Non-volatile method for extracting zinc, iron and indium from solution of zinc, iron and indium
A technology of solution and iron indium, which is applied in the field of extracting indium, can solve the problems of low recovery rate, high processing cost, and high processing cost, and achieve the effect of eliminating volatilization treatment, simplifying process steps, and reducing production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
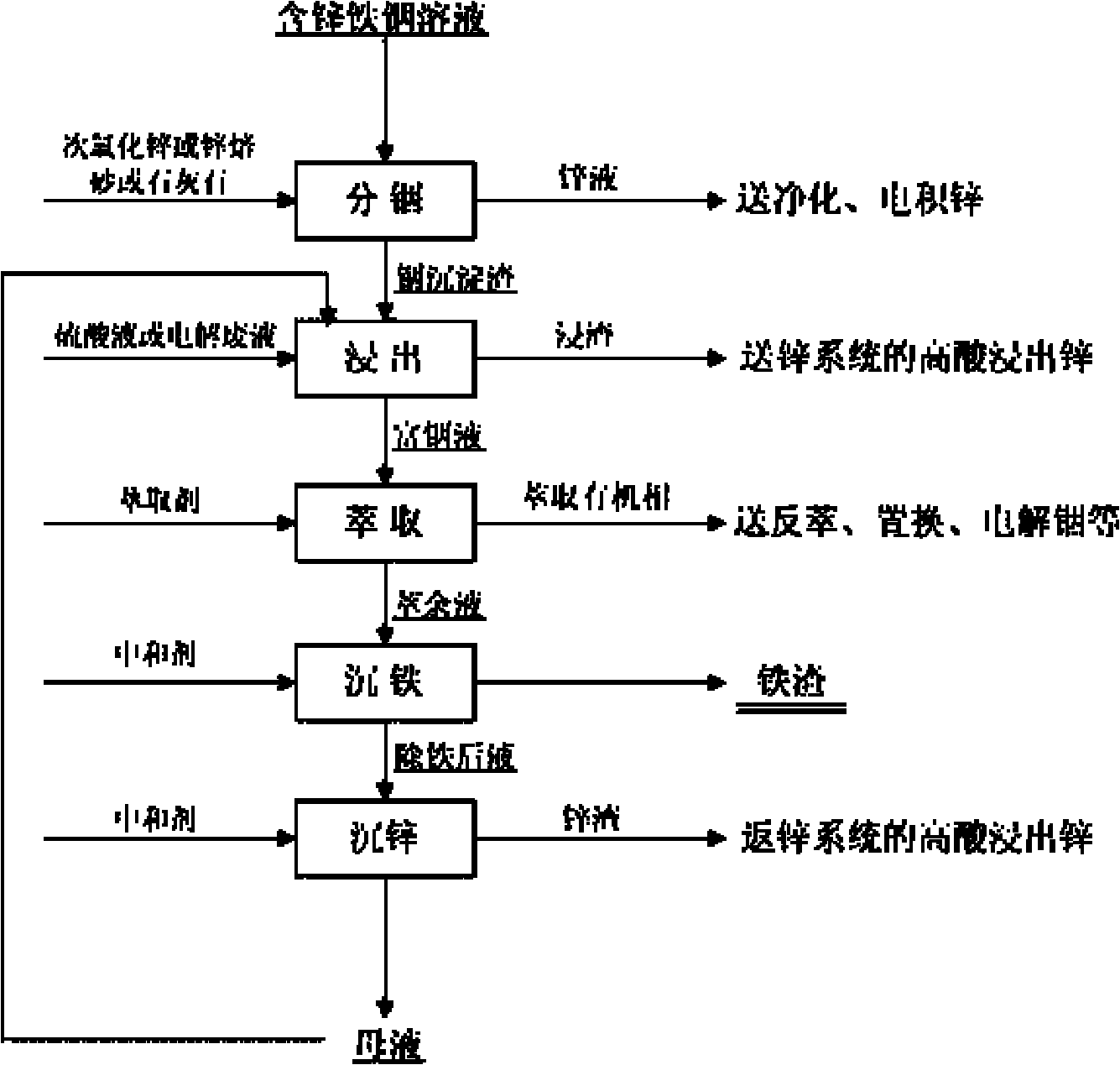
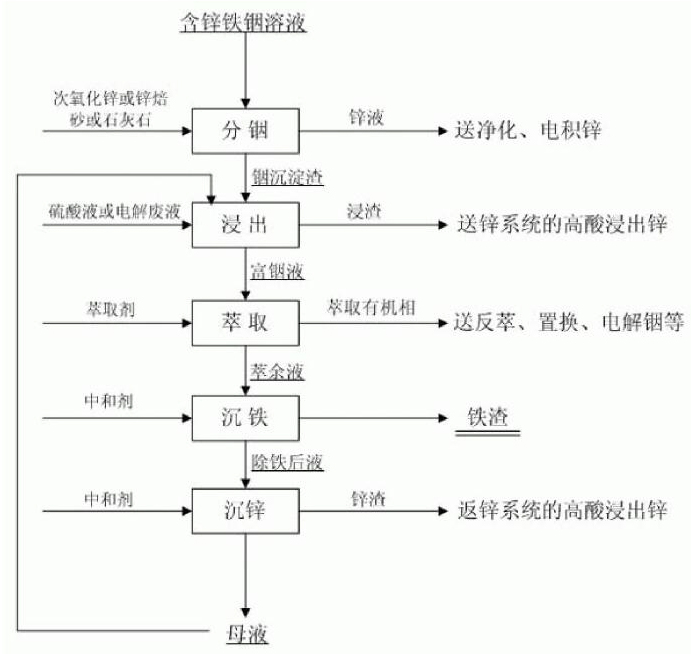
[0016] A method for extracting zinc, iron and indium from zinc-iron-indium solution without volatilization:
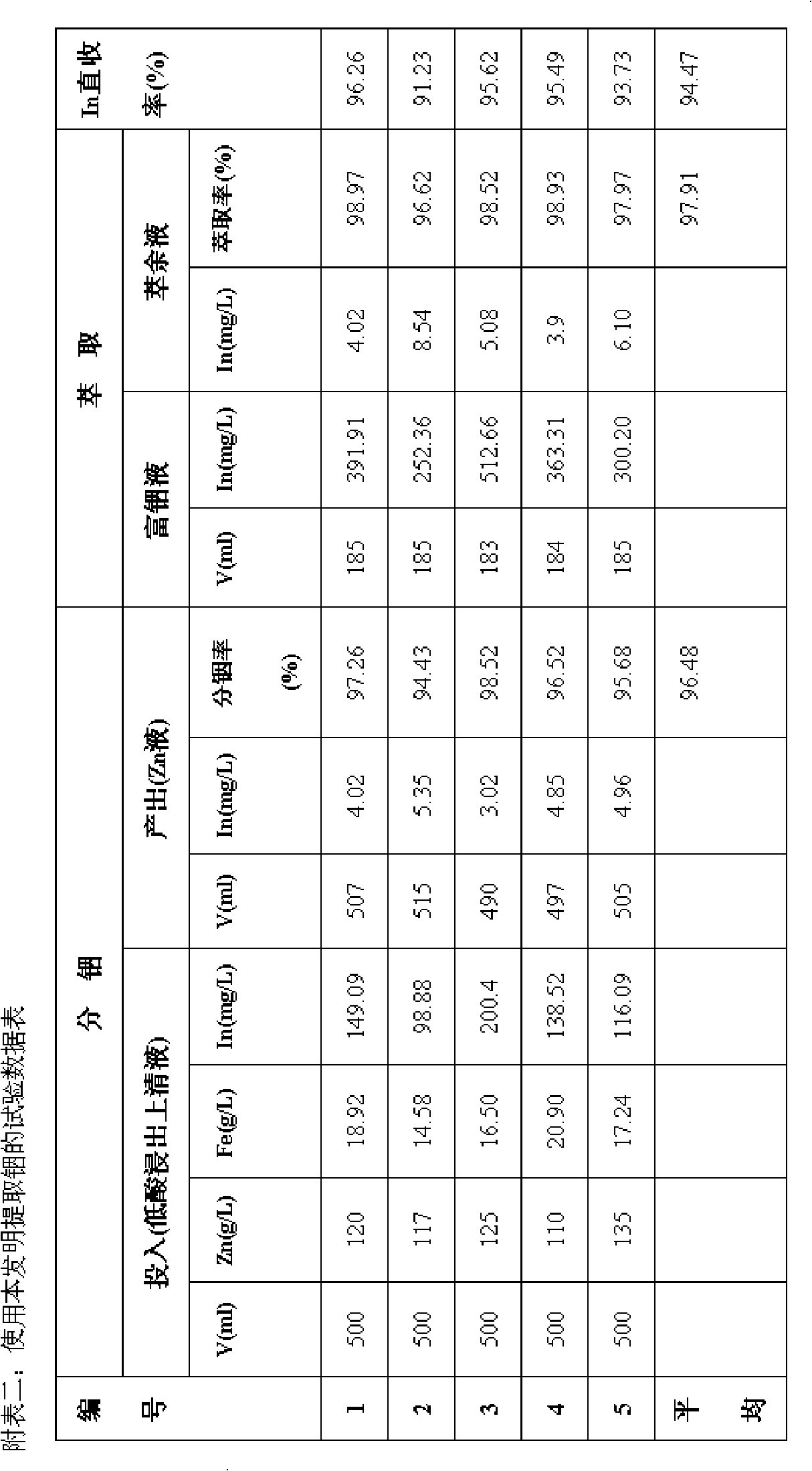
[0017] Get 1# low-acid leaching supernatant liquid 500ml (zinc 120g / L in this solution, iron 18.92g / L, indium 149.09mg / L) containing zinc, iron, indium in a certain wet process zinc smelting plant, under normal temperature, the solution Heat to 90°C, gradually add 20g of secondary zinc oxide powder containing about 50% zinc, and control the pH value of the zinc-iron-indium solution at 4.5 during the separation of indium and zinc. After stirring and reacting for 2 hours, perform liquid-solid separation and filter to obtain indium precipitate