Qualitative and quantitative analysis method for polyoses
A technique for quantitative analysis and polysaccharides, applied in the field of qualitative and quantitative analysis of polysaccharides, can solve the problems of high equipment requirements, poor practicability, and difficulty, and achieve the effects of improving sensitivity, separation effect and ultraviolet absorption characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
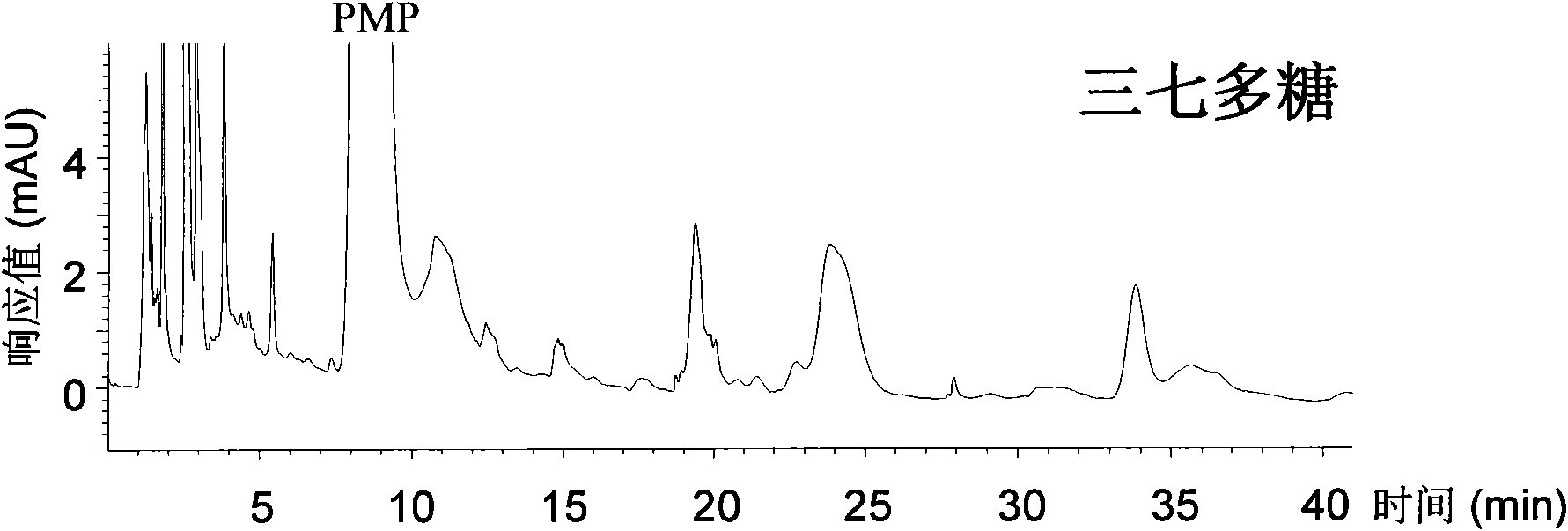
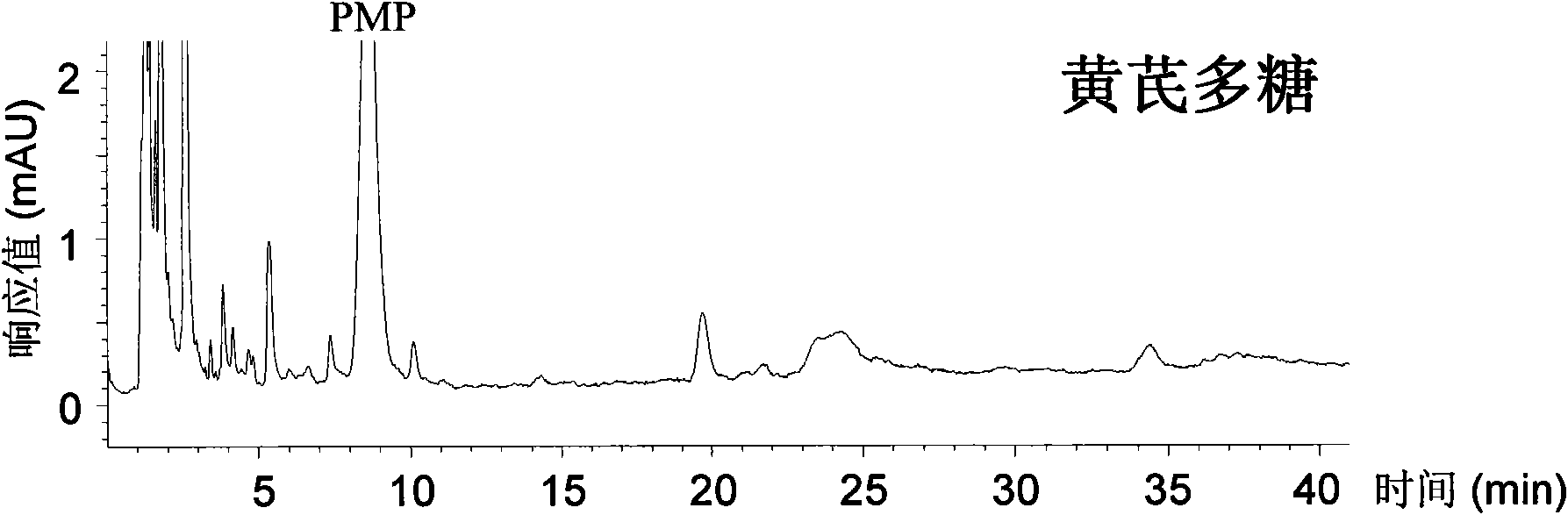
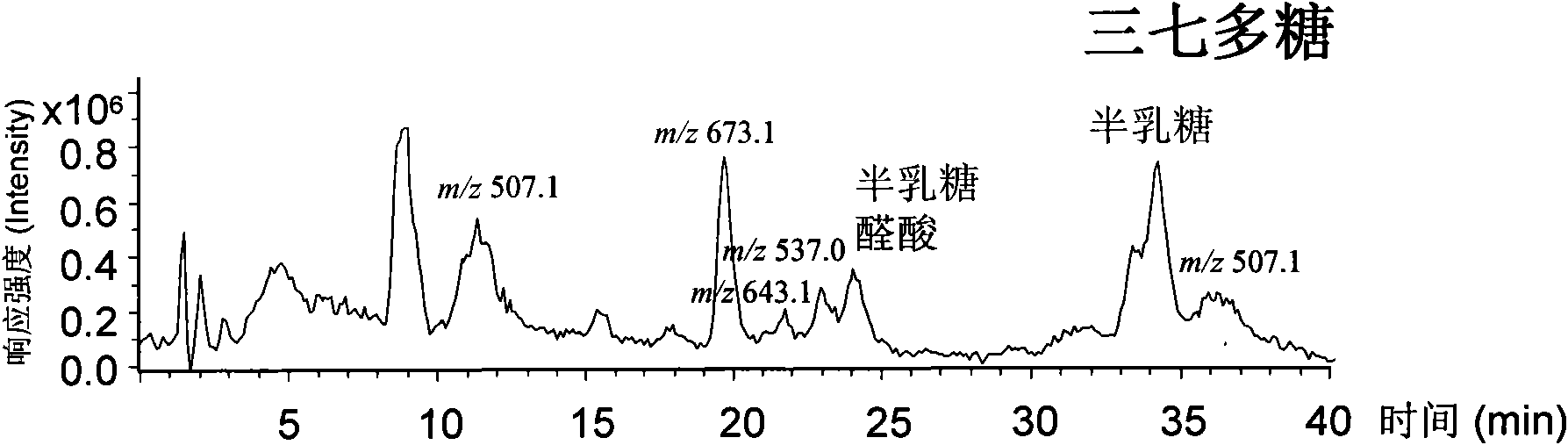
[0031]Extraction of polysaccharides from traditional Chinese medicine: Weigh 0.5g each of 9 kinds of Chinese herbal medicine powders of ginseng, Panax notoginseng, American ginseng, Cordyceps sinensis, Cordyceps militaris, Chizhi, Zizhi, Astragalus and Angelica, add 20 times the weight-to-volume ratio of water, and extract at 100°C high temperature water for 1 hours, the extract was centrifuged to obtain a supernatant, and 5 mL of the supernatant was added with absolute ethanol to a final concentration of 75%, and left to settle overnight at 4°C. After centrifugation, the precipitate was washed twice with 4 mL of 95% ethanol at 60°C. The alcohol was evaporated to dryness on a water bath, the residue was redissolved with 5 mL of hot water (60°C), and the supernatant was centrifuged to obtain the polysaccharide extract. Using the phenol-sulfuric acid colorimetric method as a quantitative reference, adjust the extract to a relative sugar content of 0.15 mg / mL (calculated as glucos...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Extraction of polysaccharides from traditional Chinese medicines: Weigh 0.5 g of the medicinal powders of Panax notoginseng and Astragalus membranaceus, and the rest of the operations are the same as the extraction steps of polysaccharides in Example 1.
