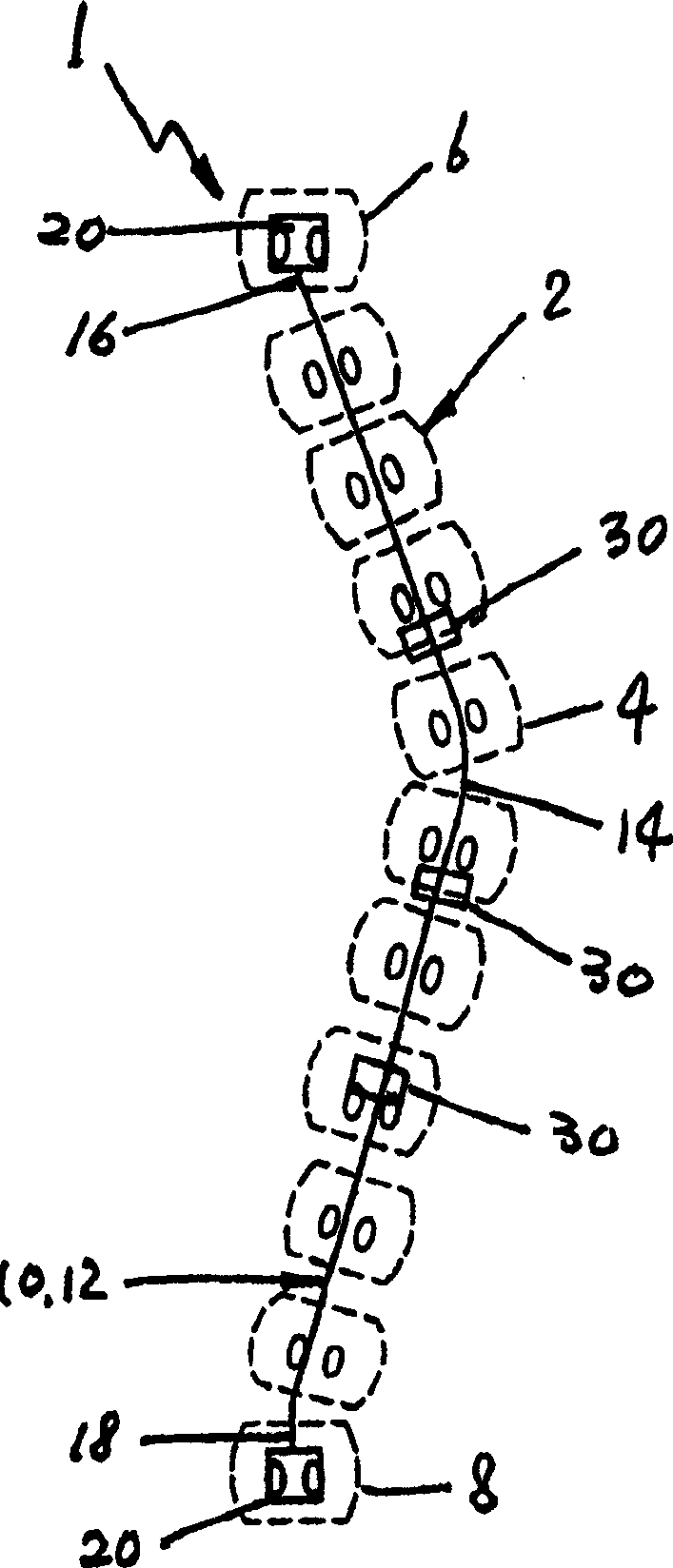
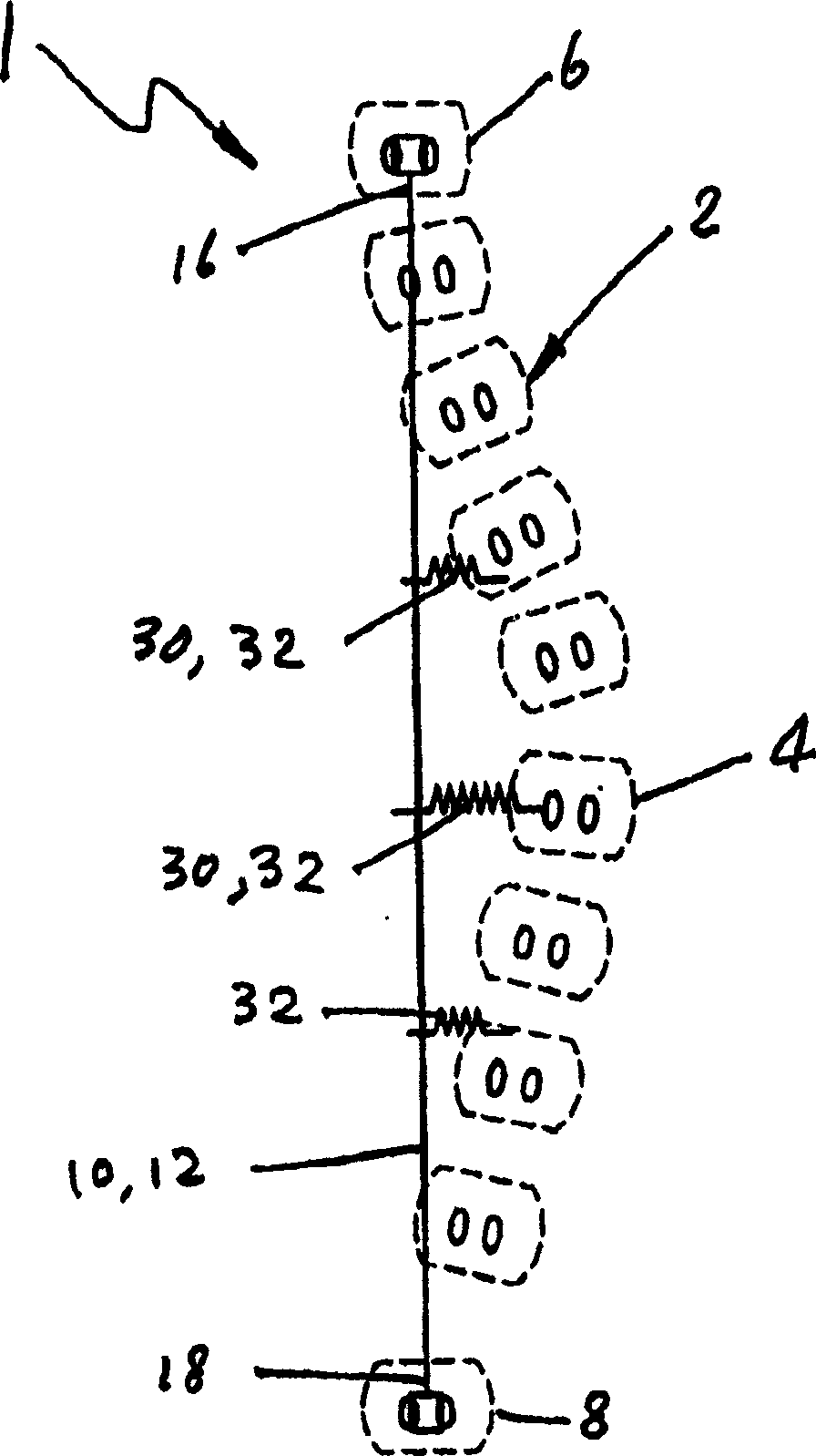
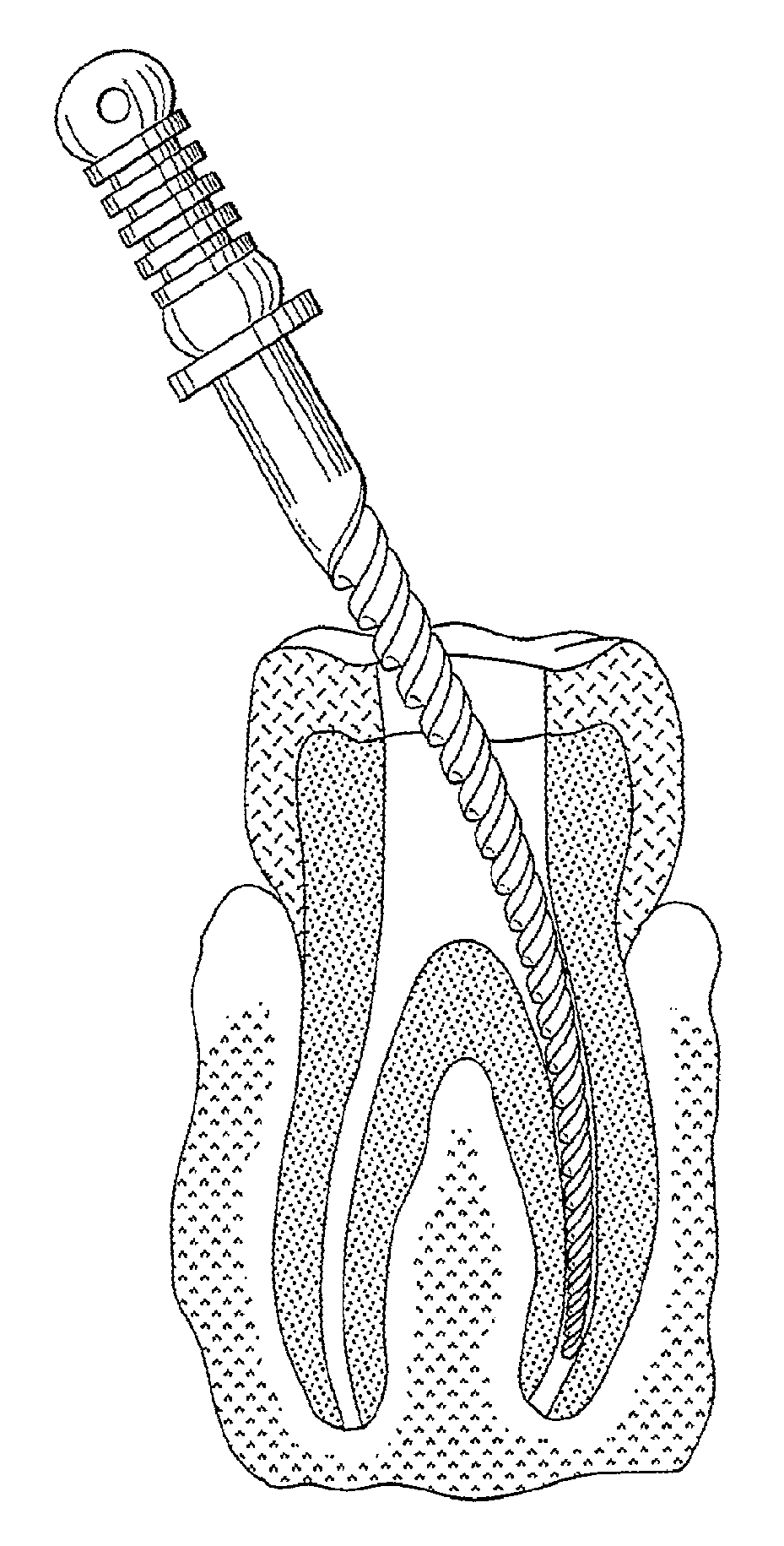
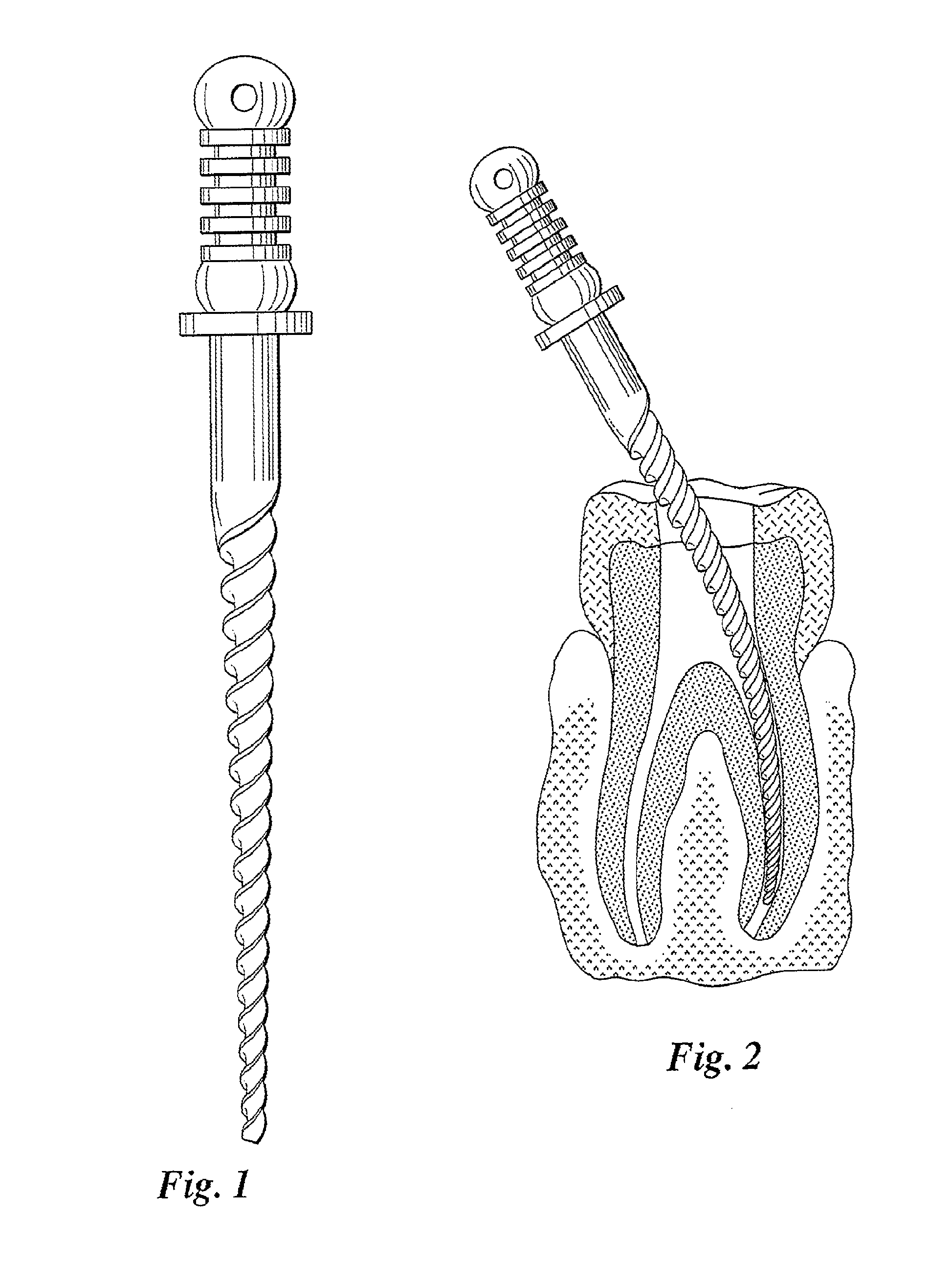
Ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium alloy root canal file and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102743233AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceTeeth cappingTeeth nerve/root treatment implementsAlloyMartensite
The invention discloses an ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium alloy root canal file and a preparation method thereof, relating to a root canal file and a preparation method thereof and aiming to solve the technical problems of low cutting efficiency and high probability of breakage in a curved root canal of the conventional nickel-titanium root canal file. The ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium alloy root canal file is prepared from ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium alloy with particle size of 200-300 nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: 1, performing ultra-fine graining treatment on the nickel-titanium alloy; 2, preparing an ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium alloy wire; 3, machining and performing surface treatment on a cutting edge of the root canal file; and 4, thermally treating the ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium alloy root canal file. The phase composition of the ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium root canal file consists of martensite and austenite at room temperature; the diffraction peak is obviously widened because of grain refinement, and the ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium root canal file is austenite at application temperature; the prepared ultra-fine grained nickel-titanium alloy root canal file has good hardness and wear resistance; and the cutting efficiency during clinical use is obviously improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Metal composite material and fused deposition 3D printing method of bone implant of metal composite material
ActiveCN105817629AHigh strengthLow elastic modulusAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantComputer printingBone implant
The invention discloses a metal composite material and a fused deposition 3D printing method of a bone implant of the metal composite material. The metal composite material comprises a nickel-titanium alloy and double-component composite bone cement, and the mass ratio of the nickel-titanium alloy to the double-component composite bone cement is 10-16:8-14. The 3D printing method includes the steps that firstly, an STL model file is input; secondly, the nickel-titanium alloy and powder of the double-component composite bone cement are subjected to ball milling mixing, and a discharged mixture is added into a powder charging barrel; thirdly, liquid of the double-component composite bone cement is added into a liquid charging barrel; and fourthly, technological parameters of a 3D printer are adjusted, the discharged material of the powder charging barrel and a discharged material of the liquid charging barrel are input into a printing nozzle after being evenly mixed, printing forming is conducted, and sintering is conducted after curing. The binding force of the composite bone cement and the nickel-titanium alloy can be improved, the composite bone cement is prevented from being disengaged, the biological activity of the nickel-titanium alloy is improved, and biocompatibility between the implant of the metal composite material and the human tissue is improved.
