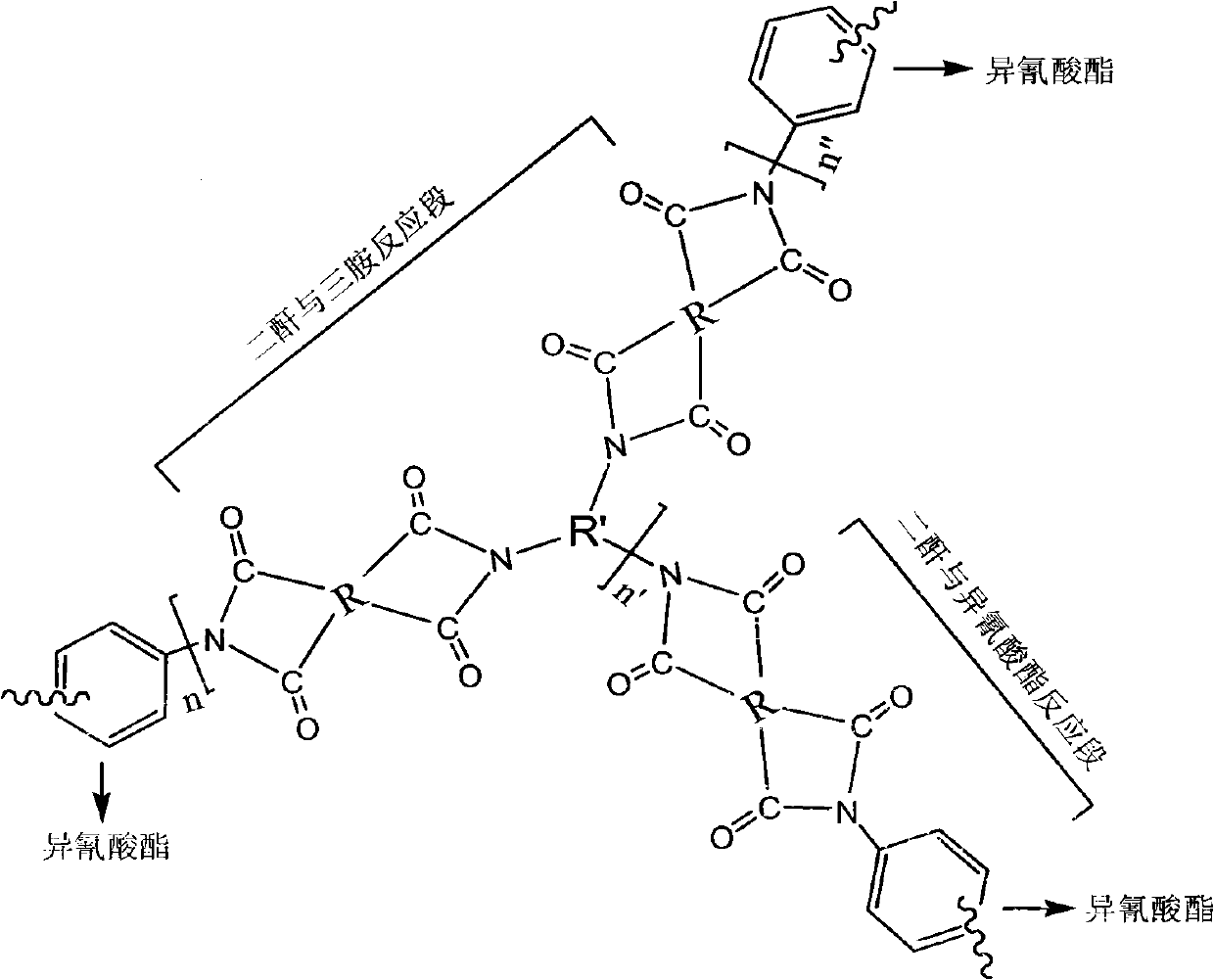
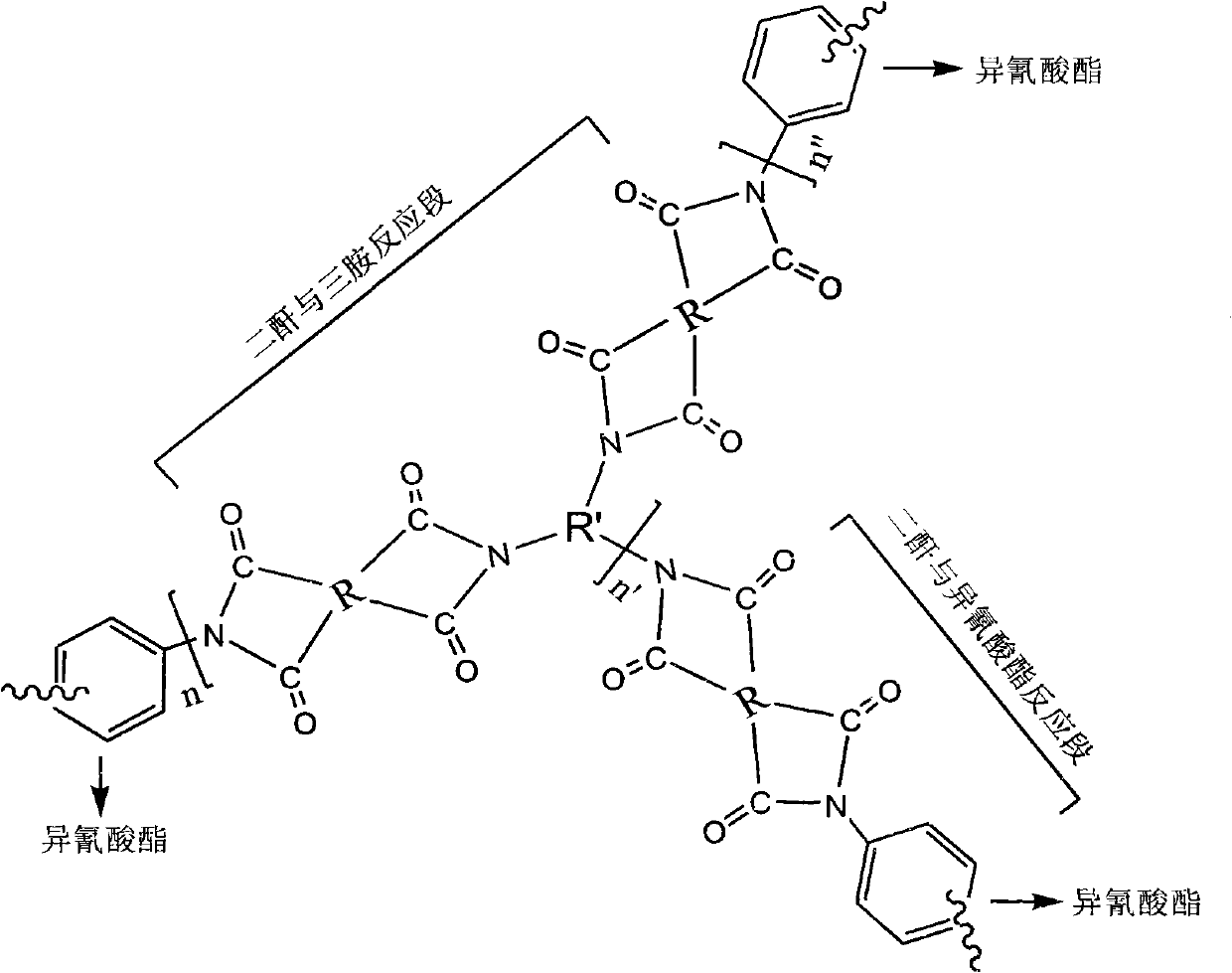
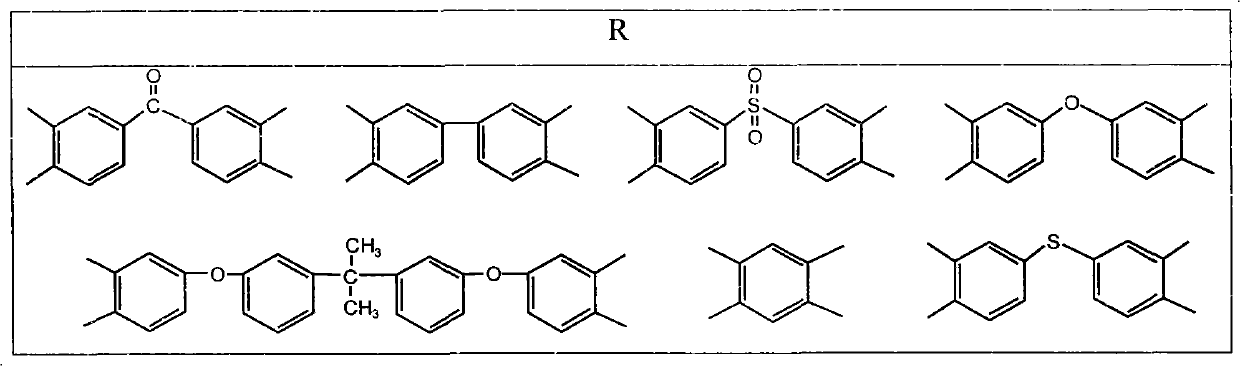
Light flexible polymide foam material and preparation method thereof
A technology of polyimide and foam materials, which is applied in the field of lightweight and flexible polyimide foam materials and its preparation, can solve the problems of inability to meet the requirements of dimensional stability, increase of cell pressure difference, high cost, etc. problems, to achieve the effects of high utilization rate of raw materials, high porosity, good sound absorption and noise reduction performance and flame retardant performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] With 210 grams of dimethylformamide, 3.60 grams of tris (4-aminophenyl) amines were dissolved in a condensing tube equipped with N 2 In the dry four-necked bottle, magnetically stirred, gradually heated to 45 ° C and kept at a constant temperature, then slowly added 4.96 grams of 3,3',4,4'-benzophenone tetracarboxylic dianhydride into the four-necked bottle within 1 hour After 8 hours, the temperature was lowered to 25°C to obtain solution I. Move solution I to a beaker, add 0.13 grams of triethanolamine, 0.11 grams of dibutyltin dilaurate, 0.24 grams of deionized water, 1.33 