[0040] Enzymatic hydrolysis of polysaccharide: same as embodiment 1.
[0041] HPSEC-ELSD analysis: same as Example 1.
[0042] PMP derivatization of polysaccharide hydrolyzate: after centrifugation of polysaccharide hydrolyzate of traditional Chinese medicine, take 600 μL of supernatant, mix it with an equal volume of ammonia water, then add 200 μL of 0.5mol / LPMP methanol solution, mix well and seal, and react at 70°C for 30 minutes. Take it out and let it cool to room temperature, add 2mL of water, shake well, evaporate to dryness at 50°C, and repeat the operation twice. The residue was dissolved in 1 mL of water, extracted with an equal volume of chloroform, and repeated three times, and the water layer was passed t...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Extraction of polysaccharides from traditional Chinese medicine: Weigh 0.5 g each of American ginseng, Cordyceps militaris and Cordyceps militaris medicinal material powders, and the rest of the operations are the same as the polysaccharide extraction steps in Example 1.
[0047] Enzymatic hydrolysis of polysaccharide: same as embodiment 1.
[0048] HPSEC-ELSD analysis: same as Example 1.
[0049] PMP derivatization of polysaccharide hydrolyzate: same as Example 2.
[0050] HPLC-DAD-MS analysis: same as embodiment 2.
[0051] Test results, refer to Table 2, Figure 5 to Figure 10 : American ginseng, Cordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris have similar hydrolysis response characteristics to 13 glycosidases. The enzymatic hydrolysis products of the three, taking the pectinase enzymatic hydrolysis as an example, after derivatization with PMP, HPLC-DAD and HPLC-MS analysis can obtain characteristic spectra for identification.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com