Comprehensive recovery method for smelted lead waste slag of blast furnace
A recycling method and blast furnace technology, which are applied in the field of metal waste slag recycling, can solve problems such as difficult recycling of iron metal resources, and achieve the effects of controlling environmental pollution and alleviating the lack of mineral resources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
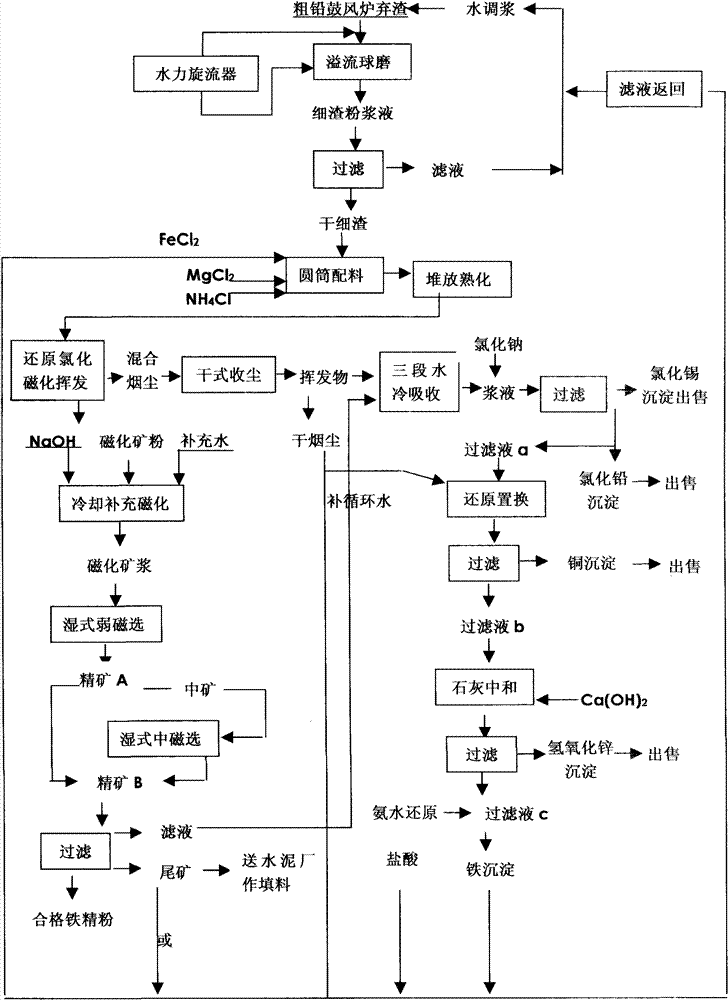
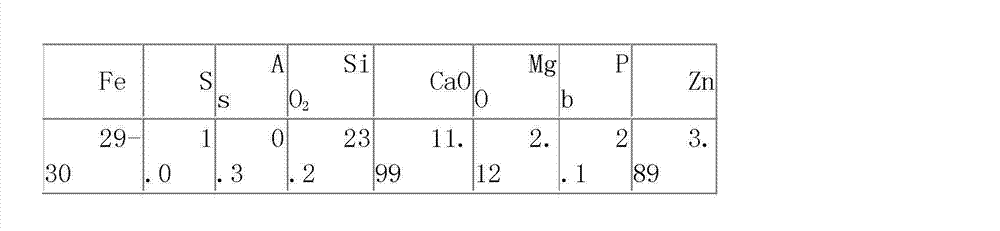
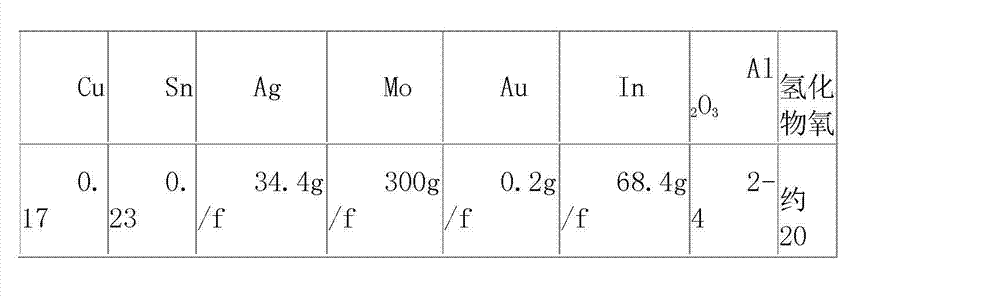
[0022] 1) First, carry out wet overflow ball milling to 160 mesh of the waste slag of the lead smelting blast furnace, and the filtrate filtered by the fine slag slurry enters the liquid circulation, and the dry fine slag is collected by filtration, and ammonium chloride and ferric chloride are added to the dry fine slag , iron trichloride, then chlorinated with a reducing agent (coking coal powder), matured for 24 hours, and roasted in a rotary kiln at a roasting temperature of 1200-1250°C, which is conducive to the volatilization of all non-ferrous metal oxides and the magnetization of iron. Make the iron in the ore powder form ferric oxide, leave the kiln at a temperature higher than 400°C, and cool it with circulating water to obtain reduced ore pulp.
[0023] The above-mentioned dry fine residue, chlorinating agent and reducing agent are in parts by weight: 100:10:12.
[0024] 2) The reduced ore pulp is subjected to weak magnetic separation with a magnetic field strength ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] 1) First, carry out wet overflow ball milling to 200 mesh of the waste slag of the lead smelting blast furnace, and the filtrate filtered by the fine slag slurry enters the liquid circulation, and the dry fine slag is collected by filtration, and ammonium chloride and ferric chloride are added to the dry fine slag , ferric chloride, in order to prevent the formation of iron silicate with low softening temperature, add magnesium chloride to oxidize it into magnesium oxide to increase the softening point of slag by 50-100°C, and add a reducing agent (coking coal powder) for chlorination and reduction for 24 hours. Rotary kiln roasting, the roasting temperature is 1200 ~ 1250 ℃, so that the iron in the ore powder will form ferric oxide, the temperature is higher than 400 ℃ out of the kiln, using circulating water plus 1.5% (V / V) sodium hydroxide to supplement the reduction and magnetization process, and the reduction pulp.
[0029] The weight ratio of the dry fine slag, ch...
Embodiment 3
[0034] 1) First, carry out wet overflow ball milling to 200 mesh of the waste slag of the lead smelting blast furnace, and the filtrate filtered by the fine slag slurry enters the liquid circulation, and the dry fine slag is collected by filtration, and ammonium chloride and ferric chloride are added to the dry fine slag , Ferric trichloride, in order to prevent the formation of iron silicate with low softening temperature, add magnesium chloride to oxidize it into magnesium oxide to increase the softening point of slag by 50-100°C, then add reducing agent (coking coal powder) to chlorinate and mature for 24 hours, Roast in a rotary kiln at a temperature of 1200-1250°C to make the iron in the ore powder form ferric oxide, exit the kiln at a temperature greater than 400°C, and use circulating water plus 2% (V / V) sodium hydroxide to supplement the reduction magnetization process. Restore the ore pulp.
[0035] The ratio of the dry fine slag, chlorination agent, magnesium chlorid...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com