Preparation method of cationic liposome nanoparticles of amino acid
A cationic liposome and nanoparticle technology, which is applied to the preparation method of peptides, liposome delivery, and the preparation of organic compounds, can solve the problem of high synthesis cost of amino acid cationic liposomes, achieve efficient preparation, easy operation, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
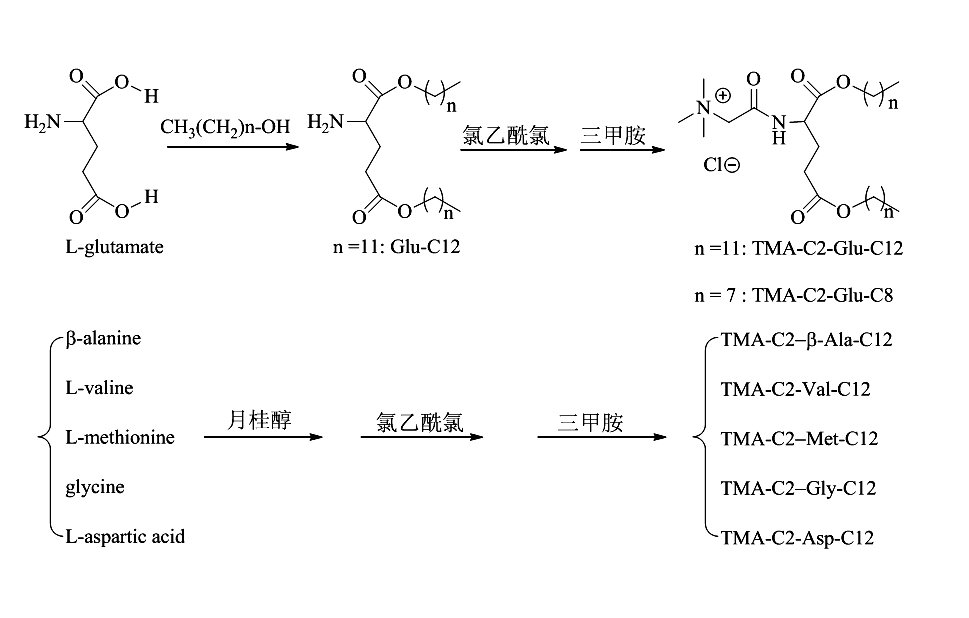
[0018] Example 1. Preparation of cationic liposome Glu-C12 and TMA-C2-Glu-C12 nanoparticles: Add L-glutamic acid (1.47 g, 10.0 mmol), lauryl alcohol ( 6.1 mL, 13.0 mmol), p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (0.99 g, 5.0 mmol) and toluene (16 mL), the water trap was refluxed for about 6 h, until the reaction mixture became clear, TLC (ethyl acetate Ester: methanol = 5: 1) detection, the reaction is complete. The toluene was distilled off, the residue was dissolved in dichloromethane, washed successively with 5% aqueous sodium carbonate solution and distilled water, the organic phase was dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and dichloromethane was distilled off. The residue was dissolved in acetone, a small amount of dilute hydrochloric acid was added dropwise to the acetone solution, a white solid was precipitated, filtered by suction, and dried in vacuum to obtain L-glutamic acid dilauryl hydrochloride (3.94 g, 8.1 mmol, 81.9% ). 1 H NMR (500MHz, CDCl 3 ), d (ppm): 8.89 (s, ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Example 2. Preparation of cationic liposome TMA-C2-Glu-C8 nanoparticles: Add L-glutamic acid (4.40 g, 30.0 mmol), n-octanol (12.2 mL, 78.0 mmol), p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (5.00 g, 30.0 mmol) and toluene (30 mL), reflux water separation reaction, TLC (ethyl acetate: methanol = 5 : 1) detection, the reaction was complete after 6 h . Evaporate toluene, dissolve dichloromethane, wash with 5% sodium carbonate solution and distilled water successively, dry the organic phase with anhydrous sodium sulfate, and distill dichloromethane. Separation by column chromatography gave bis-n-octanol L-glutamate (6.43 g, 17.3 mmol, 57.9%).
