Method for simultaneously treating waste water and recovering rare earth of rare earth separation plant
A waste water and rare earth technology, which is applied in the direction of neutralizing water/sewage treatment, improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of rare earth separation plant waste water recovery of rare earth, ammonia nitrogen COD and other indicators are difficult to meet the discharge standards, high energy consumption and other problems , to achieve good economic benefits, reduce environmental pollution, and reduce production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
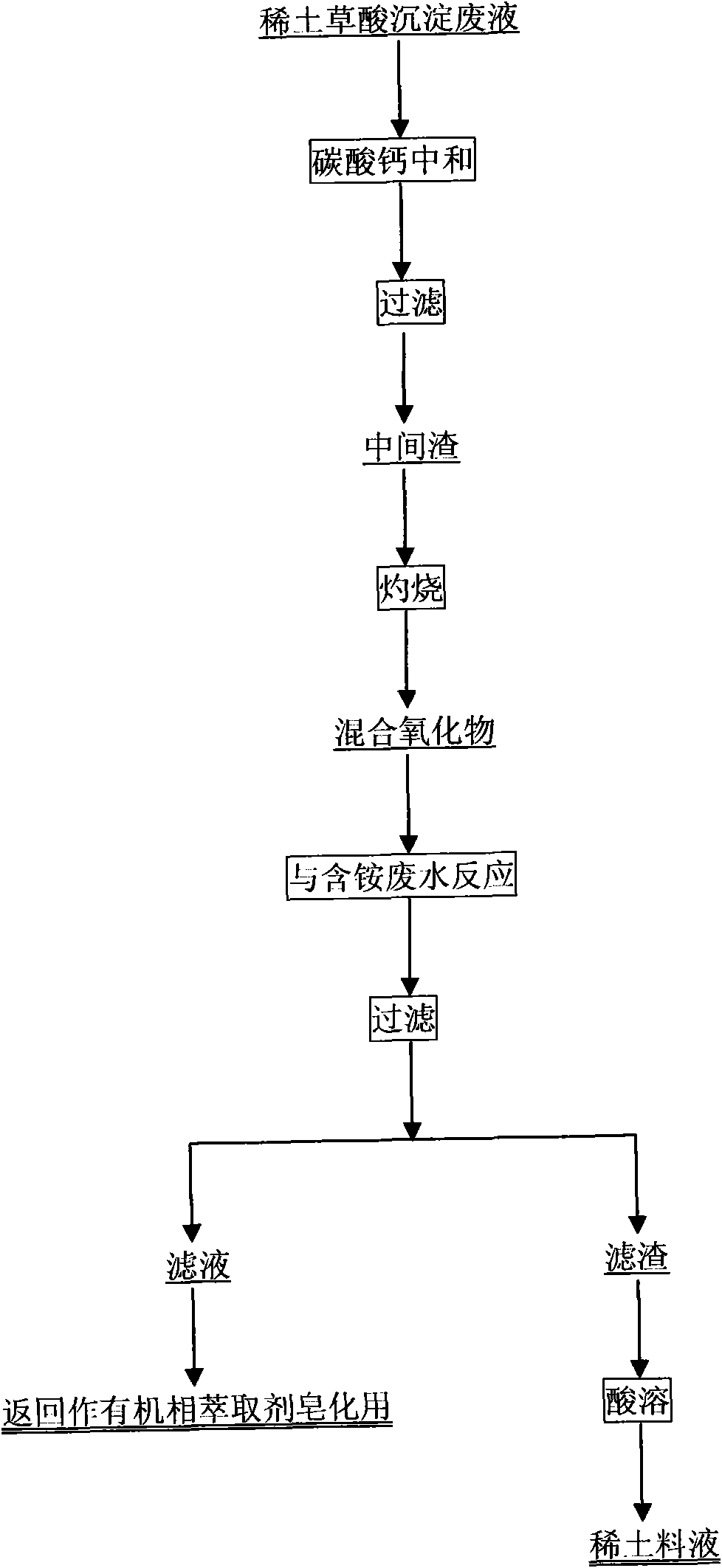
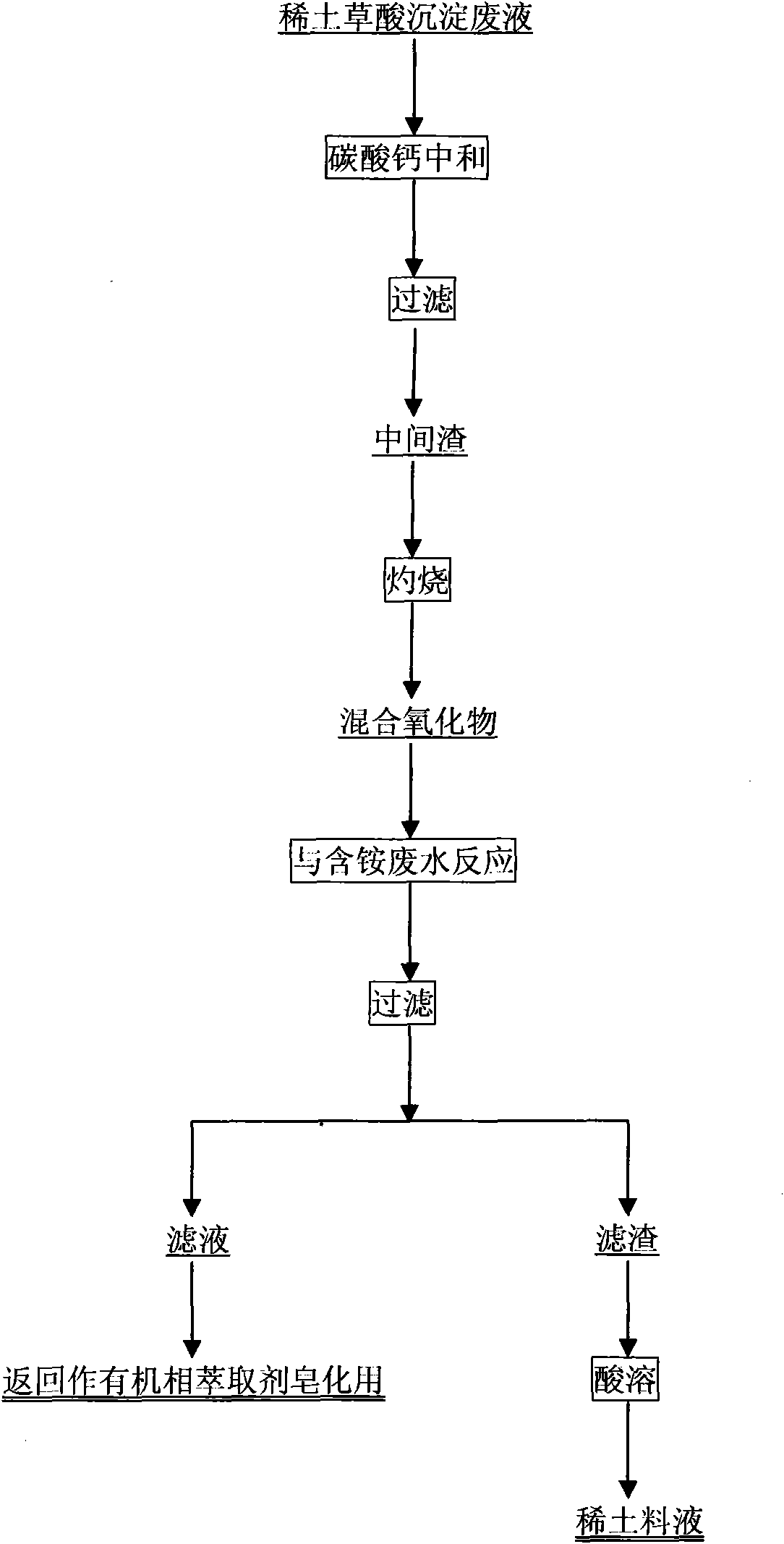
[0042] see figure 1 , the C 草酸 =12.7g / L, REO=0.73g / L praseodymium neodymium oxalate precipitation wastewater 5m 3 Add calcium carbonate to react to pH = 1.5, filter the suspension and wash the filter residue to obtain an intermediate residue; the intermediate residue is burned at 850-900°C to obtain 43.1kg of mixed oxide. The mixed oxide and the C produced in the production of lanthanum carbonate 氯化铵 =75g / L, REO=0.86g / L ammonium bicarbonate precipitation filtrate 1m3 is reacted in the stirred tank to pH=9 and then filtered, and the filtrate is returned to the extraction line for the saponification of the organic extractant, and the filter residue is washed and leached with sulfuric acid to obtain the rare earth material liquid, return to production use. The total recovery of rare earths is equivalent to REO=4.1kg, and the recovery rate of rare earths is 90.9%.
Embodiment 2
