Method for preparing protective film playing a role in protecting glass micro-fluidic chips in etching process
A technology of protection and protective film, which is applied in the process of producing decorative surface effects, microstructure technology, microstructure devices, etc. Corrosion by hydrofluoric acid, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing production cost, improving quality, and improving corrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
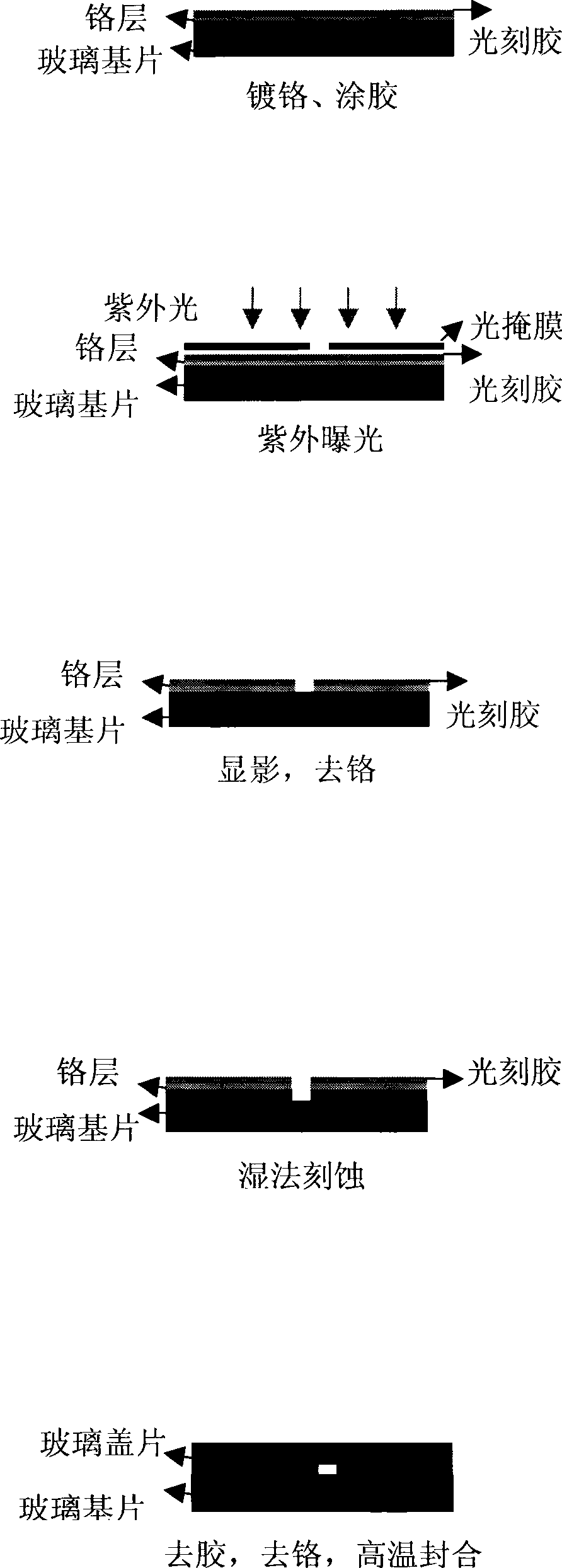
[0038] See Figure 3B .
[0039] (1) At first on the clean common float glass substrate, chrome-plated sacrificial layer with the method for vapor deposition;
[0040] (2) Utilize spin coater, on the glass substrate that is plated with chromium sacrificial layer that step (1) obtains, spin coat one deck to contain the positive photoresist photoresist resist of novolac resin; Wherein, spin coater is earlier with 400 Spin coating at the speed of rpm for 10 seconds; then spin coating at 2000 rpm for 20 seconds; volatilize the organic solvent in the positive photoresist containing novolak resin at 110°C (baking glue) for 10 minutes , to obtain a positive photoresist protective film containing a novolac resin with a smooth surface;
[0041] (3) Contact exposure under ultraviolet light (mainly 365nm) with photomask, the figure of mask is copied to step (2) be coated with the chromium sacrificial layer that is coated with the positive photoresist that contains novolac resin On the...
Embodiment 2
[0052] After completing step (4) in Example 1, use at least one of the group consisting of oxalic acid, maleic acid and its anhydride, acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, benzenesulfonic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, racemic malic acid It is 2 that the pH of the aqueous solution of formaldehyde that is 15% or the aqueous glutaraldehyde solution that mass concentration is 2% is adjusted mass concentration, then at room temperature the glass substrate obtained in step (4) in Example 1 is soaked in above-mentioned pH that is 2 Formaldehyde aqueous solution or glutaraldehyde aqueous solution for 10 minutes, make formaldehyde molecules or glutaraldehyde molecules infiltrate in the middle of the positive photoresist matrix containing novolac resin; rinse the soaked glass substrate with distilled water, adjust the oven temperature, At 100°C, formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde cross-links with the novolac resin component in the novolac resin-containing positive photoresist, keeps this t...
Embodiment 3
[0056]After completing step (4) in Example 1, use at least one of the group consisting of oxalic acid, maleic acid and its anhydride, acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, benzenesulfonic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid, racemic malic acid The pH of the 18% formaldehyde aqueous solution or the 6% glutaraldehyde aqueous solution is adjusted to be 2.8 in mass concentration, and then the glass substrate obtained in step (4) in Example 1 is soaked in the above-mentioned pH of 2.8 at room temperature. Formaldehyde aqueous solution or glutaraldehyde aqueous solution for 15 minutes, make formaldehyde molecules or glutaraldehyde molecules infiltrate in the middle of the positive photoresist matrix containing novolac resin; rinse the soaked glass substrate with distilled water, adjust the oven temperature, At 110°C, formaldehyde or glutaraldehyde cross-links with the novolac resin component in the novolac resin-containing positive photoresist, keeps this temperature for 15 minutes, and fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com