Natural rubber latex protein fixation method
A technology of natural rubber latex and fixing method, which is applied in the field of rubber treatment or chemical modification, can solve problems such as protein allergy in latex products, and achieve the effect of solving allergy problems, being cheap, and overcoming environmental problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] One, the preparation of dialdehyde sodium alginate
[0043] In a black bottle, dissolve 10.00 g of sodium alginate in 600 mL of distilled water, add 100 mL of sodium periodate while stirring, and dilute the total volume of the solution to 1 L with distilled water. The molar ratio of sodium alginate to sodium periodate was 1:0.05. After 24 hours, 3.5 mL of ethylene glycol was added and stirred for 0.5 hours to terminate the reaction. Oxidized natural polysaccharides were purified by precipitation with 3 g of sodium chloride and 1 L of ethanol. The precipitate was redissolved in 500 mL of distilled water, and 500 mL of ethanol and 1 g of sodium chloride were added to precipitate again. Repeat the precipitation with 1 L of acetone containing 0.5 g of sodium chloride until its sodium salt is formed. Finally, the precipitate was stirred and washed with 500 mL of ethanol for 15 min, filtered, and dried under vacuum at room temperature.
[0044] 2. Preparation of dialdehyde...
Embodiment 2
[0048] 1. For the preparation of dialdehyde sodium alginate, see Example 1.
[0049] 2. Preparation of dialdehyde sodium alginate latex film
[0050] Take 10 g of dialdehyde sodium alginate ammonia solution with a concentration of 1% (w / w), add it to 50 g (solid content 30 g) of natural rubber latex under stirring, and weigh 40 g of the blended solution after 1 hour of action and place it horizontally in a petri dish. Dry at 50°C for 2d.
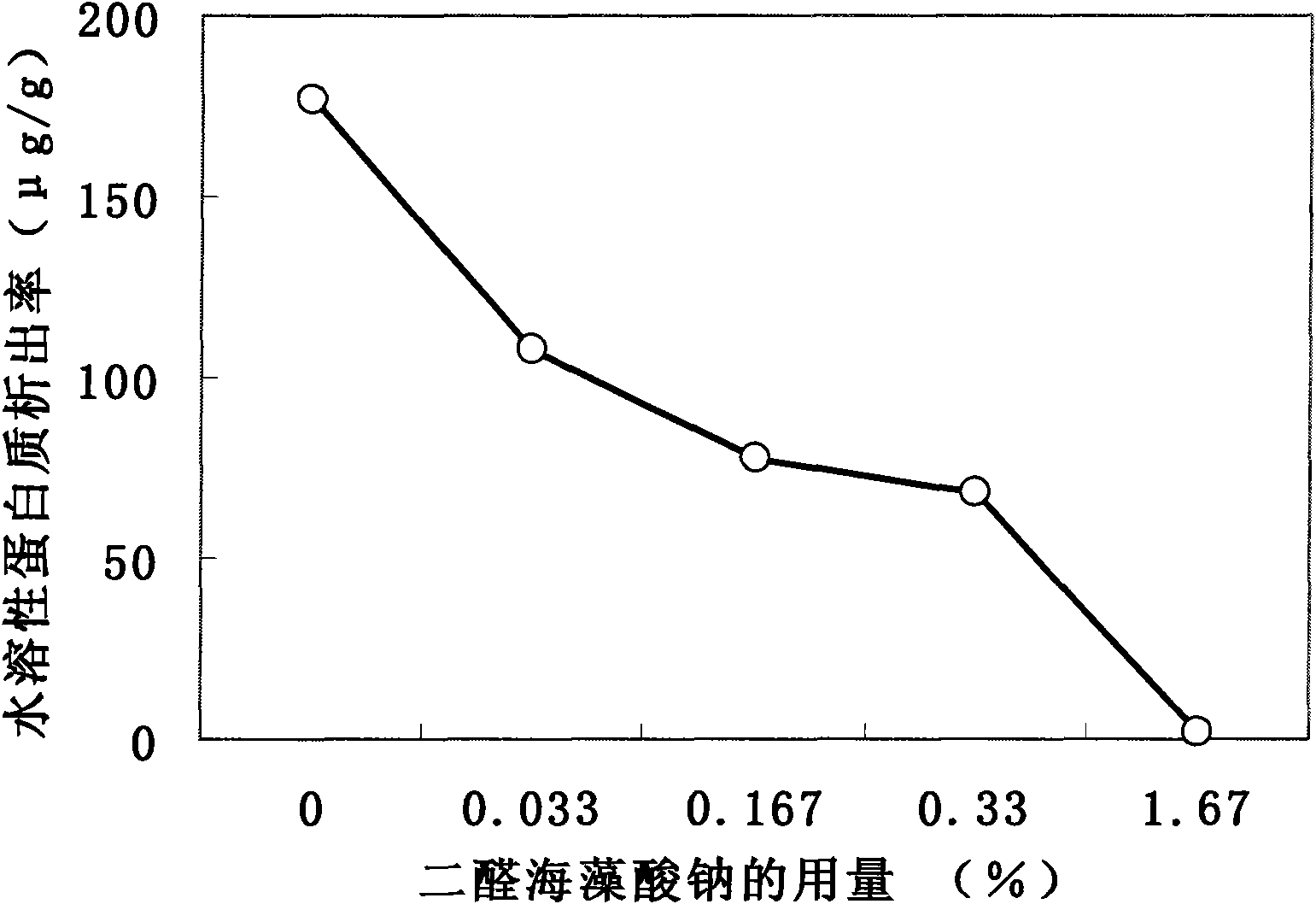
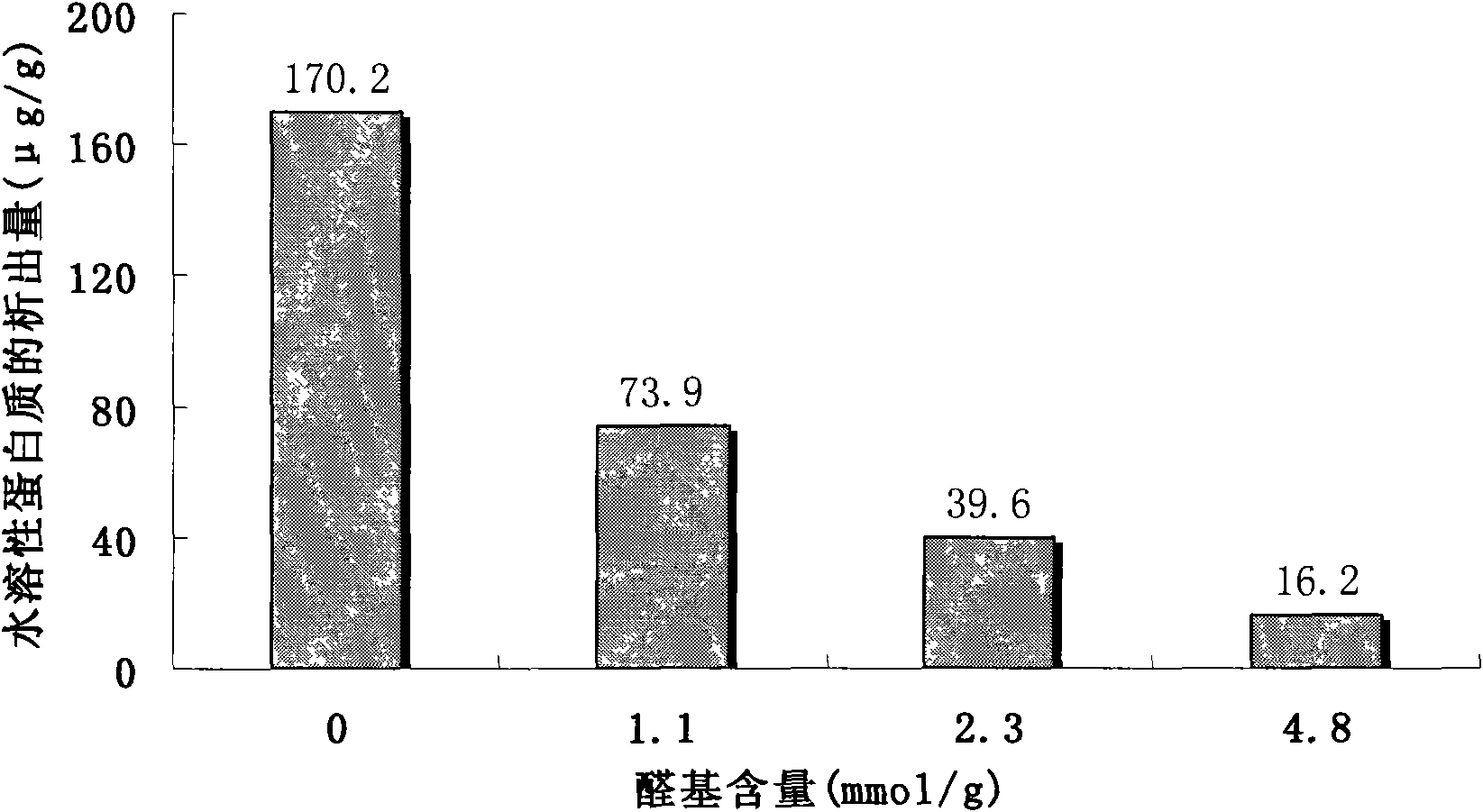
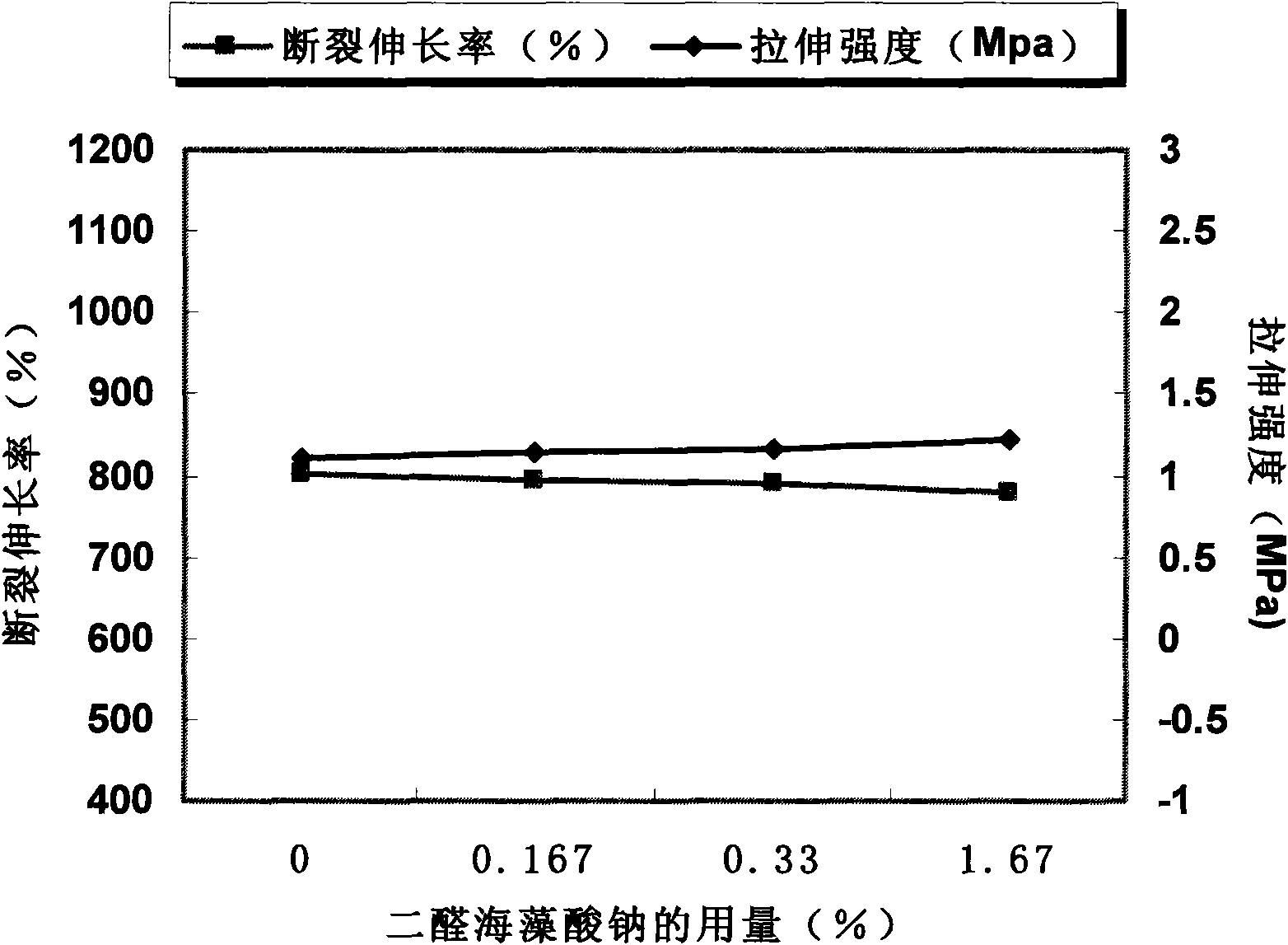
[0051] After inspection, the precipitation rate of the water-soluble protein in the latex film is about 68 μg / g (see figure 1), which is higher than the minimum allowable protein content of 50 μg / g (ASTM, 2005) for latex protein sensitization; the mechanical properties have no significant change compared with the natural latex film without adding dialdehyde sodium alginate (see image 3 ).
Embodiment 3
[0053] 1. For the preparation of dialdehyde sodium alginate, see Example 1.
[0054] 2. Preparation of dialdehyde sodium alginate latex film
[0055] Take 10 g of dialdehyde sodium alginate ammonia solution with a concentration of 5% (w / w), add it to 50 g (solid content 30 g) of natural rubber latex under stirring, and weigh 40 g of the blended solution after 1 hour of action and place it horizontally in a petri dish. Dry at 50°C for 2d.
[0056] After inspection, the precipitation rate of the water-soluble protein in the latex film is about 2 μg / g (see figure 1 ); the mechanical properties have no significant change compared with the natural latex film without dialdehyde sodium alginate (see image 3 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Separation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Separation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Separation rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com