Method for manufacturing black microcrystalline glass plates from molybdenum tailings
A technology for glass-ceramic and molybdenum tailings, which is applied in the field of making black glass-ceramic plates from molybdenum tailings, can solve the problem of aggravating the erosion of molten glass on refractory materials of furnaces, aggravating the erosion of molten glass on refractory materials of furnaces, and affecting the use of equipment. life and other issues, to achieve the effect of improving furnace efficiency, reducing energy consumption and reducing harm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
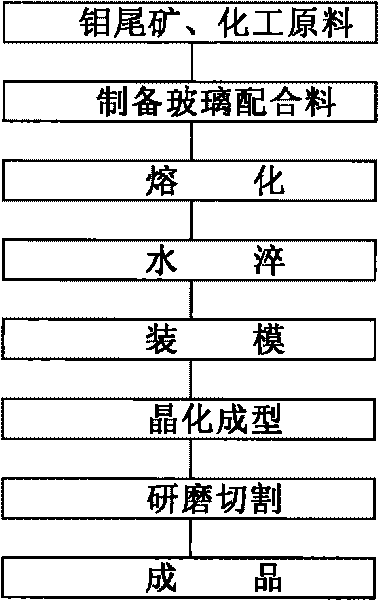
[0019] The glass batch is made by weighing and mixing. The components of the glass batch are calculated in parts by weight: 60 parts of molybdenum tailings, 25 parts of quartz sand, 28 parts of limestone, 3.5 parts of soda ash, 3.2 parts of zinc oxide, 3.2 parts of barium carbonate , 4 parts of iron oxide, 0.5 parts of manganese dioxide, 0.2 parts of nickel oxide.
[0020] Put the above-mentioned glass batch in a mullite crucible and melt it in a box-type electric furnace at a temperature of 1480°C for 3 hours. After the melting is completed, the molten glass is poured into water to become glass particles. Spread 500 grams of glass pellets in a refractory mold with a size of 100×100 mm, and perform crystallization in a box-type electric furnace with a crystallization temperature of 1020°C. After grinding and cutting the crude black glass-ceramic, a sample of 100×100×18 mm black glass-ceramic can be obtained.
Embodiment 2
[0022] The glass batch is made by weighing and mixing. The composition of the glass batch is calculated in parts by weight: 50 parts of molybdenum tailings, 20 parts of quartz sand, 33 parts of limestone, 5 parts of soda ash, 4 parts of zinc oxide, and 6 parts of barium carbonate. , 6 parts of iron oxide.
[0023] The above-mentioned glass batch materials are melted in a glass tank furnace at a temperature of 1480°C for 3 hours, and the molten glass is directly poured into the water to become glass particles after the melting is completed. Spread 26 kilograms of glass particles in a refractory mold with a size of 6000×9000 mm, and crystallize in a shuttle kiln using liquefied petroleum gas as fuel, and the crystallization temperature is 1050°C. After grinding and cutting the crude black glass-ceramic product, a 600×900×18 mm black glass-ceramic product can be obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0025] The glass batch is made by weighing and mixing. The composition of the glass batch is calculated in parts by weight: 70 parts of molybdenum tailings, 15 parts of quartz sand, 27 parts of limestone, 3.5 parts of soda ash, 2 parts of zinc oxide, 3 parts of barium carbonate , 3 parts of iron oxide, 0.05 parts of cobalt oxide, 0.2 parts of nickel oxide.
[0026] The above-mentioned glass batch material is melted in a glass tank furnace at a temperature of 1480°C for 3 hours. After the melting is completed, the glass liquid is directly poured into the water to become glass particles. Spread 26 kilograms of glass particles in a refractory mold with a size of 6000×9000 mm, and crystallize in a shuttle kiln using liquefied petroleum gas as fuel. The crystallization temperature is 1060°C. After grinding and cutting the crude black glass-ceramic product, a 600×900×18 mm black glass-ceramic product can be obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com