Method for preparing chiral monomer mandelic acid
A technology of mandelic acid and p-hydroxymandelic acid, which is applied in the field of obtaining chiral monomer mandelic acid, can solve the problems of high price, conversion rate not exceeding 50%, unfavorable long-term effective development of methods, etc. friendly effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0068] Example 1 , Recombinant plasmid construction
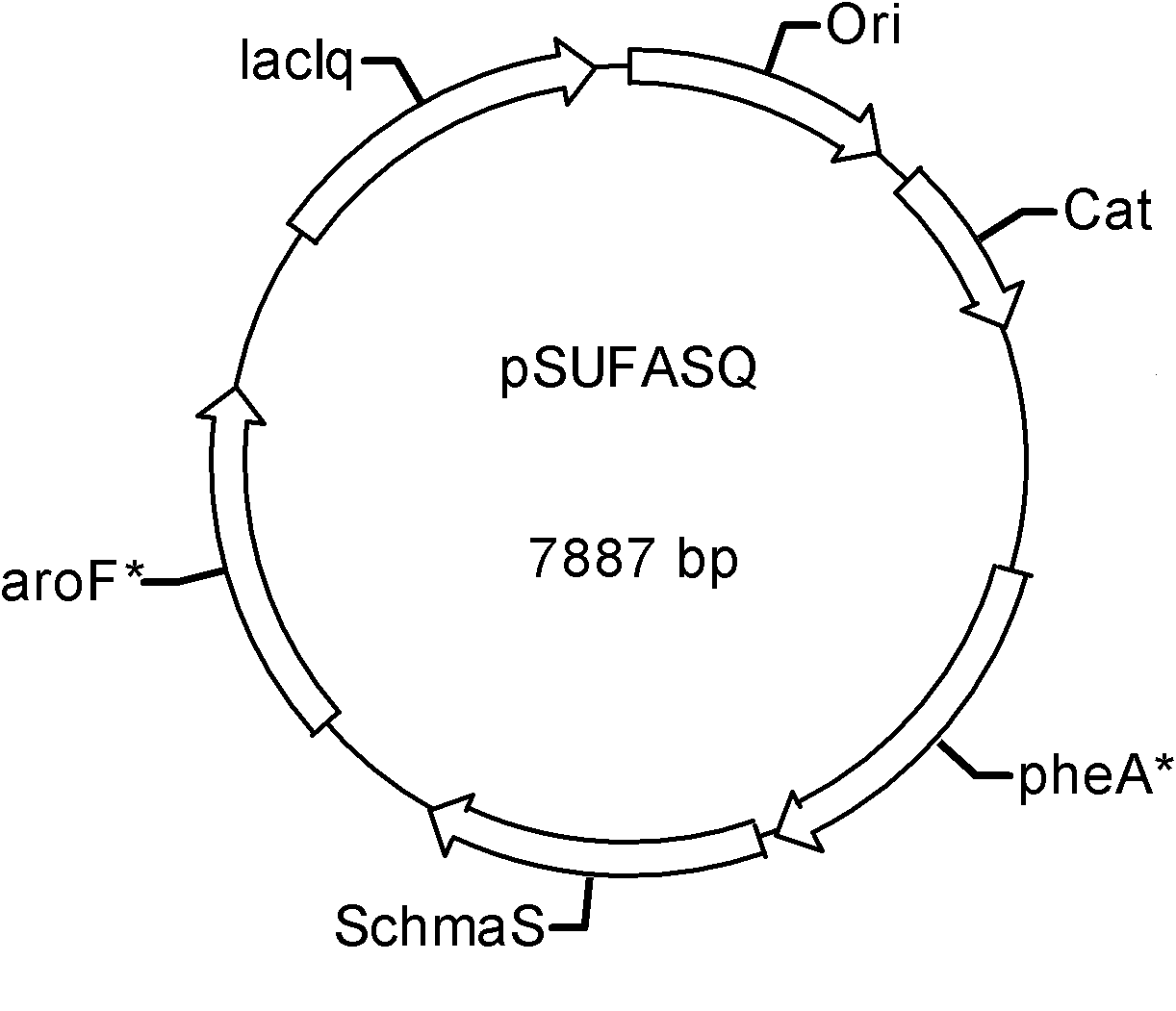
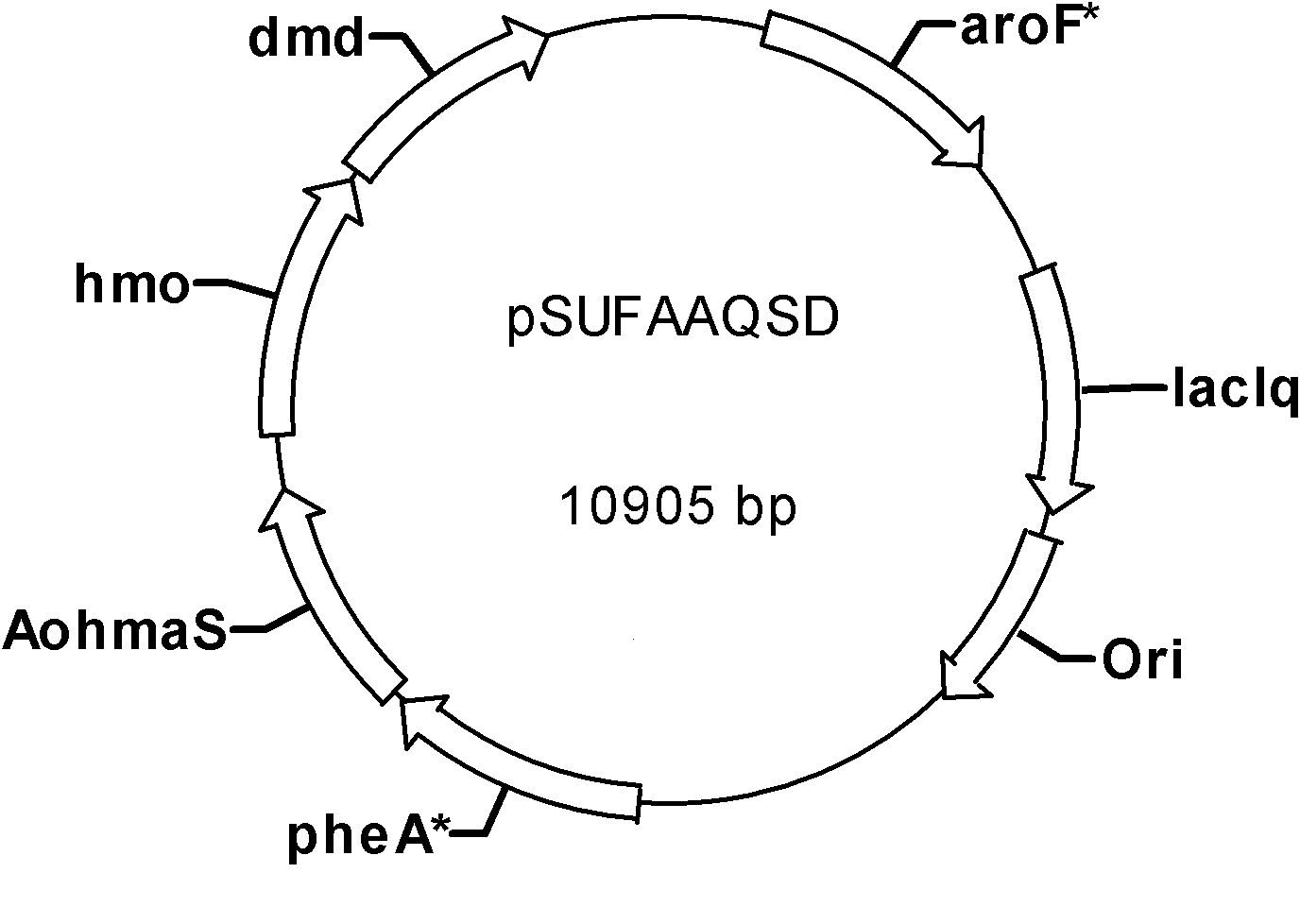
[0069] In this embodiment, the aroF fbr and pheA fbr The gene was cloned into plasmid pSU2718 (Martinez, E., B. Bartolome, and F. de la Cruz, 1988. pACYC 184-deribed cloning vectors containing the multiple cloning site and lacZa reporter gene of pUC8 / 9and pUC18 / 19plasmids. Gene68:159 -162), the recombinant plasmid pSUFA was obtained, and the AohmaS and SchmaS genes were respectively cloned into the recombinant plasmid pSUFA to obtain pSUFAAohmaS and pSUFASchmaS, and then the lacI q The genes were cloned into pSUFAAohmaS and pSUFASchmaS respectively to obtain pSUFAAQ and pSUFASQ, the specific process is as follows:
[0070] 1.1. Construction of recombinant plasmid pSUaroF
[0071] Referring to the method provided in Molecular Cloning III, the genome of E. coli DH5α (purchased from Amersham Company) was obtained by extraction.
[0072] Using the genome of E.coli DH5α as a template, primers P148L(+), P148L(-), aroFSacI(+...
Embodiment 2
[0168] Example 2 , Construction of deletion mutants
[0169] In this example, two single mutants were firstly constructed, and then the four single mutants constructed and purchased were used as starting strains, and transduced with P1 phage to obtain multiple mutants for use in mandelic acid genetically engineered bacteria Constructed host bacteria, the specific process is as follows:
[0170] 2.1 Knockout of tyrB and aspC genes in W3110
[0171] In this example, referring to the literature of Gust.B. et al. (PCR-targeting system in Streptomyces coelicolor, Gust.B., Kieser T.et al, 2002), PCR-targeting technology was used to knock out the original strain E. The aromatic amino acid transaminase gene (tyrB) and aspartate aminotransferase gene (aspC) of coli W3110 were single-deleted mutants W3110(ΔtyrB) and W3110(ΔaspC), and the specific process was as follows:
[0172] 2.1.1. Preparation of single knockout strain W3110(ΔtyrB)
[0173] Using the plasmid pIJ778 (purchased f...
