A simple and rapid method for DNA extraction from peanut healthy tissue and diseased tissue
A technology of healthy tissue and extraction method, which is applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, DNA preparation, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming, etc., and achieve the effect of short time-consuming, fast and effective research process, and less sample consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] Example 1: DNA Extraction from Peanut Leaves
[0042] 1. Test materials and reagents
[0043] Materials: 3 genotypes were used in this experiment, including wild species (Arachis.duranensis), a hybrid offspring of a cultivated species and wild species A. glabrata, and a chemical mutant material.
[0044] Reagents: alkaline lysate, Tris-HCl buffer containing 5-8mg / ml PVP40.
[0045] 2. Test method
[0046] 1. Template Preparation
[0047] A. Select a small leaf on the peanut plant, and use a gel pen core to punch a hole on one side of the main vein to obtain a leaf disc with a diameter of about 1.12 mm. When the peanut material is relatively precious or the number of leaves in the early stage of peanut growth is small, in order to minimize the impact on its growth and development, it can be directly punched and sampled on the plant.
[0048] B. Place the leaf disk in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube (which can be frozen for future use) added with 60 μl of alkaline lysate, and u...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2: Extracting DNA from Peanut Germ
[0062] 1. Test materials and reagents
[0063] Materials: 5 genotypic materials were used in this experiment, including the hybrid offspring of 1 cultivated species and wild species A. rigonii, 1 chemical mutant, and 3 peanut cultivars.
[0064] Reagents: alkaline lysate, Tris-HCl buffer containing 5-8mg / ml PVP40.
[0065] 2. Test method
[0066] 1. Template Preparation
[0067] Take a peanut seed, peel off two cotyledons, and use a knife to cut off the germ part, that is, several immature leaves. The following steps are the same as Scheme 1 B, C, D, E.
[0068] 2.PCR
[0069] PCR system: 12.5 μl 2×Taq PCR MasterMix, 0.5 μL each of 10 nM primers (TBPfex1 / TBPrex1), 2 μL DNA template, and 9.5 μL sterile deionized water.
[0070] PCR conditions: 35 cycles of pre-denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, 50 sec at 94°C, 1 min at 55°C, 1.5 min at 72°C, and 7 min at 72°C.
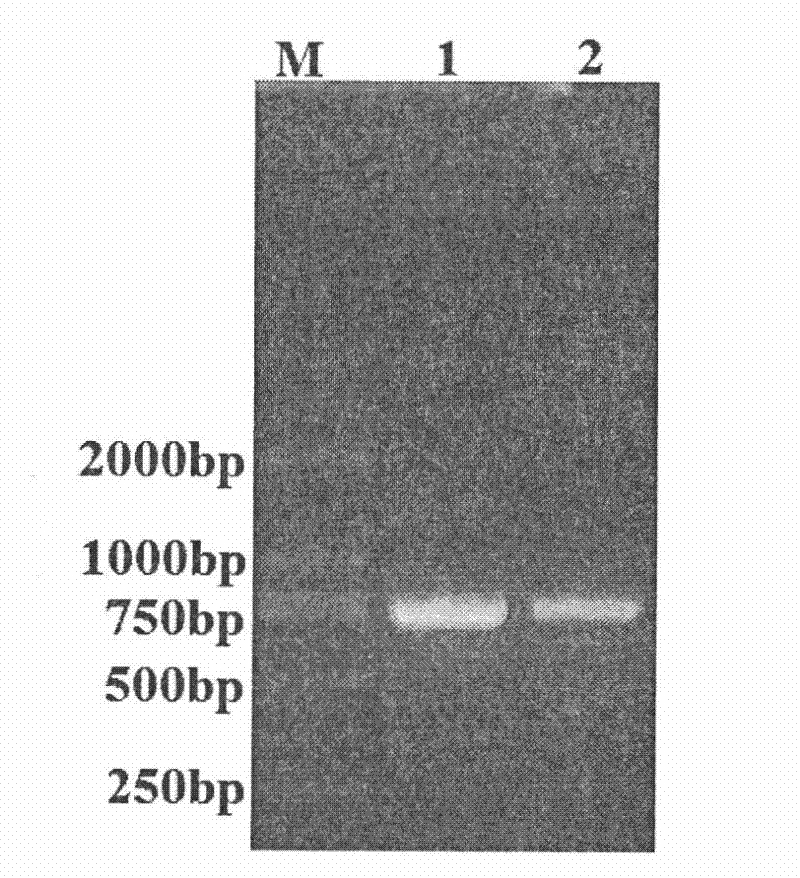
[0071] 3. Electrophoretic separation of PCR products
[0072...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3: Cloning fungal 18S rDNA from scab disease tissue
[0076] 1. Test materials and reagents
[0077] Material: Peanut scab diseased tissue.
