Organosol containing magnesium fluoride hydroxide, and manufacturing method therefor
A magnesium fluoride hydroxide, organosol technology, applied in magnesium fluoride, magnesium halide, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problem of no hydrophilic, low refractive index, no fluorine-based magnesium Compound hydrophilicity and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0293] Preparation of "Example 1" organosol (Mg compound separate system)
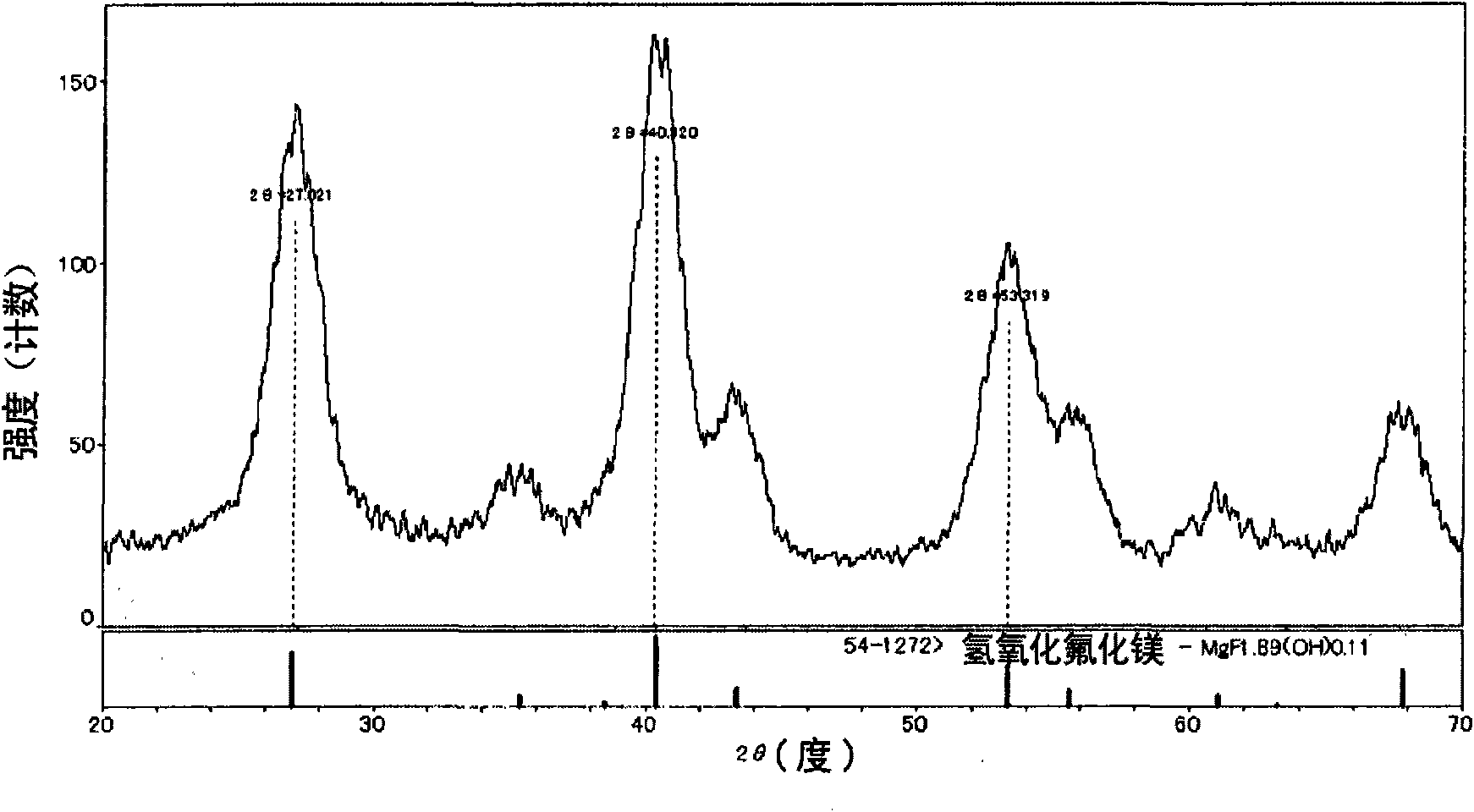
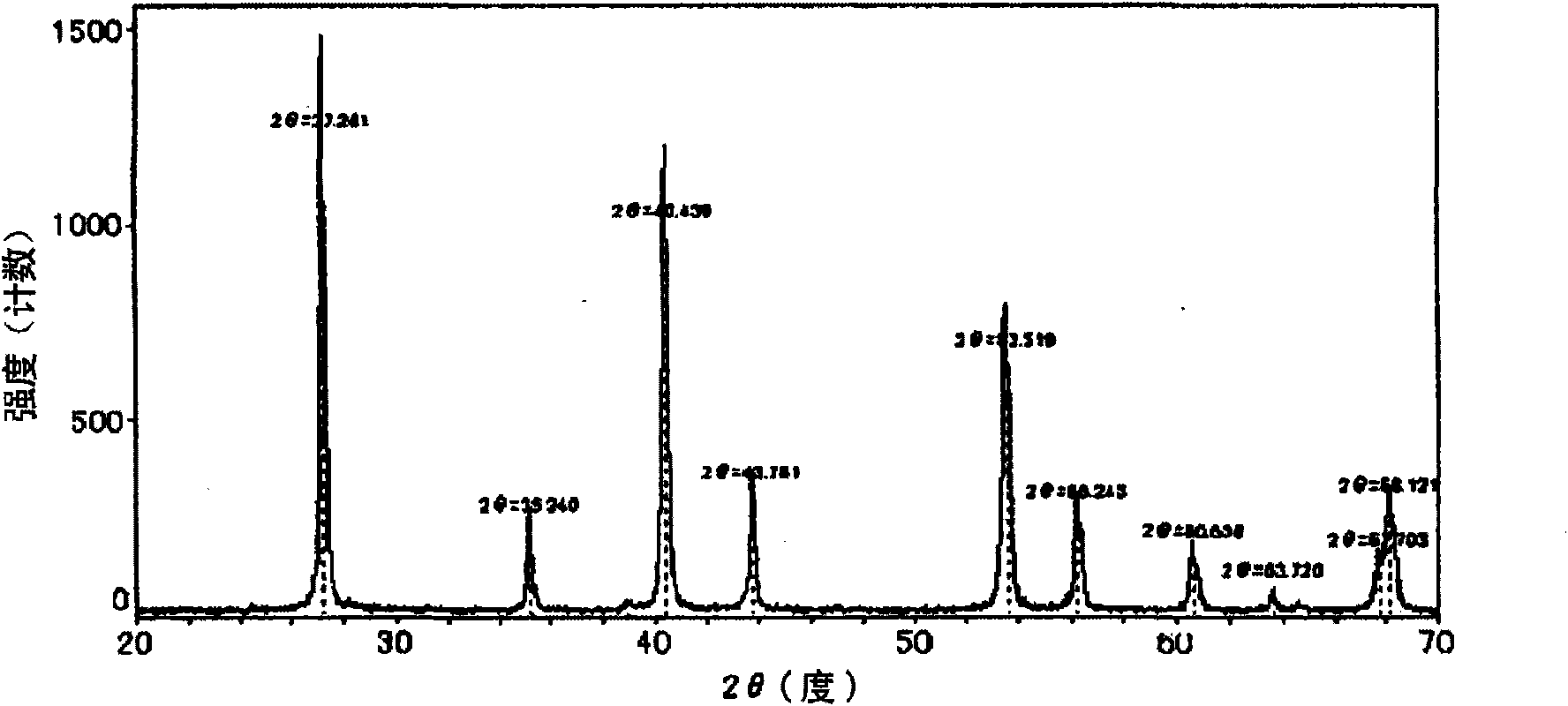
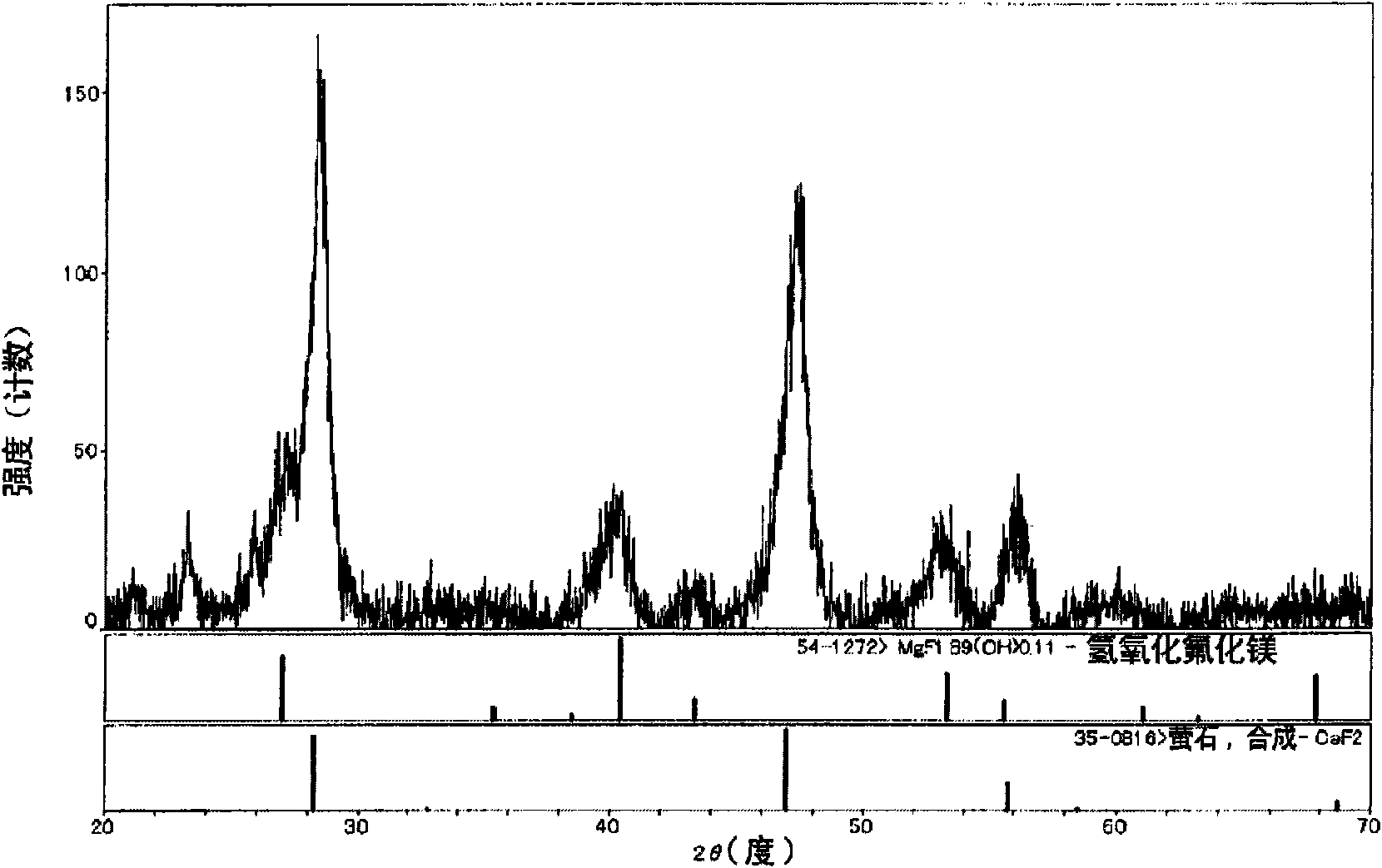
[0294] Hereinafter, in "Example 1-1" to "Example 1-7", preparation examples of the organosol in the Mg compound-only system are shown. After drying the prepared organosol at 120°C, XRD (RINT-UltimaIII manufactured by Rigaku) was used to diffract at a voltage of 40Kv×current of 40mA and a scan angle of 10-70°. As a result, an intensity of about 50-160cps and a half-width It is a broad peak of ±0.7-1.2°. This suggests that it is