Method for detecting total number of bacterial colonies in activated lactobacillus drink
A technology of active lactic acid bacteria and total number of colonies, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve problems such as insufficient detection sensitivity, influence of detection accuracy, and reduction of result accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Embodiment 1: TTC nutrient agar preparation
[0013] Weigh 33g of nutrient agar, add 1 liter of distilled water or deionized water, divide into Erlenmeyer flasks, stir, heat and boil to dissolve, and autoclave at 121°C for 15min. After sterilization, when the culture medium is cooled to about 45°C, add sterile TTC to make the concentration of TTC reach 2.5mg / 100ml, mix well, and pour onto the plate.
Embodiment 2
[0014] Embodiment 2: Detection of the total number of bacterial colonies in artificially polluted samples
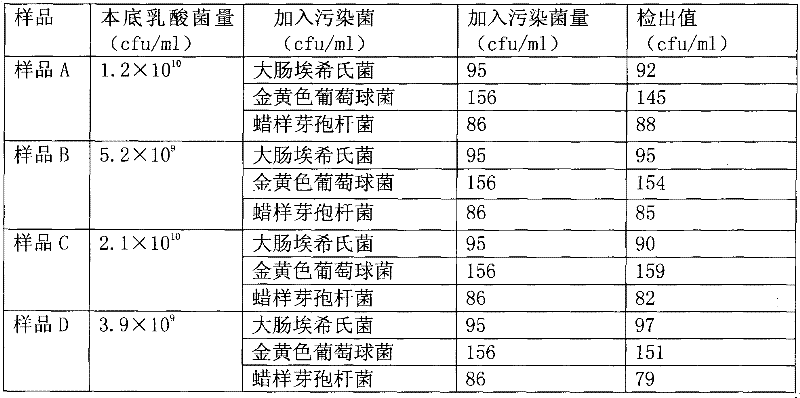
[0015] Take fresh cultures of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Bacillus cereus, dilute them with sterile saline to a concentration of 0.5 McFarland turbidimetric tubes, and then serially dilute them 10 times. Add the solution to sterile samples A, B, C, and D respectively, so that the concentration of each contaminating bacteria in the sample reaches about 1000cfu / ml. Take 1ml of the bacterium-added sample and mix it with 9ml sterile normal saline to make a 10-fold dilution, take 1ml of the diluted solution and mix it with an appropriate amount (25ml) of sterile normal saline, filter it through a 0.45μm filter membrane, and then use 25ml Rinse the filter membrane with physiological saline, and stick it on the TTC nutrient agar plate described in Example 1 with the filter side up after rinsing. 37 ℃, 48 ± 2h inverted culture. Its count is as follows:
[001...
Embodiment 3
[0018] Embodiment 3: Comparison between the present invention and ISO 13559:2002 (E) "Butter, fermented milk products and fresh cheese. Enumeration of contaminating microorganisms. Colony counting method at 30°C"
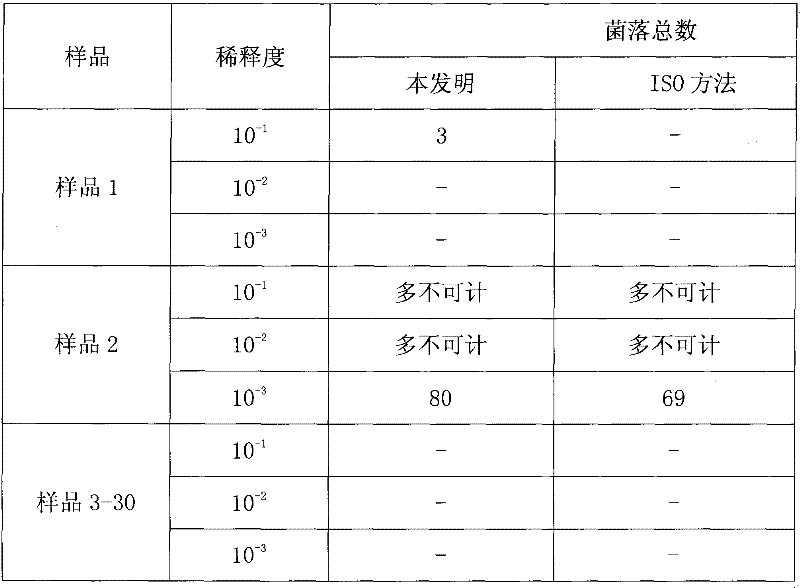
[0019] 30 kinds of yoghurt samples were purchased in the market, and the method of the present invention and ISO 13559: 2002 (E) "Butter, fermented milk products and fresh cheese. Counting of contaminating microorganisms. Colony counting method at 30°C" was adopted respectively to check the total number of colonies .
[0020] The present invention detects that 2 samples are positive for the total number of colonies, and the ISO method detects 1 sample. In the present invention, at 10 times dilution concentration, 28 samples have no colony growth on the filter membrane, and sample 1 grows 3 colonies. After identification, none of them are lactic acid bacteria, which can be included in the total number of colonies. The total number of colonies in sample 1 is 30cfu / ml....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com