[0078] Reagents: alkaline lysate, Tris-HCl buffer containing 5-8mg / ml PVP40.
[0079] 2. Test method
[0080] 1. Template Preparation
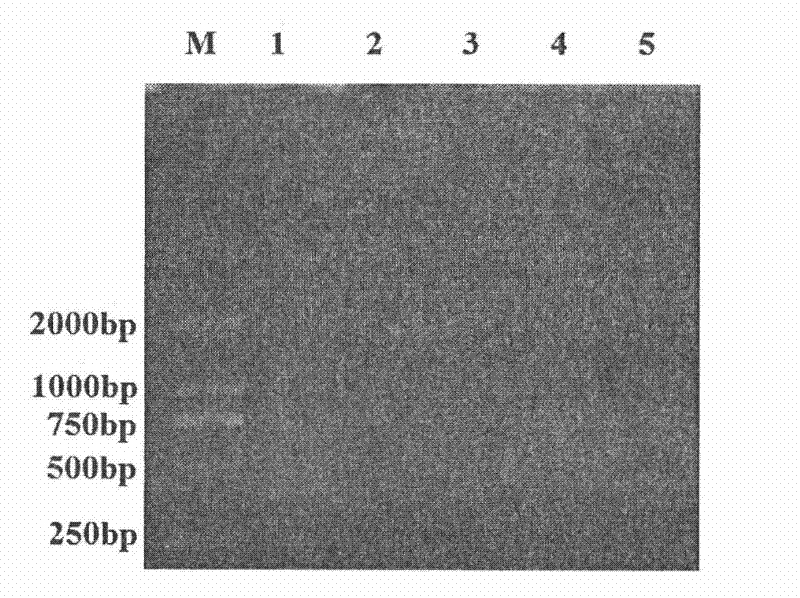
[0081] Select a piece of scab diseased leaf on the peanut plant, punch a hole on the side of the main vein with a neutral pen core, and obtain a leaf disc with a diameter of about 1.12 mm; cut the diseased tissue of the stem into a thin slice with a diameter of about 4 mm with a razor blade. The following steps are the same as steps B, C, D, and E of "template preparation" in Example 1.
[0082] 2.PCR
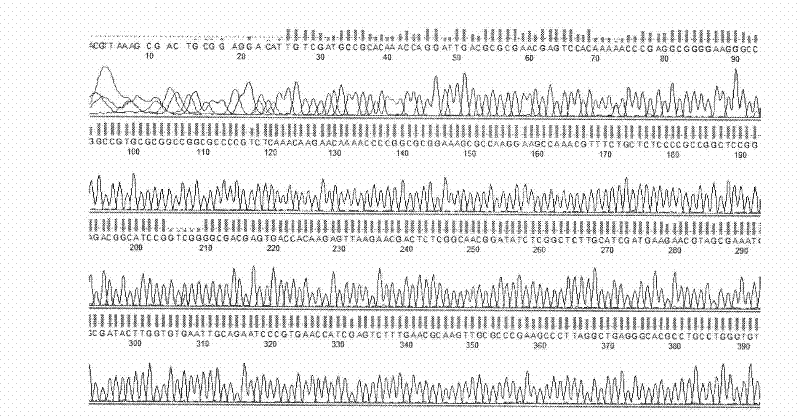
[0083] PCR system: 25 μl 2×Tiangen Taq PCR MasterMix, 10 μM fungal-specific primers (NS26: 5’-CTGCCCTATCAACTTTCGA-3’ / R518: 5’-ATTACCGCGGCTGCTGG-3’) 2 μl each, 1 μL DNA template, 20 μl sterile deionized water.
[0084] PCR conditions: 95°C pre-denaturation for 6min, 94°C for 1min, 55°C...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com