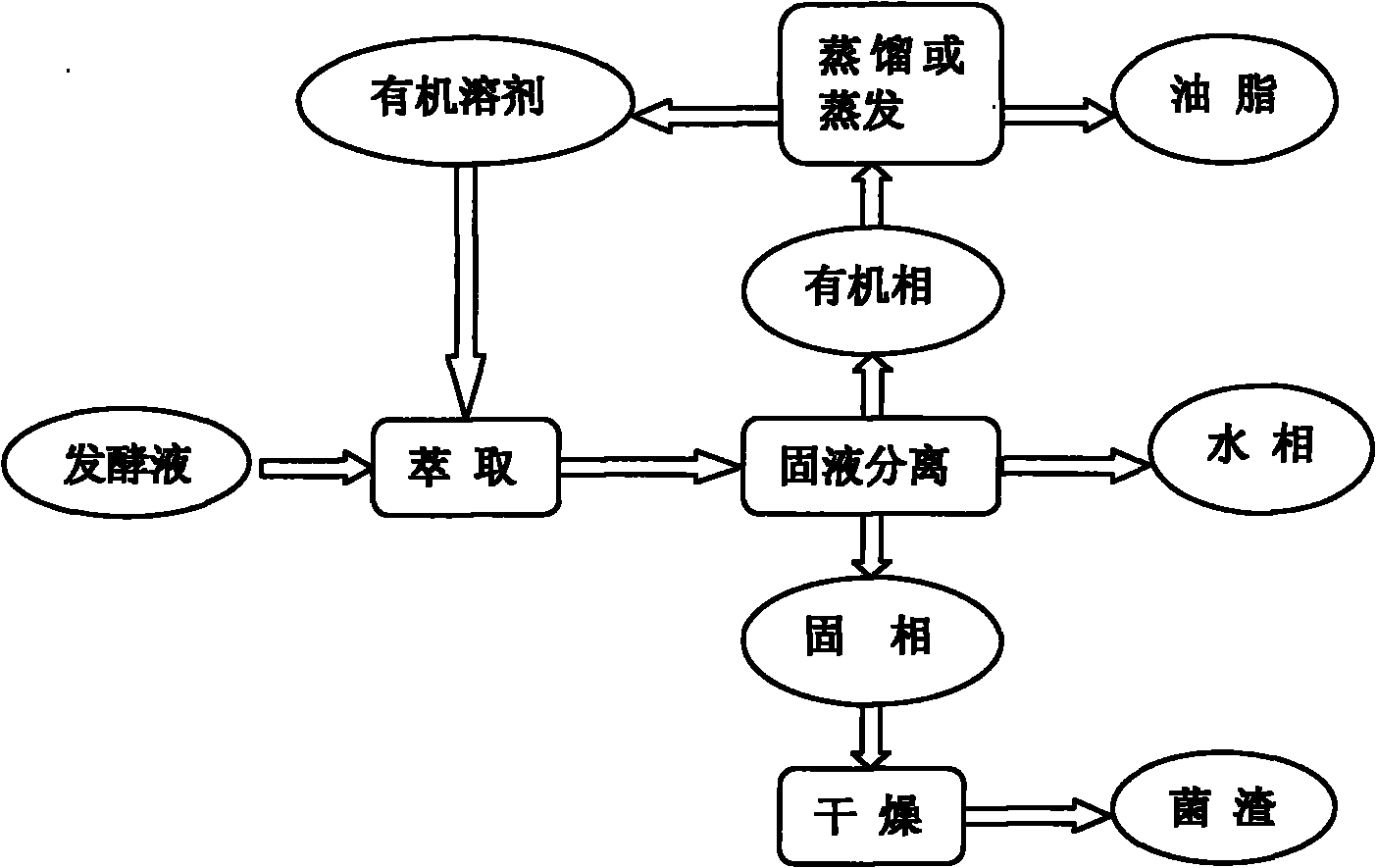
Method for separating microorganisms from grease
A technology of microbial oil and separation method, which is applied in the downstream post-processing field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of difficult separation and recovery of bacteria, reduction of application value of bacteria residue, and large loss of pressing method, etc., and achieves simple and effective technology, which is conducive to large-scale industrialization The effect of less investment in production and equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] According to the method described in literature (Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Bai, F. Enzyme Microb. Technol., 2007, 41: 312-317), the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides AS 2.1389 grown in YEPD medium (the bacterial strain originates from the China Common Microorganism Strain Preservation Management Center) is inserted in the fermentation medium according to 10% inoculum size, 30 ℃, ventilation rate 0.8vvm, the glucose 500ml of supplementary material 1000g / L five times, obtain after cultivating 120h Fermentation broth with a dry cell weight of 92g / L (oil content 60.1%). Take 50ml of the above fermentation broth, add 50ml of chloroform, stir and extract at 20°C for 1h, settle and separate layers, remove the lower organic solvent phase, distill and dry to obtain 2.06g of oil, the oil extraction rate is 74.6%. The residue was centrifuged to obtain a solid phase, which was dried to obtain 2.31 g of bacteria residue.
Embodiment 2
[0022] According to the method described in the literature (Huang Jianzhong, Shi Qiaoqin, Zhou Xiaolan, etc. Microbiology Bulletin, 1998, (4): 187-191), the oleaginous mold Mortierella isabellina AS 3.3410 (bacterial strain derived from the Chinese Common Microorganisms Collection) was cultivated for 28h. Management center) seed solution is inserted in the fermentation medium with 10% inoculation amount, 280rpm, cultivates 70h under 25 ℃, obtains the fermentation liquid of dry cell weight 34g / L (oil content 47.2%). Take 25ml of the above fermentation broth, add 75ml of chloroform:methanol 2:1 (V / V), at 70°C, stir and extract for 1h, remove the lower organic solvent phase after centrifugation, evaporate and dry to obtain 0.37g of oil, the oil extraction rate is 92 %. The upper layer was filtered to obtain wet fungus residue, and the residue mass after drying was 0.25g.
Embodiment 3
[0024] With reference to the method described in Example 1, feed twice, obtain the oleaginous yeast Lipomyces starkeyi AS 2.1560 of dry cell weight 48g / L (fat content 55.2%) after fermenting 62h (bacterial strain originates from China Ordinary Microorganism Strain Preservation Management Center ) fermented liquid 100ml, add No. 6 solvent of 25ml, at 30 ℃, after 10min of stirring and extracting, settling and layering, take the upper solvent phase, evaporate after drying to obtain 0.72g of oil and fat, the oil extraction rate is 27%. The lower phase was centrifuged to obtain a solid phase, and 2.80 g of bacteria residue was obtained after drying.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com