Tissue engineered artificial optic nerve conduit and preparation method thereof
A technology of tissue engineering and optic nerve, which is applied in the field of biomedical engineering, can solve the problems of virus transfection, biological safety, limited application prospects, short half-life of nutritional factors, and limited duration, etc., to achieve small foreign body reactions, promote axon regeneration, and avoid The effect of injurious manipulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Example 1 Preparation of tissue-engineered artificial optic nerve (filled with common Schwann cells)
[0058] The Schwann cells cultured in vitro were divided into 5×10 6 Cell / ml density was inoculated into 6-well plates, 10% FBS / DMEM culture medium was added, and when the confluence of cell growth reached 90%, it was digested with trypsin and transplanted.
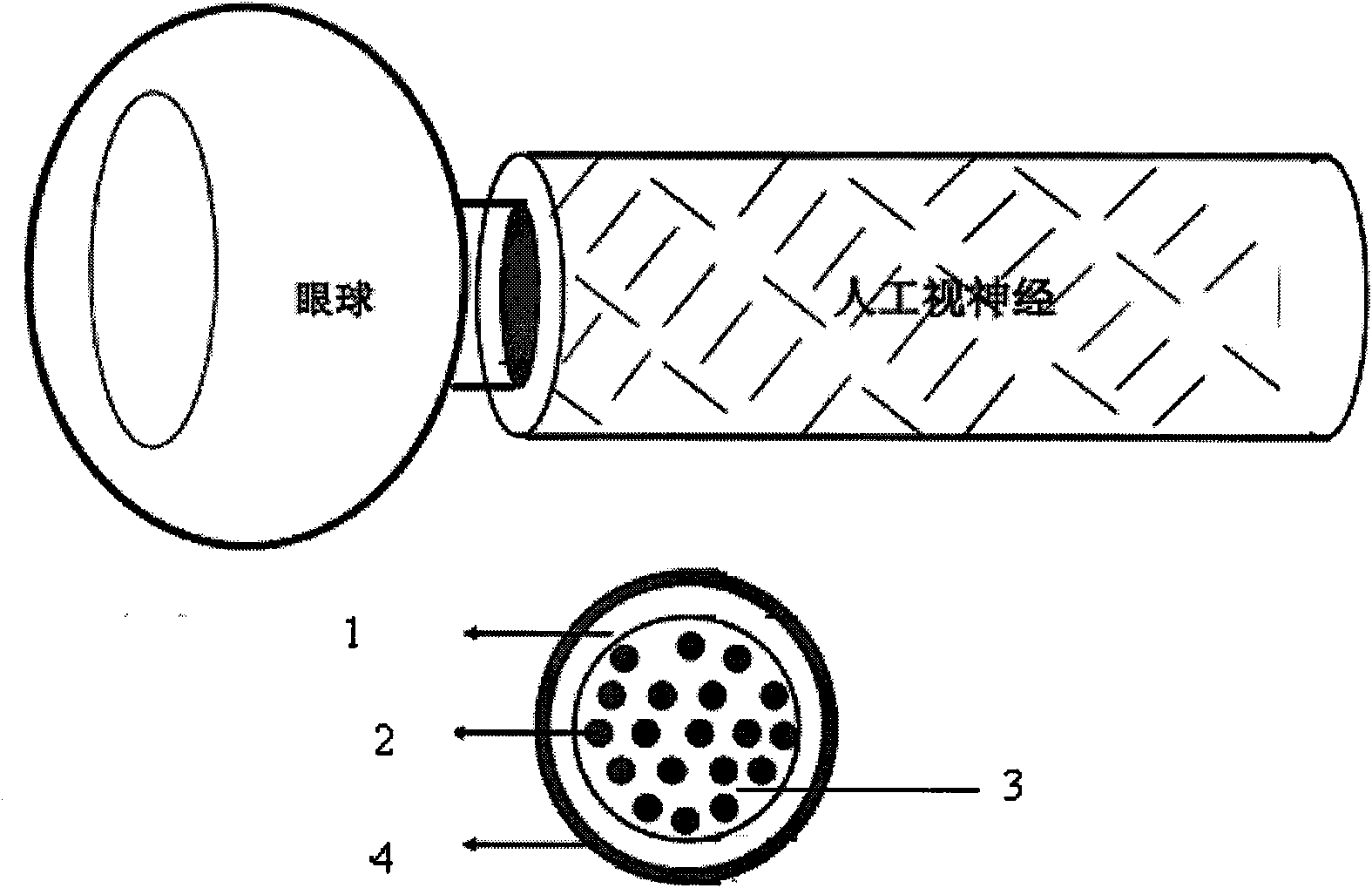
[0059] The PLGA filament is woven into a hollow catheter as required, and the surface of the catheter is coated with a layer of chitosan polymer, and ethylene oxide is fumigated for sterilization. The surgical 4-0 PGA absorbable suture was disassembled into PGA filaments under a microscope, and the PGA filaments (with a diameter of 10 μm) were evenly filled into the PLGA hollow catheter as the internal scaffold of the artificial optic nerve. Then put the catheter into 75% alcohol to sterilize for half an hour, then rinse it with PBS three times, dry it naturally in an ultra-clean bench, and then fill it with cells...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2 Preparation of tissue-engineered artificial optic nerve (filled with transgenic Schwann cells)
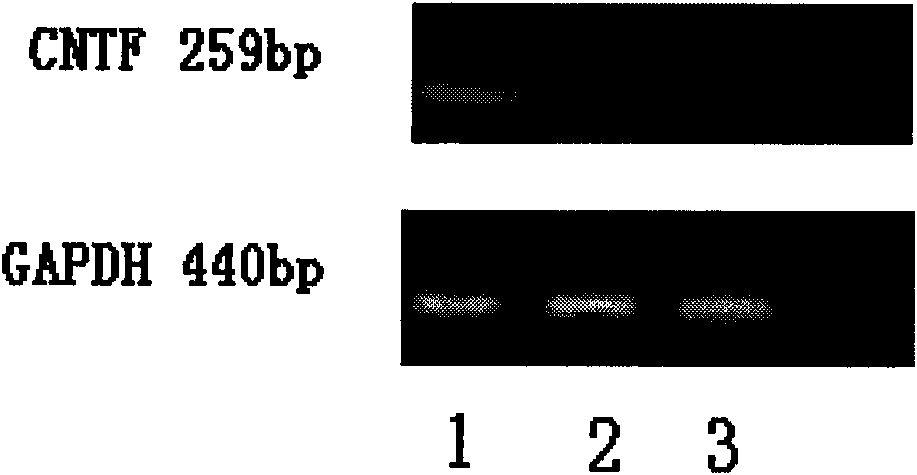
