Micropropagation method of fraxinus rhynchophylla
A micropropagation technology of Astragalus chinensis, applied in the field of micropropagation, can solve the problems of long reproduction cycle, low reproduction efficiency, and poor genetic stability of offspring, etc., and achieve the effects of short reproduction cycle, high reproduction efficiency and fast reproduction speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
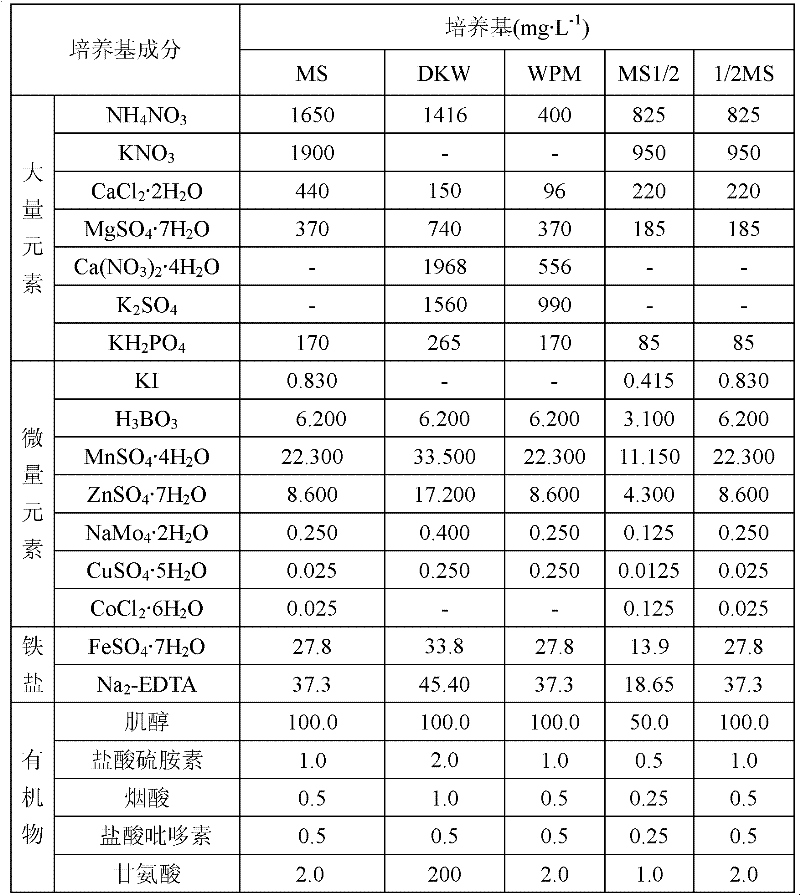
[0016] Specific embodiment one: the micropropagation method of the present embodiment is realized by the following steps: 1. Get the seeds of Astragalus and carry out disinfection treatment, strip off the zygotic embryo, cut the single cotyledon of the zygotic embryo and inoculate it into a seedling containing 0.25~0.75 mg / L cytokinin, 0.5-2.0 mg / L auxin, 100-700 mg / L acid hydrolyzed casein, 30-100 g / L sucrose and 5-7 g / L agar induction medium, at a temperature of 20 Cultivate for 2-4 weeks at ~30°C, humidity 40%-70%, and no light to obtain cotyledon-shaped somatic embryos;
[0017] 2. Inoculate the cotyledon-shaped somatic embryos on the mature medium containing 30-100g / L sucrose and 5-7g / L agar, at a temperature of 20-30°C, a humidity of 40%-70%, and a light intensity of 20-30%. 60μmol·m -2 ·s -1 , Cultivate under the condition of 16-20 hours of light every day for 3-5 weeks;
[0018] 3. Inoculate the mature cultured cotyledon-shaped somatic embryos on the germination med...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Specific embodiment two: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the process of disinfection treatment in step one is: peel off the pericarp coated on the outside of the seeds, rinse the seeds with running water for 20-40min, and use a volume concentration of 70%-80%. Soak the seeds in alcohol for 30-120s, then soak the seeds in NaClO with a volume concentration of 2%-6% for 10-20min to sterilize the body surface, and rinse the soaked seeds with sterile water for 3-7 times. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0035] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in step 1, the temperature is 25° C., the humidity is 50%, and the condition of no light is cultivated for 2 weeks to obtain cotyledon-shaped somatic embryos. Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com