Hyperbranched polyester micro-optical photoresist
A technology of hyperbranched polyester and hyperbranched polymer, applied in the field of photoresist, can solve the problems of uneven photoresist etching section, unsuitable microfabrication, difficult surface shape control, etc., and achieve unique linear etching Performance, the effect of reduced structural divergence, low viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Raw materials and ratio:
[0032] Inositol 9~30g
[0033]Succinic anhydride 30~300g
[0034] Tetrabutylammonium bromide 0.06~0.56g
[0035] N,N-Dimethylformamide 17~167g
[0036] Preparation Process:
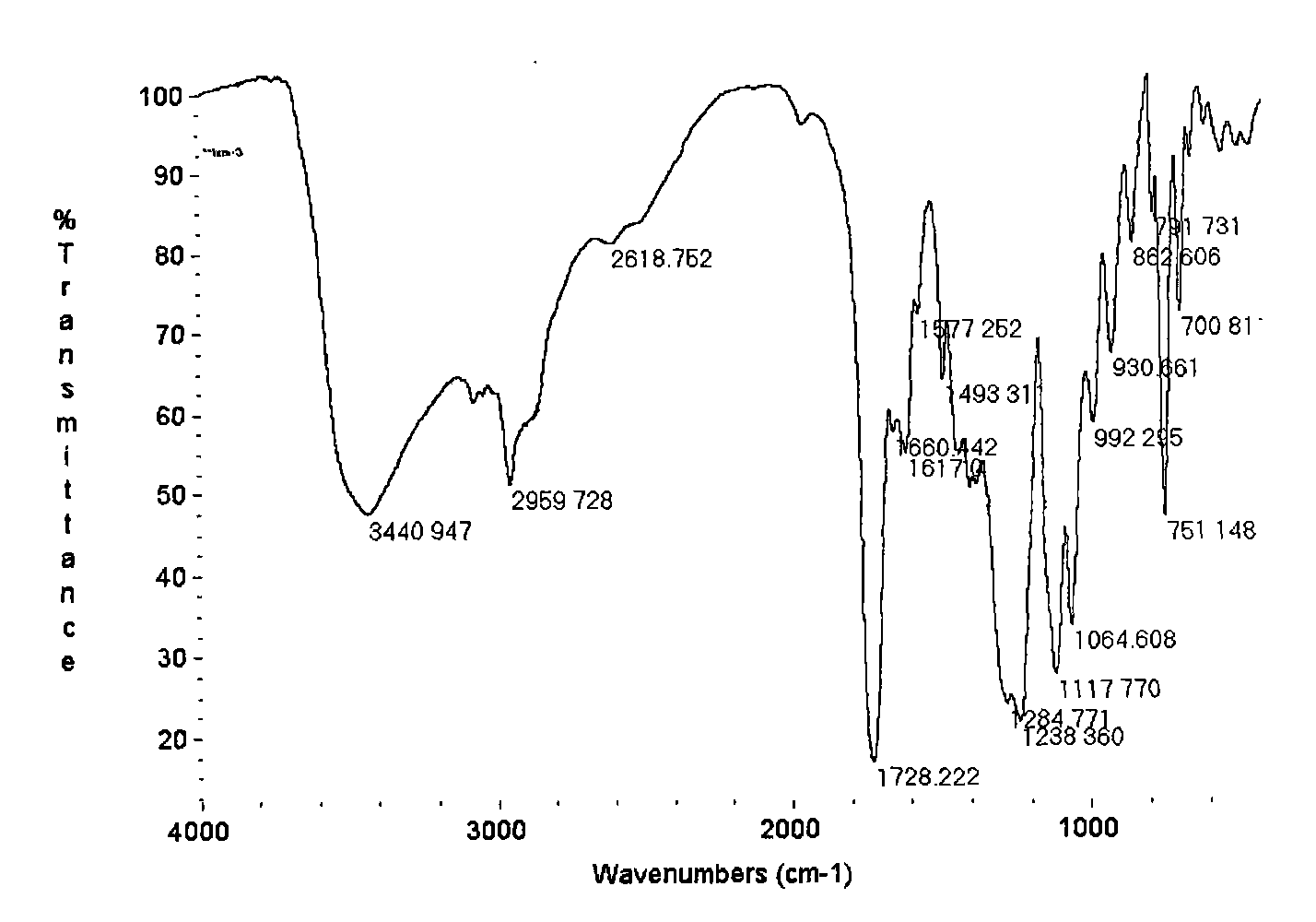
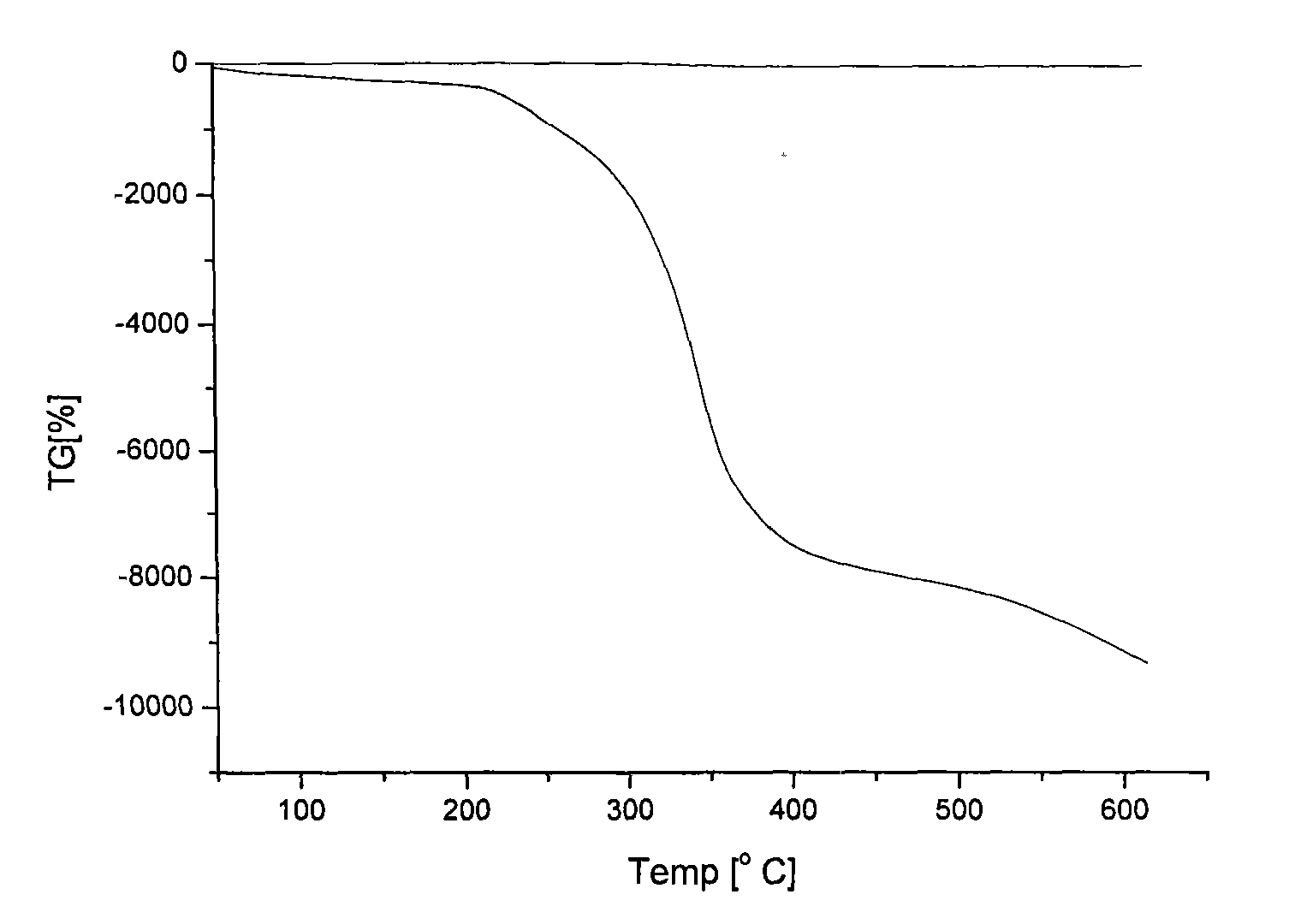
[0037] Add inositol, succinic anhydride, tetrabutylammonium bromide, N,N-dimethylformamide into a four-neck flask, under nitrogen protection, heat up to 110±5°C, keep warm until the acid value is constant, then add 27.76-277.56g of epichlorohydrin, react at 110±5°C until the acid value is constant, then add 57.6-576g of trimellitic anhydride, react at 110±5°C until the acid value is constant. Add 55.51~555.12g of epichlorohydrin, react at 110±5°C until the acid value is constant, then add 115.2~1152g of trimellitic anhydride, react at 110±5°C until the acid value is