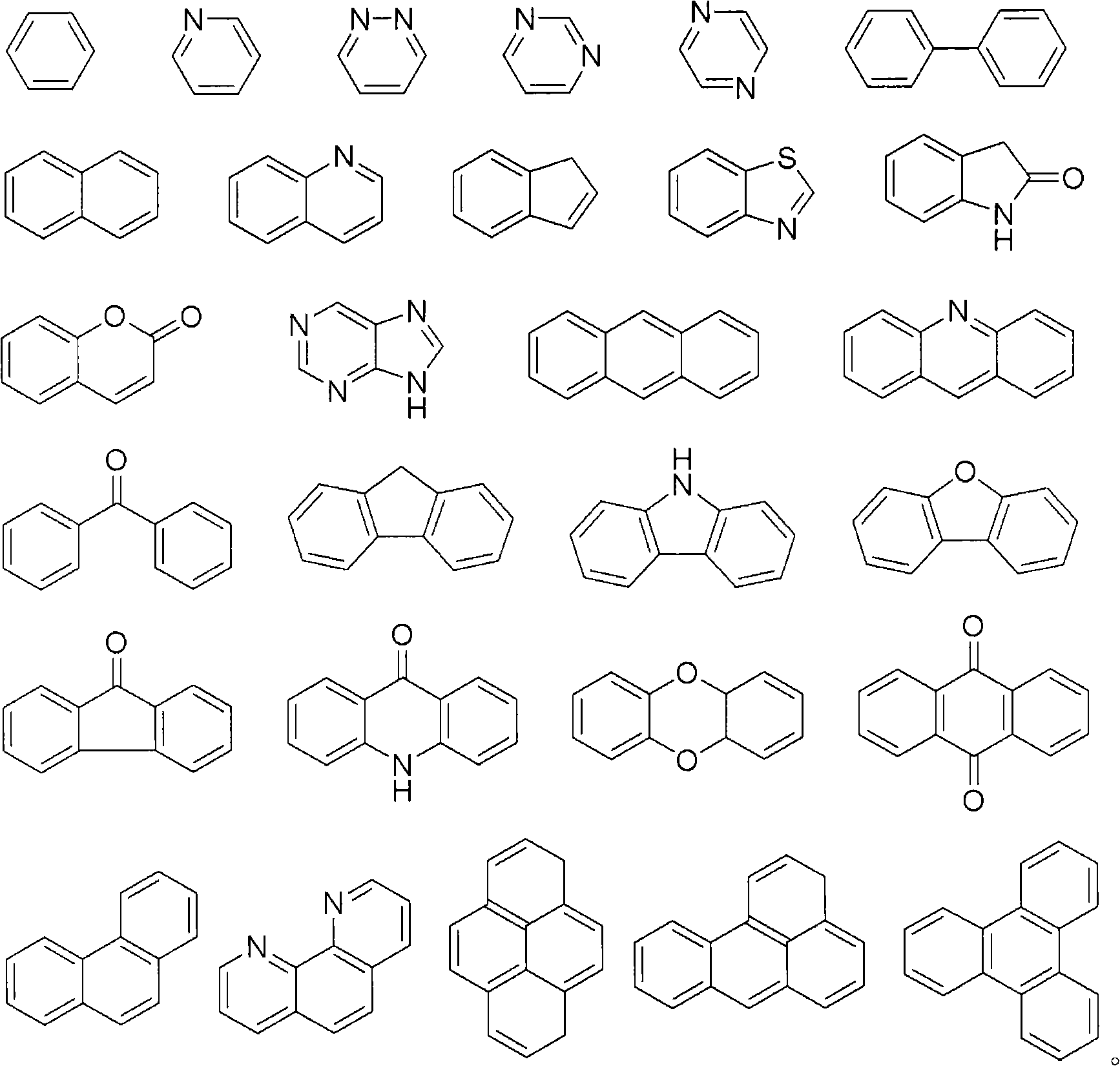
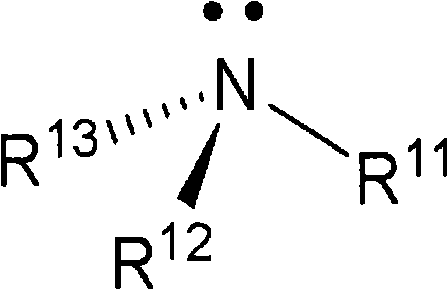
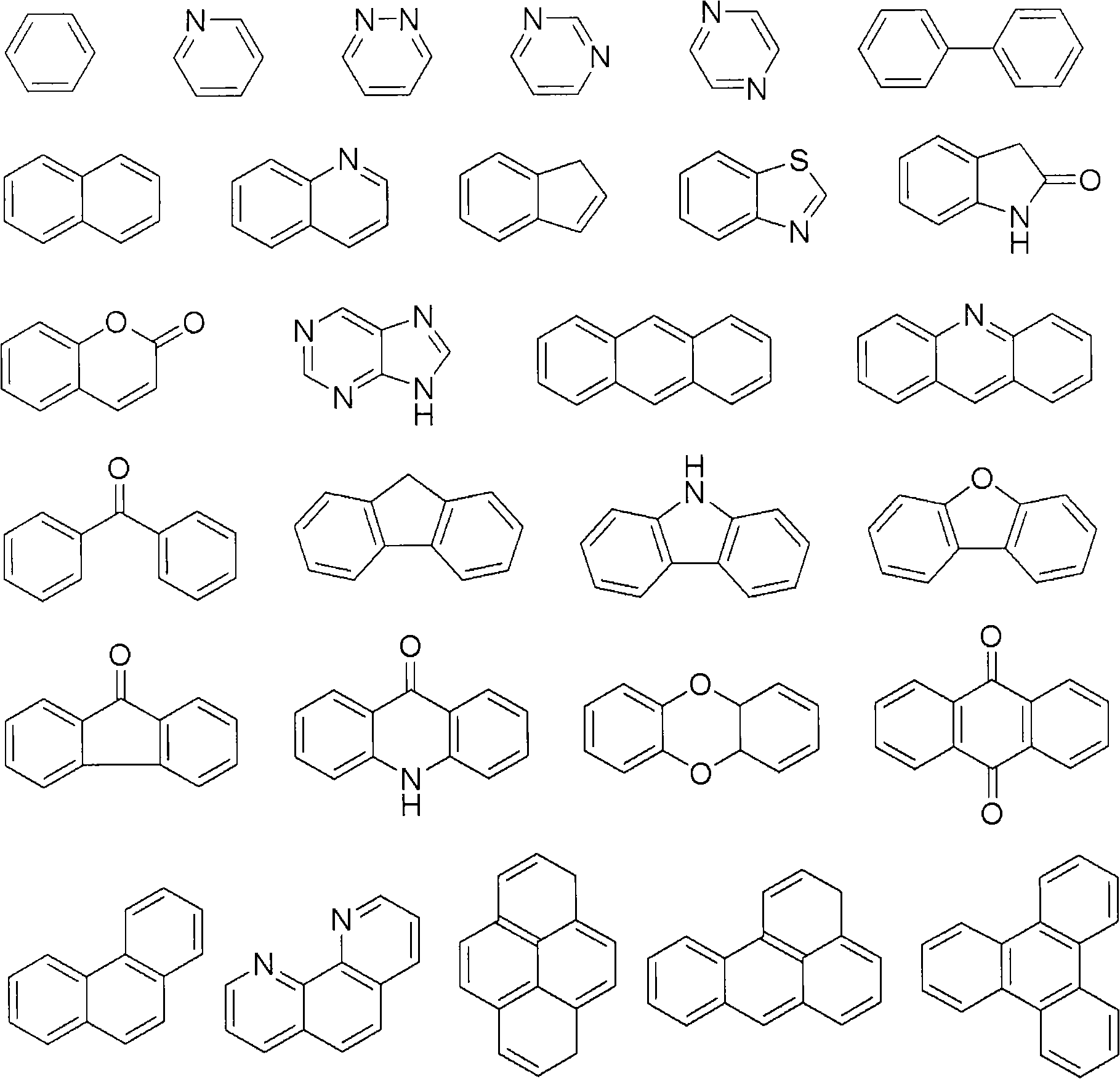
Advanced preparation method of organic-transition metal hydride used as hydrogen storage materials
一种过渡金属、氢化物的技术,应用在钛有机化合物、有机化学、周期表第5/15族元素的化合物等方向,能够解决难以稳定分离、难分离、难分离和提纯等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0072] MAH Method I: Hydrodehalogenation Reaction
[0073] Under argon flow, 0.4 g (1.6 mmol) of phenoxytitanium trichloride (reactant II) was dissolved using 30 ml of toluene in a 100 ml two-neck round bottom flask container. Dissolve 0.184 g (4.85 mmol) of LiAlH in 70 ml of toluene in a 250 ml single necked round bottom flask vessel under argon flow 4(Reactant I). After reflux at 25° C. for 36 hours while slowly dropping reactant II into reactant I, the reaction was completed. The solvent was removed under an argon atmosphere by the Schlenk method, and only the phenoxytitanium aluminum hydride complexes (multiple target compounds A) were selectively extracted using 2-propanol as products (synthetic state (as -synthesis) Substance A). Next, 2-propanol was removed by the Schlenk method, whereby phenoxytitanium hydride (a target compound A) was obtained in a yield of 95%.