grams of DC-193, 3.3 grams of polyethylene glycol (PEG-600), 1.93 grams of anhydrous Methanol, and another 43.17 grams of 3,3',4,4'-benzophenone tetracarboxylic dianhydride, fully stirred evenly, gradually heated to 145 ° C, and cooled to room temperature after 4 hours of reaction to obtain a viscous precursor Body Solution II.
[0059] Measure 25 grams of the above-mentioned precursor solution I...
Embodiment 2
[0066] With 2330 grams of dimethylformamide, 29.91 grams of tris (4-aminophenyl) amines are dissolved in a condensing tube, connected with N 2 In the dry four-necked bottle, magnetically stirred, gradually heated to 45°C and kept at a constant temperature, then slowly added 35.60 grams of 3,3',4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride into the four-necked bottle within 3.5 hours, After 12 hours, the temperature was lowered to 25° C. to obtain solution I. Move solution I to a beaker, add 0.53 grams of triethanolamine, 0.71 grams of dibutyltin dilaurate, 2.87 grams of deionized water, 9.38 grams of AK-8805, 10.65 grams of polyethylene glycol (PEG-600), 8.12 grams of anhydrous Methanol, and another 353.06 grams of 3,3',4,4'-biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride, fully stirred, gradually heated to 125°C, and cooled to room temperature after 5 hours of reaction, a viscous precursor solution can be obtained II.
[0067] Measure 150 grams of the above-mentioned precursor solution II, ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Dissolve 10.11 grams of 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenoxy)benzene with 375 grams of dimethylacetamide in a condensing tube equipped with N 2 In the dry four-necked bottle, magnetically stirred, gradually heated to 40 ° C and kept at a constant temperature, then slowly added 5.52 grams of 1,2,4,5-pyromellitic dianhydride into the four-necked bottle within 2 hours, 10 hours After cooling down to 25°C, solution I was obtained. Move solution I to a beaker, add 0.21 grams of triethanolamine, 0.34 grams of dibutyltin dilaurate, 1.48 grams of deionized water, 9.76 grams of AK-8805, 6.77 grams of polyethylene glycol (PEG-600), 3.24 grams of anhydrous Methanol and another 76.34 g of 1,2,4,5-pyromellitic dianhydride were stirred well, gradually heated to 90° C., and cooled to room temperature after 3.5 hours of reaction to obtain a viscous precursor solution II.
[0075] Measure 20 grams of the above precursor solution II, stir rapidly with 9 grams of polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocya...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com