[0044] see figure 1 , the C 草酸 =16.9g / L, REO=0.78g / L Dysprosium oxalate precipitation wastewater 5m 3 Add calcium carbonate and mix until pH=4, filter the suspension and wash the filter residue to obtain an intermediate residue; the intermediate residue is burned at 950-1000°C to obtain 56.2kg of mixed oxide. The mixed oxide and the C produced in the extraction line 氯化铵 = 100g / L extraction saponification waste water 1m 3 After reacting in the stirred tank to pH=8, filter, return the filtrate to the extraction line for saponification of the organic extractant, wash the filtered filter residue and leaching with acetic acid to obtain a rare earth material liquid, which is returned to production for use. The total recovery of rare earths is equivalent to REO=3.7kg, and the recovery rate of rare earths is 94.9%.
Embodiment 3
[0046] see figure 1 , the C 草酸 =8.6g / L, REO=0.41g / L Terbium oxalate precipitation wastewater 5m 3 Add calcium carbonate and mix until pH=2.5, filter the suspension and wash the filter residue to obtain an intermediate residue; burn the intermediate residue at 850-1000°C to obtain 29.8kg of mixed oxide. The mixed oxide and the C produced in the extraction line 氯化铵 = 48.5g / L extraction saponification waste water 1m 3 After reacting in the stirred tank to pH ≤ 12, filter, return the filtrate to the extraction line for saponification of the organic extractant, and wash the filtered filter residue with a mixed acid of hydrochloric acid and nitric acid to obtain a rare earth material liquid, which is returned to production. The total recovery of rare earth is equivalent to REO1.9kg, and the recovery rate of rare earth is 92.7%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com