Owner:广州尤尼智康生物科技有限公司
Bendable, reusable medical instruments with improved fatigue life
InactiveUS7604609B2Incomplete hysteresisImprove fatigue lifeSurgeryDental toolsEngineeringTitanium alloy
A needle device which is manufactured from shape memory or pseudo-elastic materials, such as Nickel Titanium alloys, is provided which may be formed and used repeatedly without adverse effects, such as permanent deformation or fatigue failure. The device in accordance with the present disclosure may be provided having an initial shape which a doctor may bend to a desired shape. The device may be easily returned to its initial shape after use by heating the device above a predetermined sterilization temperature. This cycle may be repeated during subsequent uses, substantially extending the life of the instrument, due to the reduced work hardening and enhanced fatigue properties of the Nickel Titanium device.
Owner:GEN SURGICAL INNOVATIONS
Intravascular stent applied to interventional operation as well as use method, manufacturing method and manufacturing device of intravascular stent
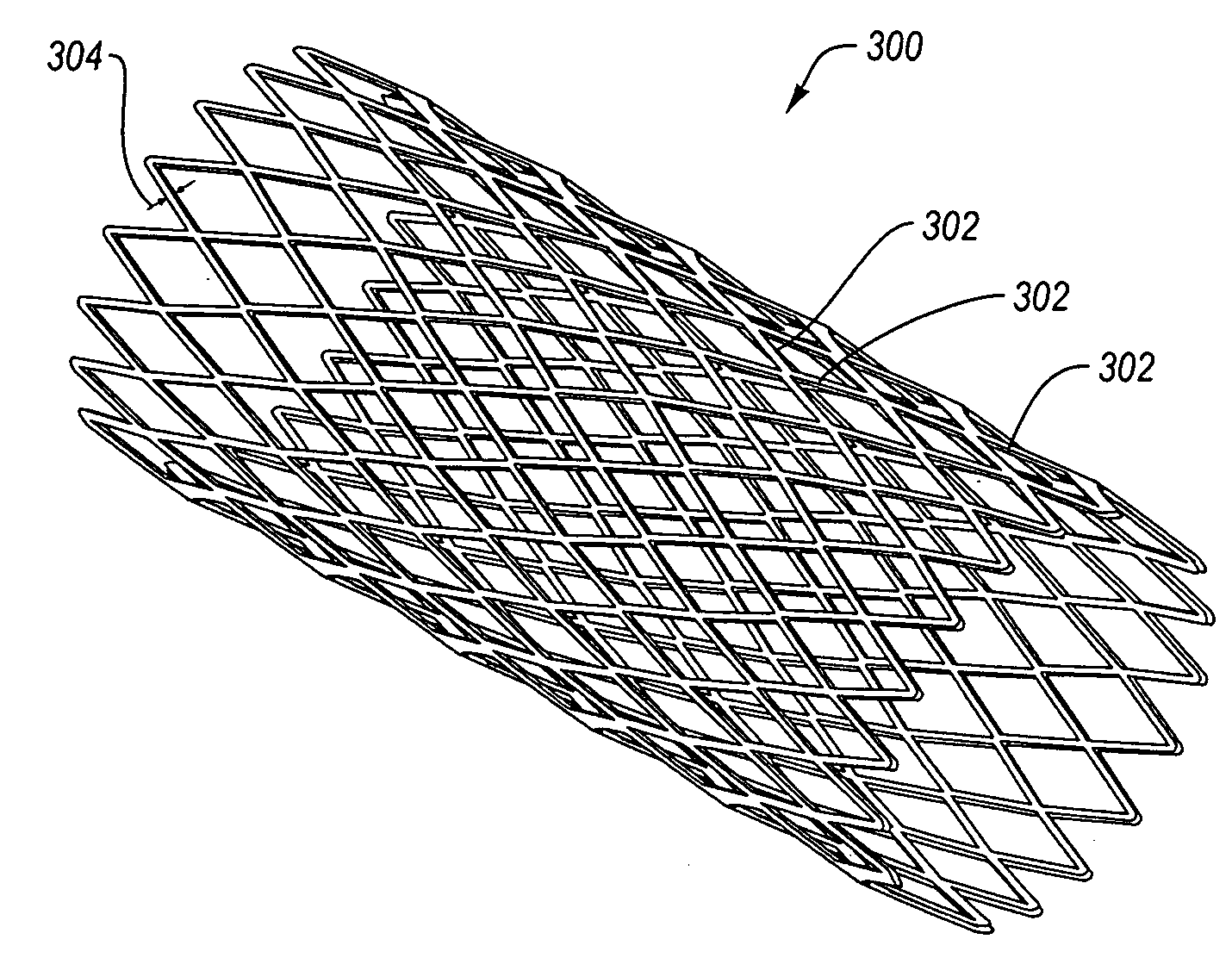
The invention provides an intravascular stent applied to interventional operation as well as a use method, a manufacturing method and a manufacturing device of the intravascular stent. The intravascular stent is formed by winding at least one nickel-titanium alloy wire and comprises a cylindrical body and convoluted round-angle parts, wherein the round-angle parts are arranged at the two ends of the body, the body is made from the nickel-titanium alloy wire in a positive-rotation and reverse-rotation staggered superposition manner and is formed by a group of rhombus-shaped grid units, each rhombus-shaped grid unit is formed by adjacent positively and reversely rotated nickel-titanium alloy wires in a surrounding manner, and a positive rotation and reverse rotation conversion part of each nickel-titanium alloy wire forms each of the convoluted round-angle