Apoptosis methods, genes and proteins
A cell and genotype technology, applied in the field of genes and proteins, which can solve problems such as inability to die, lack of "small" cells, and inability to respire functional mitochondria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0564] Example 1: Generation of DNA constructs
[0565] Generation of construct DNA allowing expression of pro-apoptotic Bax
[0566] Constructs that induce expression of Bax from different chromosomal loci in yeast
[0567] Yeast integration vectors pRS305 (with S. cerevisiae LEU2 gene as selectable marker), pRS402 (with S. cerevisiae ADE2 gene as selectable marker) and pRS404 (with S. Saccharomyces cerevisiae TRP1 gene).
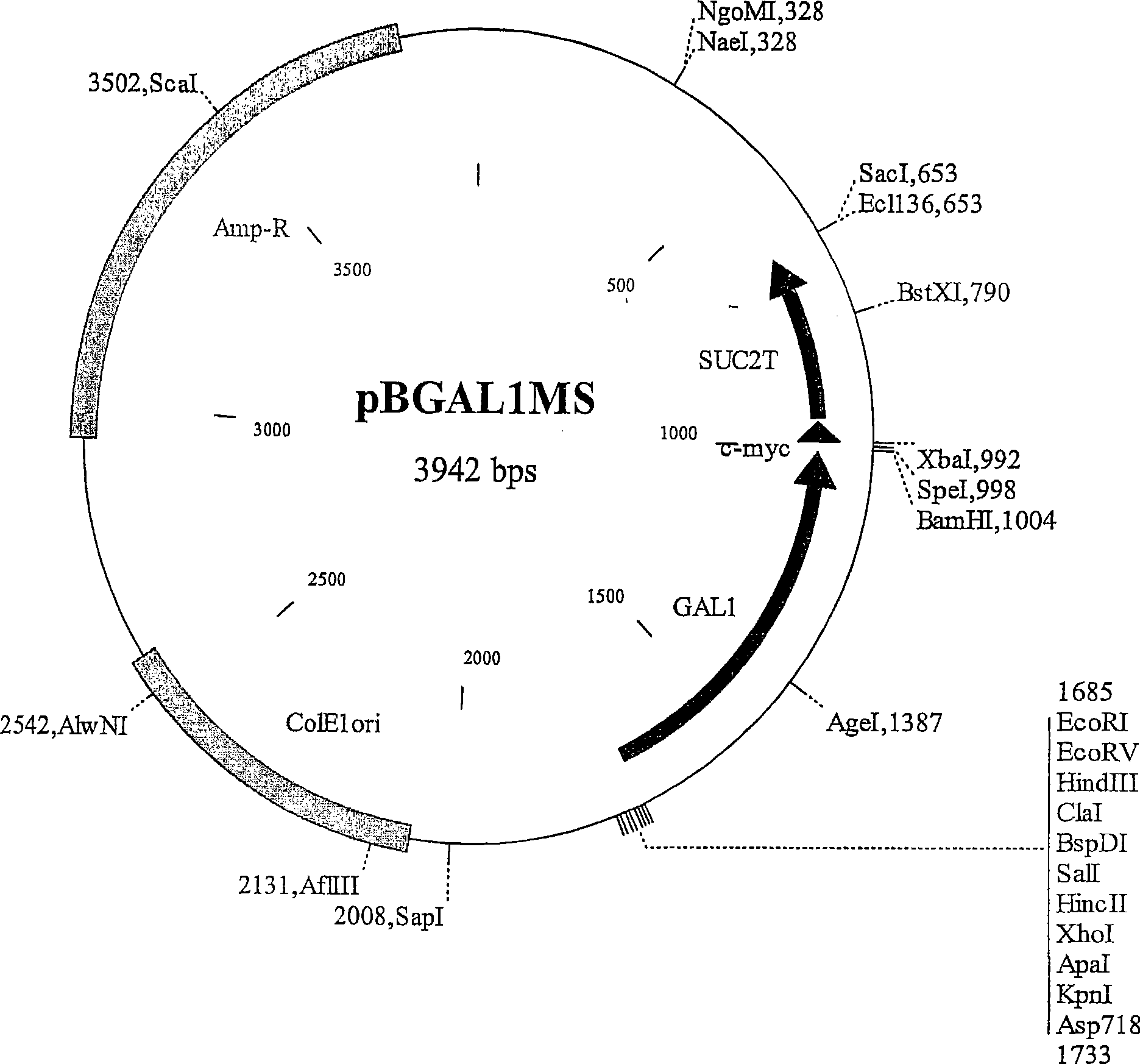
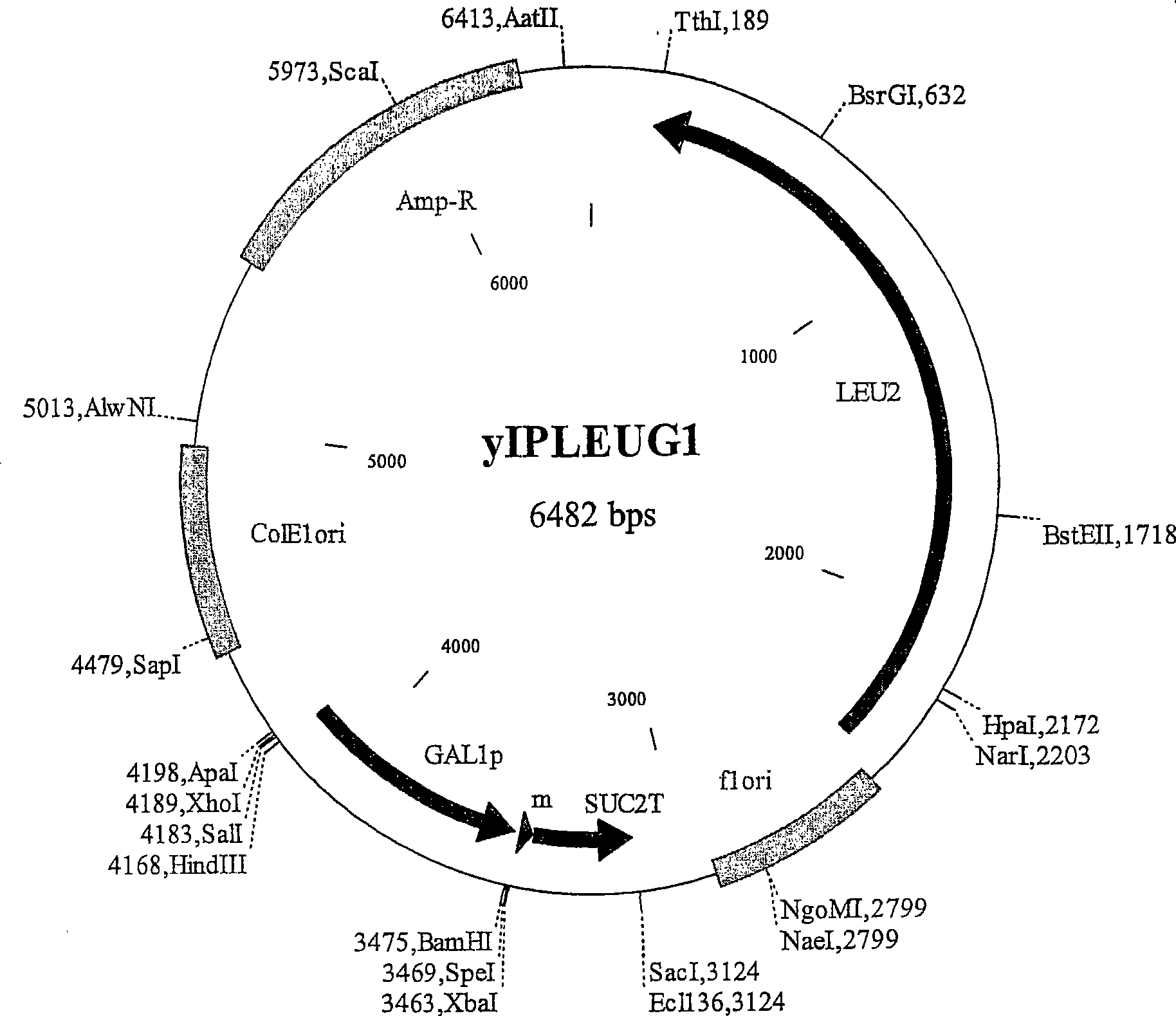
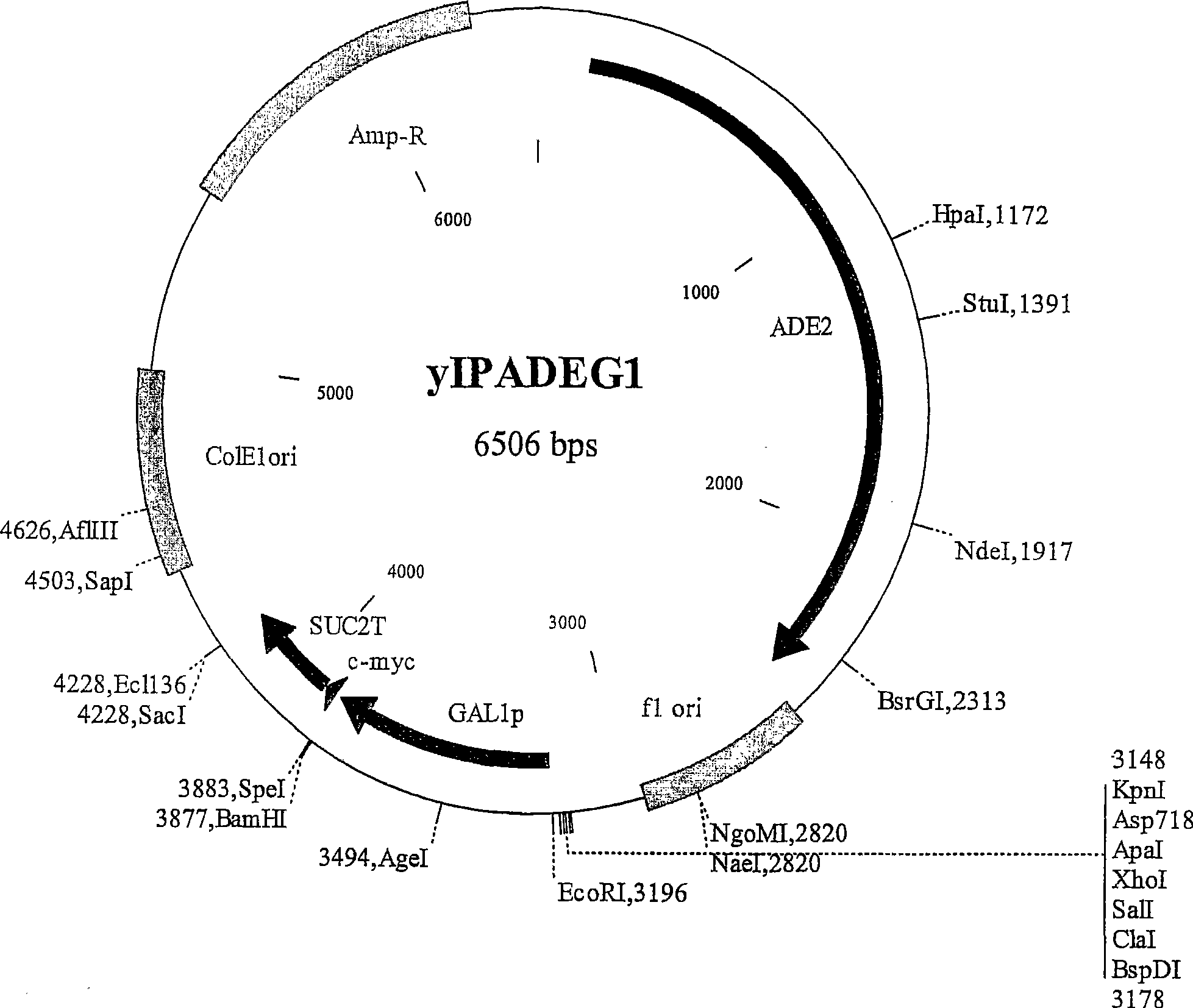
[0568] The XhoI-SacIGAL1p-MS fragment, which contains the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1 gene promoter fragment and the SUC2 gene terminator fragment (S) preceding the c-myc tag fragment (M), was isolated from construct pBGAL1MS (a pBlueScript KS(+) derivative; figure 1 ; Figure 61 GAL1MS sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1), and ligated to XhoI-SacI digested pRS305, pRS402 and pRS404 vectors, so as to integrate at LEU2, ADE2, TRP1 and HIS3 chromosomal loci. Four resulting plasmids yIPLEUG1 ( figure 2 ), yIPADEG1( image 3 ), yIPTRPG1 ( Figure 4 ) a...
Embodiment 2
[0582] Example 2: Optimization of a Yeast Screening System for Selection of New Anti-apoptosis Genes from Human Hippocampus (YAS)
[0583] Yeast growth conditions
[0584] YPD (1% Bacto yeast extract, 2% Bacto peptone and 2% glucose) is a rich medium. Synthetic minimal medium (SC) consisted of 0.67% yeast nitrogen source (Difco) and 2% glucose (SD) or 2% galactose (SG). Appropriate growth supplements (adenine, histidine, lysine, leucine, uracil or tryptophan) were added to SD or SG for growth of a particular strain depending on the plasmid carried by the strain. Save the supplement as a stock solution and add to an appropriate volume of medium. The concentrations and volumes of stock solutions given below are required to prepare 1 liter of medium. The final concentration of adenine, uracil, tryptophan and histidine is 20 mg / l, lysine and tyrosine are 30 mg / l, and leucine is 100 mg / l.
[0585] Establishment of Yeast Anti-apoptosis Screening System
[0586] In order to ...
Embodiment 3
[0616] Example 3: Screening of anti-apoptotic genes in human hippocampus
[0617] Construction and Amplification of Human Hippocampal cDNA Library
[0618] A human hippocampal cDNA library was routinely synthesized using BioCat GmbH (Heidelberg, Germany). The cDNA library was made from whole human adult normal brain hippocampus mRNA. First-strand cDNA synthesis was performed using oligo(dT)-NotI primer and M-MLV-RNase H-reverse transcriptase. Second-strand synthesis was performed using random linker primers and Klenow Exo-DNA polymerase. For directional cloning, sticky-ended cDNAs were first digested with Not I followed by size fractionation on a 1.3% agarose gel. After elution of the cDNA, the cDNA larger than 0.6 kb was ligated into NotI and BsaBI digested yeast expression vector pSYE224 (Figure 39). The plasmid cDNA library was obtained as a glycerol stock. In order to preserve all the genetic information of this library, a method using semi-solid amplification was e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com