slag and zinc-containing solution, wherein the indium precipitation rate is 97.26%, and the indium precipitation slag contains 12.6% of zinc. Dissolve in 98% sulfuric acid solution. After PH=1, add 10ml of sulfuric acid with a concentration of 98% to make the sulfuric acid concentration of the solution reach about 20g / L. After filtr...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Get 2# low-acid leaching supernatant liquid 500ml (zinc 117g / L in this solution, iron 14.58g / L, indium 98.88mg / L) containing zinc, iron, indium in a certain wet process zinc smelting plant, under normal temperature, solution Heat to 95°C, gradually add 18g of secondary zinc oxide powder containing about 50% zinc, and control the pH value of the zinc-iron-indium solution at 4.0 during the separation of indium and zinc. After stirring and reacting for 2 hours, perform liquid-solid separation and filter to obtain indium precipitate Slag and zinc-containing solution, in which the precipitation rate of indium is 94.43%, the zinc-containing solution is sent to the middle immersion or after purification and impurity removal treatment, it is sent to electricity for zinc deposition; the concentration of indium precipitation slag is added to 5% sulfuric acid 150ml to dissolve, and the concentration is replenished after PH=1 5ml of 98% sulfuric acid reaches an acid concentration of...
Embodiment 3
[0021] Get 3# low-acid leaching supernatant liquid 500ml (containing zinc 125g / L in this solution, iron 16.50g / L, indium 200.4mg / L) containing zinc, iron, indium in a certain wet process zinc smelting plant, under normal temperature, the solution Heat to 25°C, gradually add 18g of secondary zinc oxide powder containing about 50% zinc, and control the pH value of the zinc-iron-indium solution at 4.2 during the indium-zinc separation process. After stirring and reacting for 1.8 hours, perform liquid-solid separation and filter to obtain indium Precipitation slag and zinc-containing solution, in which the precipitation rate of indium is 98.52%. Send the zinc-containing solution to intermediate immersion or after purification and impurity removal treatment, and then send electricity to deposit zinc; add indium precipitation slag to 150ml of zinc-precipitating mother liquor, and use 98% sulfuric acid Dissolve 10ml, add 10ml of sulfuric acid with a concentration of 98% after PH = 1 t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com