[0074] 1 H-NMR (CD 3 CN-d 3 )δ(ppm): 7.28(d, 1H), 6.95(t, 2H), 6.85(t, 2H), 7.62(s, 1H), 4.83(s, 1...
preparation example 2
[0078] MAH Method II: Hydrodehalogenation Reaction
[0079] Take the method similar to Preparation Example 1, the difference is to use 0.262g (4.85mmol) NaAlH 4 Instead of LiAlH used in Preparation Example 1 4 , obtained the phenoxytitanium aluminum hydride complex (a target compound A) with a yield of 96%.
[0080] 1 H-NMR (CD 3 CN-d3) δ (ppm): 7.28 (d, 1H), 6.95 (t, 2H), 6.85 (t, 2H), 7.60 (s, 1H), 4.81 (s, 1H), 4.24 (s, 1H) , -1.61(s, 1H), -2.29(s, 1H); ESI-MS (positive ion mode), m / z (relative intensity): [parent molecule] +171(9.9), 172(9.4), 173 (100), 174(23), 175(10.1); Anal. Calcd. for parent molecule: C, 41.6; H, 5.8. Measured: C, 41.9; H, 5.5%.
[0081] In order to check the kind of by-products prepared according to MAH method II and the preferred separation phenomenon of target compound A with high selectivity, from the XRD, 35 Cl-NMR and 27 As can be seen from the Al-NMR analysis results, NaCl and Al can be formed as the main by-products. In addition, it c...
Embodiment 1
[0083] LB Method I: Hydrogenation Reaction
[0084] Under argon flow, 0.4 g (2.3 mmol) of the phenoxyaluminum hydride complex (reactant IV) prepared according to Preparation 1 was dissolved in a 100 ml two-necked round-bottomed flask using 30 ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF). Under argon flow, 0.70 g (6.9 mmol) of triethylamine (reactant III) was dissolved in 70 ml of tetrahydrofuran (THF) in a 250 ml single necked round bottom flask vessel. After slowly dropping reactant IV into reactant III under reflux at 25° C. for 12 hours, the reaction was completed. The solvent was removed by the Schlenk method under an argon atmosphere, and only phenoxytitanium hydride (a target compound B) was selectively extracted from the as-synthesized substance B using 2-propanol. Next, 2-propanol was removed by the Schlenk method, whereby phenoxytitanium aluminum hydride complexes (various target compounds B) were obtained in a yield of 98%.
[0085] 1 H-NMR (CD 3 CN-d3) δ (ppm): 7.28 (d, 1H), 6.9...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com