[0024] L-bis-n-octanol glutamate (3.54 g, 9.5 mmol), dry dichloromethane (30 mL) and triethylamine (2.7 mL, 20.0 mmol) were successively added into a 100 mL round neck flask and stirred for 1 h . Chloroacetyl chloride (0.94 mL, 12.3 mmol) was slowly added, stirred at room temperature for 24 h, and TLC (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 5: 1...
Embodiment 3
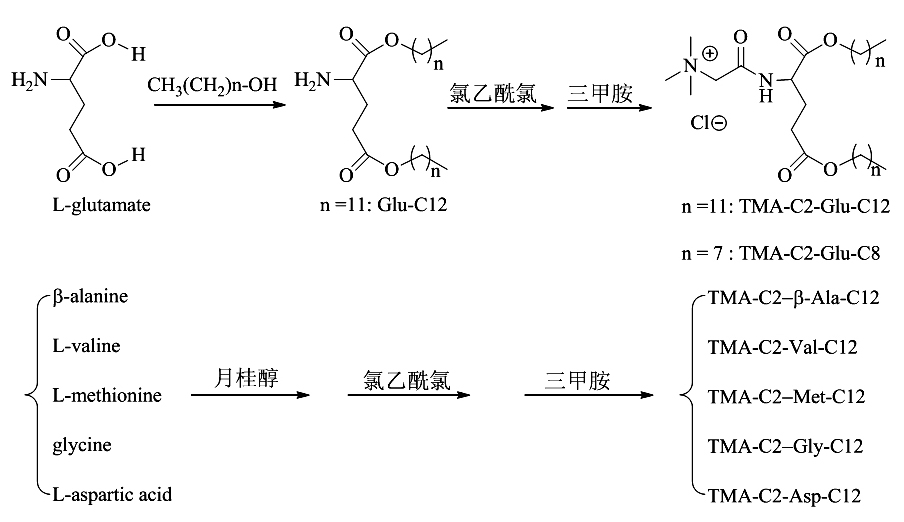
[0027] Example 3 Preparation of cationic liposome TMA-C2-β-Ala-C12 nanoparticles: β-alanine (1.78 g, 20.0 mmol), lauryl alcohol (14.0 mL, 60.0 mmol), dry HCl gas was passed into the reaction solution, and TLC (ethyl acetate: methanol = 5: 1) detected that the reaction was complete after 12 h. Ethyl acetate was added to the reaction solution, and a white solid precipitated out, which was filtered by suction and dried in vacuo to obtain β-alanine lauryl ester (3.94 g, 10.6 mmol, 67.2%).
[0028] Add β-alanine lauryl ester (1.02 g, 3.4 mmol) into a 100 mL round-necked flask, add 35 mL of dry DMF and stir to dissolve, then add triethylamine (1.0 mL, 6.8 mmol), and stir for 1 h. Chloroacetyl chloride (0.3 mL, 4.1 mmol) was slowly added, stirred at room temperature for 8 h, and TLC (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate = 5: 1) detected that the raw material had reacted completely. Concentrate, dichloromethane and water solution, the organic layer is dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, a...
PUM
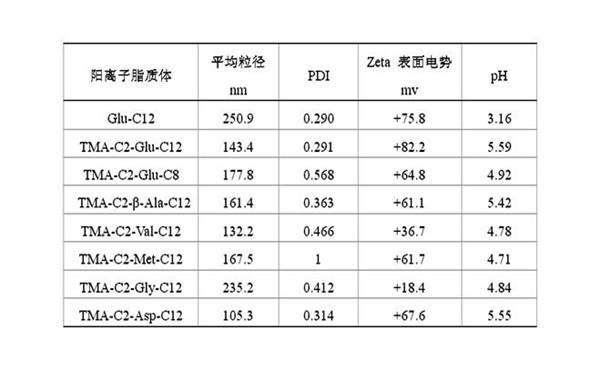
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com