parts at the two ends of the body. The intravascular stent applied to the interventional operation as well as the use method, the manufacturing method and the manufacturing device of the intravascular stent, which are disclosed by the invention, have the beneficial effects that the intravascular stent formed by winding one or more whole wires is not opened at a radial end, so that the radial rigidity and the axial flexibility of the intravascular stent are perfectly combined; and in addition, the resistance of radial pulsating load is mainly caused by the curvature of a metal wire, so that the fatigue safety of the intravascular stent is greatly improved due to the high radial resistance.
Owner:SUZHOU INNOMED MEDICAL DEVICE
Dissimilar material connecting method of nickel titanium shape memory alloy and copper alloy and clamp thereof
InactiveCN104259663AActive connectionHigh strengthWelding/cutting auxillary devicesFurnace typesNd:YAG laserTitanium alloy
The invention relates to a laser welding method of nickel titanium shape memory alloy and copper alloy in the technical field of materials, machines, electrical engineering and the like, belongs to the technical field of dissimilar material connecting. According to the method, the functions of a sensor, an executor and the like are achieved through the high conductivity of copper and the superelasticity or shape memory character of nickel titanium alloy. The method comprises the process steps that after the to-be-welded face of a nickel titanium shape memory alloy and copper alloy wire or belt or plate is polished and washed, the lap-joint or butt-joint mode is adopted, a designed clamp is utilized, the nickel titanium shape memory alloy part or the connecting position is heated through a Nd:YAG laser device, and a high-strength, defect-free and low-impedance dissimilar material welding connector can be obtained by adjusting laser and heat treatment process parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com