Embodiment 3
[0213] Example 3 , in vitro enzyme activity reaction and chiral identification
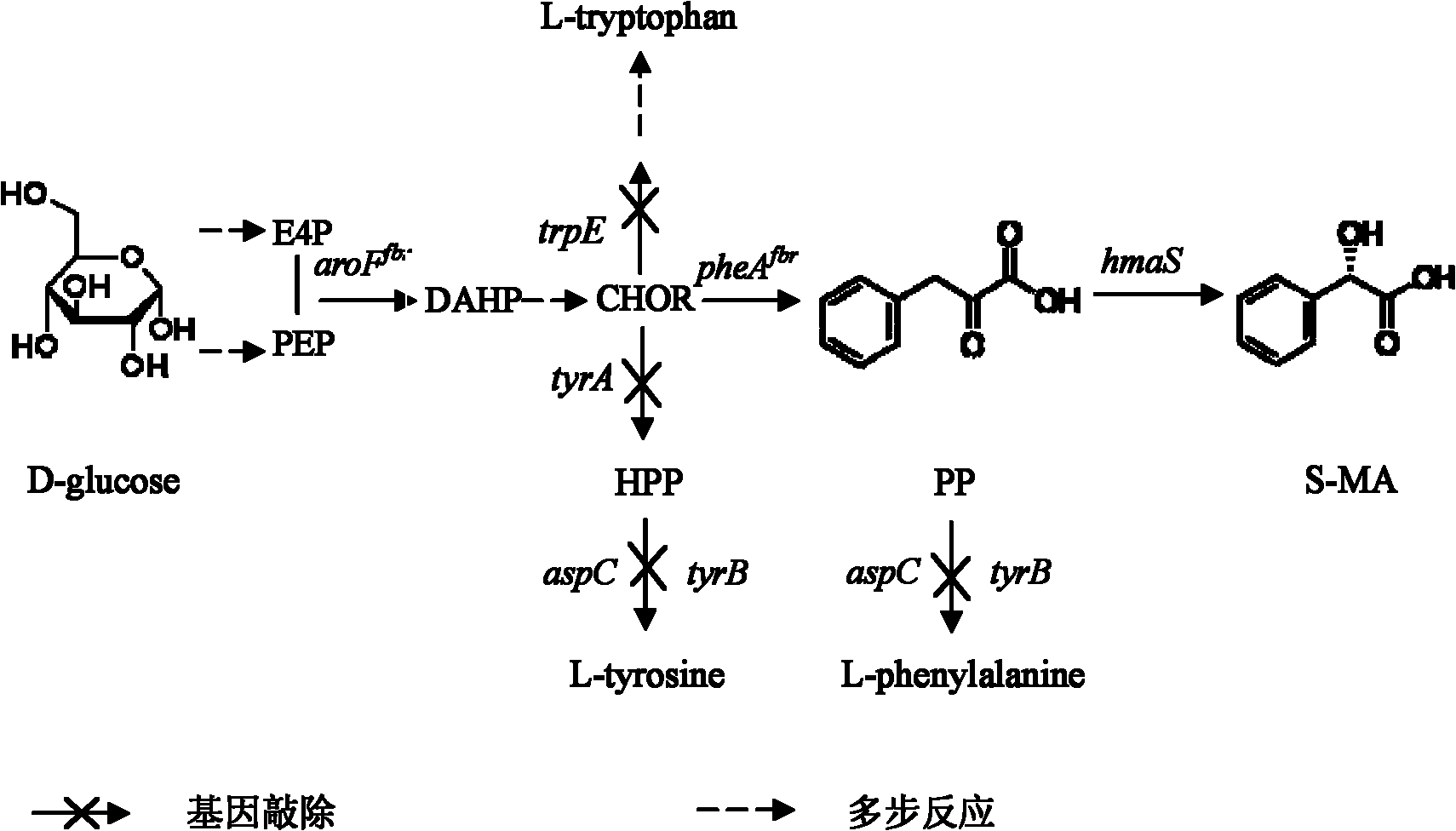
[0214] 3.1. Preparation of S-mandelic acid
[0215] The recombinant plasmids pET24a, pETAohmaS and pETSchmaS were transformed into BL21(DE3) to obtain BL21(DE3) / pET24a, BL21(DE3) / pETAohmaS and BL21(DE3) / pETSchmaS respectively, and BL21(DE3) / pET24a was used as a blank control, and the The above strains were added to LB medium, cultured to OD of 0.4-0.6, induced with 1mM IPTG for 4h, centrifuged at 4°C, 4000rpm for 10min, and the collected bacteria were resuspended in pH=7.5, 200mM potassium phosphate buffer , sonicate, and centrifuge to take the supernatant to obtain the crude p-hydroxymandelic acid synthase enzyme liquid.
[0216] Then, use the obtained crude enzyme solution of p-hydroxymandelic acid synthase to catalyze the reaction of phenylpyruvate at 28°C, the reaction system: 3ml of the assay mixture contains 200mM potassium phosphate buffer at pH7.5, 5mM phenylpyruvate, 44mM Ascorbic aci...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com