[0062] The Schwann cells cultured in vitro were divided into 5×10 6 Inoculate the cell / ml density into a 6-well plate, add 10% FBS / DMEM culture medium, when the confluence of cell growth reaches 90%, suck out the culture medium, wash 3 times with PBS solution, and then add 100ml D-Hank's solution to each well , which contains 12.5μg CNTF plasmid, after standing for 110 minutes, add 900ml D-Hank's solution, and then Petri Pulser TM Gently insert the PP35-2P electrode into the six-hole plate, immerse part of the electrode in the liquid surface, gently place it on the cell surface, and connect the electroporation instrument (ECM-830, BTX) for electric shock. The electric shock parameters are voltage 192v, time 20ms, interval 500ms, A square wave pulsed 5 times. After the electric shock is completed, stand still for 5 minutes, then aspirate the electrotransfer solut...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Embodiment 3 animal experiments
[0066] Experimental animals: 16 SD rats (200-250 g) at 8-10 weeks, purchased from the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and kept in a clean animal room in accordance with the requirements of the Experimental Animal Ethics Association of Fudan University.
[0067] Experimental method: Under general anesthesia, the optic nerve of the left eye of the rat was separated, the optic nerve sheath was incised, the axon was cut off at 0.5 mm behind the optic nerve head, and the axon at the distal stump was about 3 mm long, and the sheath was avoided during the process. One end of the 11 mm long artificial optic nerve was sutured to the sheath at the proximal end of the optic nerve with 10-0 suture, and the other end was sutured under the scalp with 8-0 suture ( Image 6 ), check the fundus after the operation, and confirm that there is no damage to the blood vessels on the optic nerve sheath to affect the blood supply of the reti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com