a substance with extremely low crystallinity, and it suggests that it is a substance close to an amorphous rather than a crystal. In addition, it was confirmed that the X-ray diffraction pattern of the ultrafine particles obtained in this example is similar to that of magnesium hydroxide fluoride (MgF 1.89 (OH) 0.11 ) consistent. As a representative example, the X-ray diffraction diagram of the organosol obtained in "Example 1-1" is shown in figure 1 .
Embodiment 1-1
[0295] "Example 1-1": MgCl 2 ·6 water salt / IPA system
[0296] Disperse 16.46 g (0.173 mol) of reagent grade magnesium chloride hexahydrate in 150 ml of isopropanol (hereinafter also referred to as IPA) at room temperature with stirring to obtain a suspension in which magnesium chloride is dispersed. To this suspension, 14.71 g (0.346 mol) of 47% hydrofluoric acid aqueous solution was added dropwise intermittently over 10 minutes at room temperature with stirring (HF / Mg=2.0). After hydrogen fluoride was added dropwise, stirring was continued for 8 hours to obtain a milky transparent slurry. The average particle diameter of the ultrafine particles present in this solution was 20 nm. The obtained sol was dried at 120°C, and the obtained X-ray diffraction pattern was shown in figure 1 .
Embodiment 1-2
[0297] "Example 1-2": MgCO 3 / EGME system
[0298] Disperse 17.331 g (0.188 mol) of special grade magnesium carbonate in 200 ml of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether at room temperature under stirring conditions to obtain a suspension formed by dispersing magnesium carbonate. To this suspension, 16.35 g (0.417 mol) of a 51% hydrofluoric acid aqueous solution was intermittently added dropwise over 10 minutes at room temperature with stirring (HF / Mg=2.22). After the hydrogen fluoride aqueous solution was added dropwise, stirring was continued for 8 hours to obtain a milky transparent slurry. The average particle diameter of the ultrafine particles present in this solution was 15 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com