Method for producing high-concentration reduced sugar by combining enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose and membrane separation
A lignocellulase, lignocellulose technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, sugar derivatives, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable, low reducing sugar concentration, unfavorable microbial fermentation, etc. The effect of continuity, easy automation and industrialization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
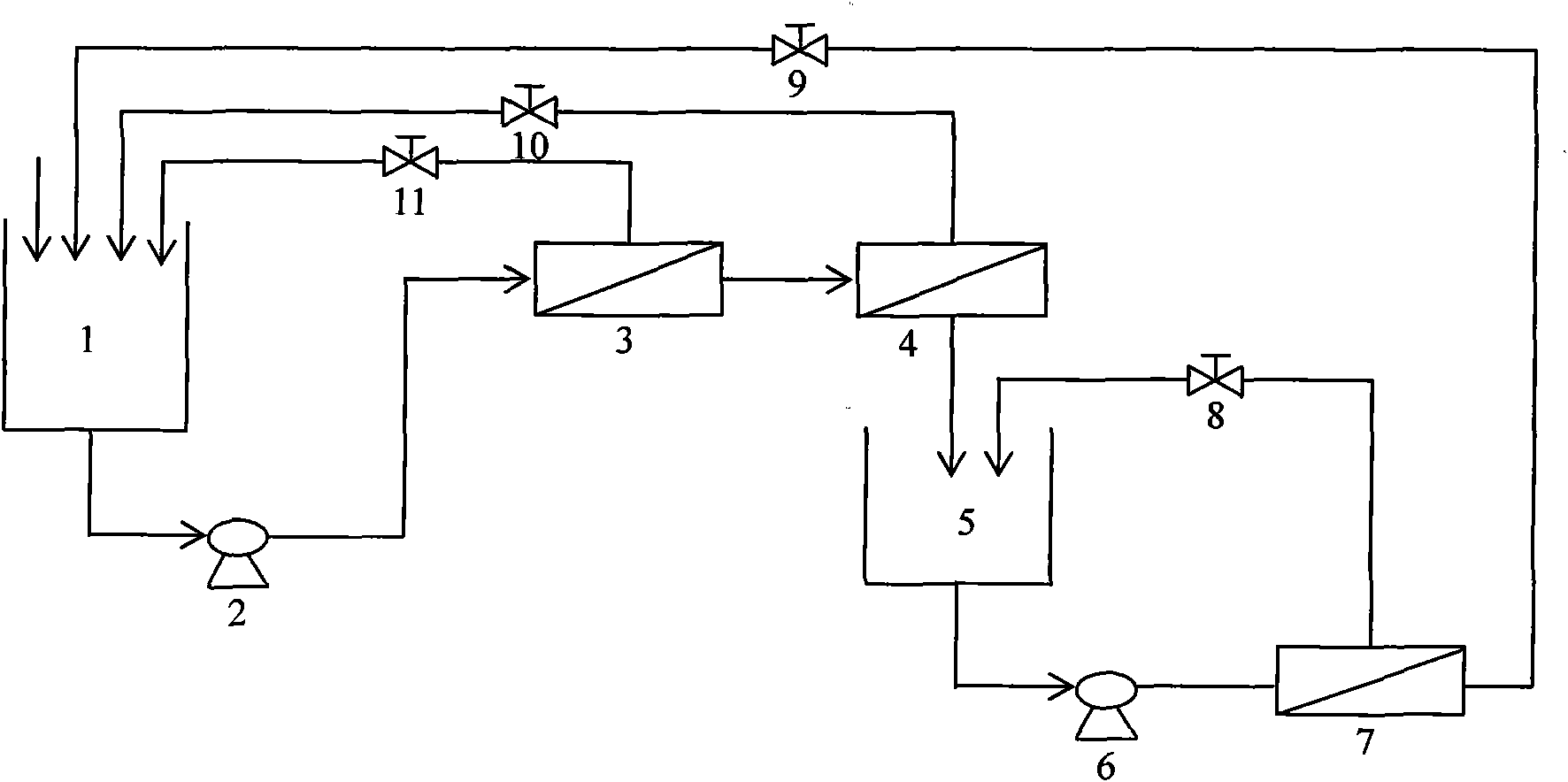
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: A kind of method that lignocellulosic enzymatic hydrolysis and membrane separation are coupled to produce high-concentration reducing sugars comprises the following steps:
[0021] (1) add dilute acid-treated bagasse, cellulase and β-glucosidase in the enzymolysis reactor in a ratio of 5% (w / v), and the consumption of cellulase and β-glucosidase is 20IU respectively / g substrate and 20IU / g substrate. The pH was adjusted to 4.8, and incubated at 50°C for 1 day.
[0022] (2) Turn on the feed pump, pump the enzymolysis solution into the microfiltration module (polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane), and return the retained lignocellulose substrate to the enzymolysis reactor. The pore size of the microfiltration membrane is about 0.45 microns, and the pressure inside the module is 0.1-0.2 MPa.
[0023] (3) The permeate obtained in step (2) enters the tubular polyamide ultrafiltration module with a molecular weight cut-off of 10,000 Daltons, and the retaine...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: A kind of method that lignocellulosic enzymatic hydrolysis and membrane separation are coupled to produce high-concentration reducing sugars comprises the following steps:
[0026] (1) Add poplar sawdust, cellulase and β-glucosidase treated with dilute alkali in the ratio of 3% (w / v) in the enzymolysis reactor, and the consumption of cellulase and β-glucosidase is respectively 10IU / g substrate and 20IU / g substrate. The pH was adjusted to 4.8, and incubated at 50°C for 1 day.
[0027] (2) Turn on the feed pump, pump the enzymolysis solution into the microfiltration module (PVDF membrane), and return the retained lignocellulose substrate to the enzymolysis reactor. The pore size of the microfiltration membrane is about 0.45 microns, and the pressure inside the module is 0.1-0.2 MPa.
[0028] (3) The permeate obtained in step (2) enters the flat polyethersulfone ultrafiltration module with a molecular weight cut-off of 5000 Daltons, and the retained hydrola...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Embodiment 3: a kind of method for coupling lignocellulosic enzymatic hydrolysis and membrane separation to produce high-concentration reducing sugars, comprising the following steps:
[0031] (1) Add steam-exploded wheat straw, cellulase, β-glucosidase and xylanase in the enzymolysis reactor in a ratio of 10% (w / v), cellulase, β-glucoside The enzyme and xylanase dosages were 40 IU / g substrate, 20 IU / g substrate and 20 IU / g substrate, respectively. The pH was adjusted to 4.8, and incubated at 50°C for 1 day.
[0032] (2) Turn on the feed pump, pump the enzymolysis solution into the microfiltration module (ceramic membrane), and return the retained lignocellulose substrate to the enzymolysis reactor. The pore size of the microfiltration membrane is about 0.22 microns, and the pressure inside the module is 0.1-0.2 MPa.
[0033] (3) The permeate obtained in step (2) enters the hollow fiber polyethersulfone ultrafiltration module with a molecular weight cut-off of 10,000 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com