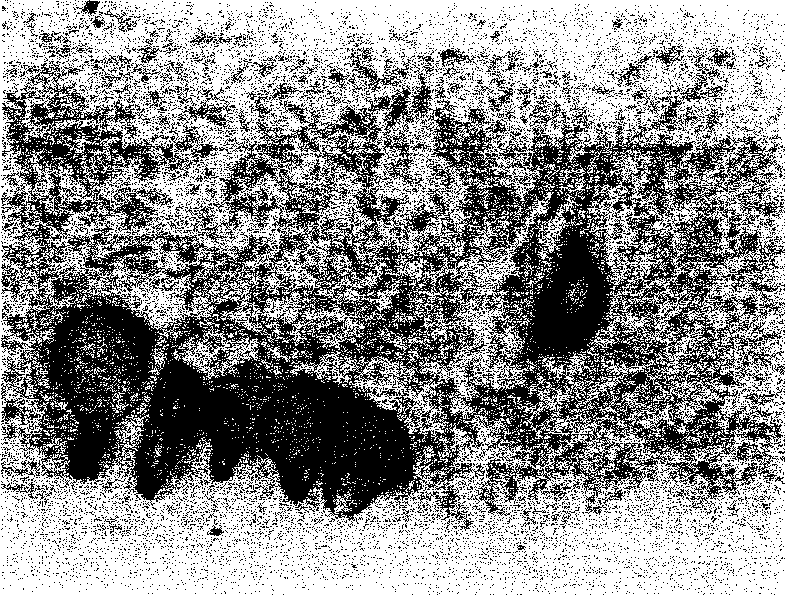Heterogeneous dermis reticular layer stent without basement membrane and cell as well as preparation method thereof
A mesh layer and basement membrane technology, applied in the field of medical biomaterials, can solve the problems of incomplete cell elution, low survival rate, poor nutrient permeability, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Using rats as the material source, the specific preparation process steps are as follows:
[0043] 1. Aseptically cut the back skin and subcutaneous tissue of rats;
[0044] 2. Soak in 0.1% bromogeramine solution for 20 minutes;
[0045] 3. Wash three times with phosphate buffer (pH7.2);
[0046] 4. Use a sterile skin extractor to remove the subcutaneous tissue to obtain full-thickness skin with a thickness of 0.5mm;
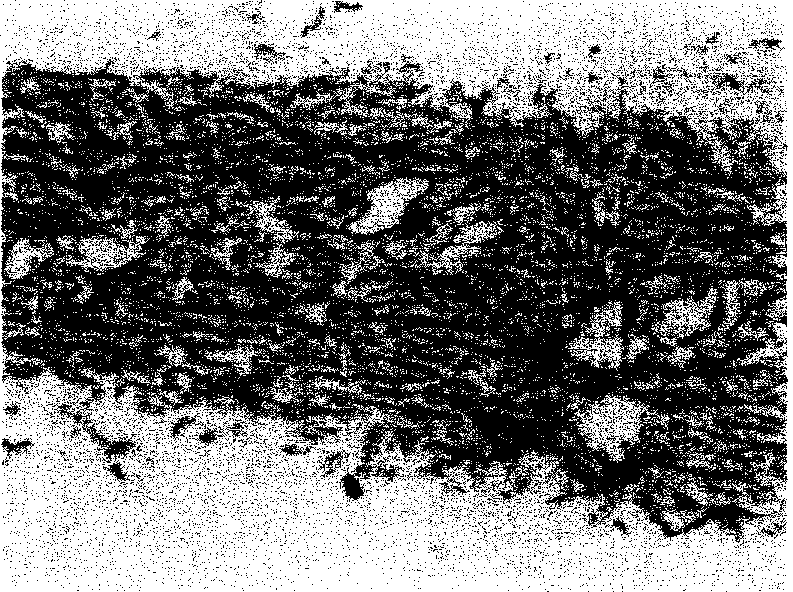
[0047] 5. Remove the epidermis, basement membrane and papillary dermis together with a sterile skin extractor to obtain a dermal reticular layer with a thickness of 0.3 mm (see figure 1 );
[0048] 6. Soak the obtained dermal reticular layer with hypotonic distilled water and continue to shake at 130 times / min for 1 hour;
[0049] 7. Use the digestion solution with a weight concentration of 0.25% trypsin and 0.02% EDTA·Na2, and shake continuously at 37°C for 3 hours;
[0050] 8. Replace the digestive solution with phosphate buffered saline, continue s...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Rabbits are used as the material source, and the specific preparation process steps are as follows:
[0056] 1. Aseptically cut the back skin and subcutaneous tissue of the rabbit;
[0057] 2. Soak in 0.1% bromogeramine solution for 20 minutes;
[0058] 3. Wash three times with phosphate buffer (pH7.2);
[0059] 4. Use a sterile skin extractor to remove the subcutaneous tissue to obtain full-thickness skin with a thickness of 0.4cm;
[0060] 5. Remove the epidermis, basement membrane and papillary dermis with a sterile skin remover to obtain a reticular layer of dermis with a thickness of 0.2mm;
[0061] 6. Soak the obtained dermal reticular layer with hypotonic distilled water and continue to shake at 130 times / min for 1.5 hours;
[0062] 7. Use the digestion solution with a weight concentration of 0.2% trypsin and 0.015% EDTA·Na2 at 37°C for 3 hours;
[0063] 8. Replace the digestive solution with phosphate buffered saline, continue shaking for 10 minutes, and was...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com