constant, add 51.12~511.2g of glycidyl methacrylate, 90 React at ±5°C until the acid value is constant to obtain a hyperbranched alkali-soluble photopolymer. Figure 1 The results of the infrared spectru...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Raw materials and ratio:
[0040] Ethylene glycol 6.2~62.0g
[0041] Trimellitic anhydride 38.4~384g
[0042] Tetrabutylammonium bromide 0.113~0.892g
[0043] N,N-Dimethylformamide 17~167g
[0044] Preparation Process:
[0045] Add ethylene glycol, trimellitic anhydride, tetrabutylammonium bromide, and N,N-dimethylformamide into a four-necked flask. Under nitrogen protection, heat up to 110±5°C, keep warm until the acid value is constant, and then add 37.01 ~370.1g epichlorohydrin, react at 110±5°C until the acid value is constant, then add 40~400g succinic anhydride, react at 110±5°C until the acid value is constant. Add 37.01~370.1g of epichlorohydrin, react at 110±5℃ until the acid value is constant, add 76.8~768g of trimellitic anhydride, react at 110±5℃ until the acid value is constant, add 74.01~740.2g of epichlorohydrin, 110±5 °C until the acid value is constant, add 153.6-1536g of trimellitic anhydride, and react at 110±5°C until the acid value is constant....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com