Hydro-thermal synthesis method for copper-zinc-tin-sulfur photoelectric material
A photoelectric material, copper-zinc-tin-sulfur technology, applied in tin compounds, chemical instruments and methods, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of easy carbonization, limit the conversion efficiency of solar cells, etc., and achieve low cost, good repeatability, and simple operation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
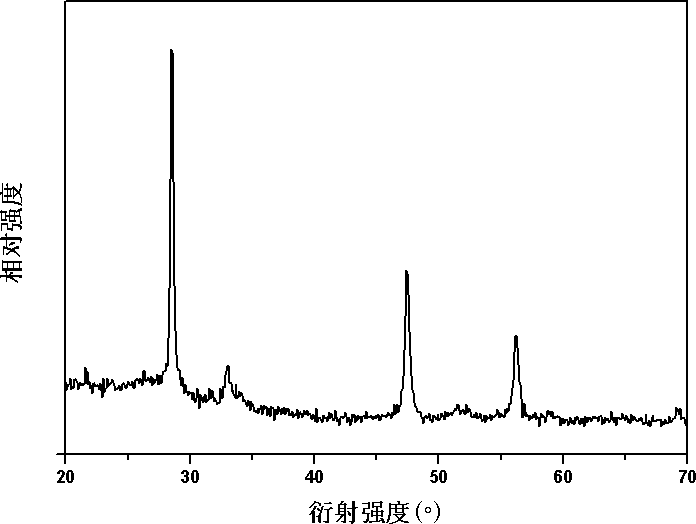
[0039] Embodiment 1: a kind of hydrothermal synthesis method of copper-zinc-tin-sulfur photoelectric material, concrete steps are as follows:
[0040] 1) Weigh 0.5 mmol of zinc chloride, 0.5 mmol of stannous chloride, 1 mmol of copper chloride, 4 mmol of thiourea, and 20 ml of water, and stir them with magnetic force to make them evenly mixed to obtain a precursor solution.
[0041] 2) Transfer the precursor solution obtained in step 1) to a stainless steel reactor lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, and react at a constant temperature of 200° C. for 10 hours. After the reaction was completed, it was naturally cooled to room temperature. The obtained product was washed 4 times with absolute ethanol at room temperature and then centrifuged. After the separated product is dried, the powder body of the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur photoelectric material is obtained.
Embodiment 2
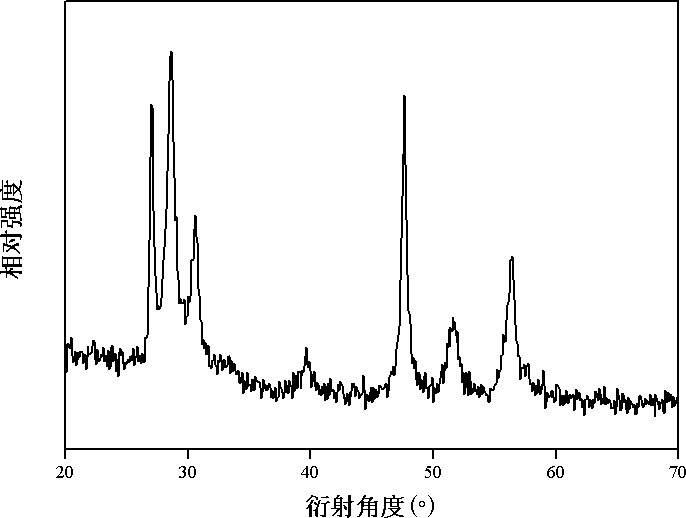
[0042] Embodiment 2: a kind of hydrothermal synthesis method of copper-zinc-tin-sulfur photoelectric material, concrete steps are as follows:
[0043] 1) Weigh respectively 0.5 mmol of zinc chloride, 0.5 mmol of tin protochloride, 1 mmol of cupric chloride, 4 mmol of thiourea, 20 ml of mixed solvent of water and ethylenediamine with a volume ratio of 1:1 , and magnetic stirring to make it evenly mixed to obtain a precursor solution.
[0044] 2) Transfer the precursor solution obtained in step 1) to a stainless steel reactor lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, and react at a constant temperature of 180° C. for 24 hours. After the reaction was completed, it was naturally cooled to room temperature. The obtained product was washed 4 times with absolute ethanol at room temperature and then centrifuged. After the separated product is dried, the powder body of the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur photoelectric material is obtained.
Embodiment 3
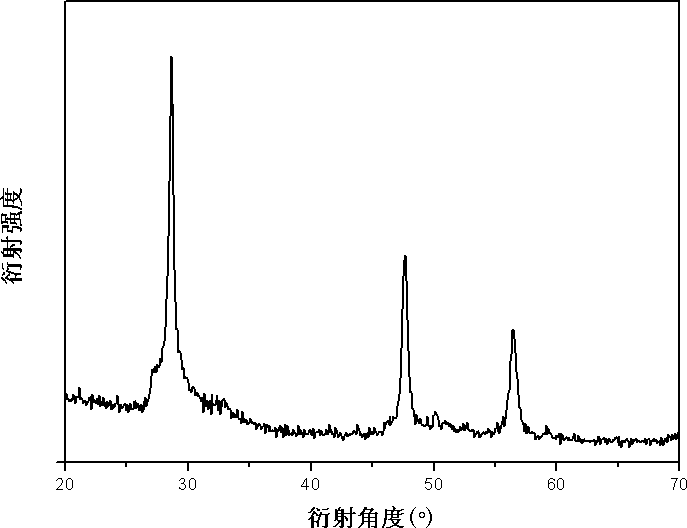
[0045] Embodiment 3: a kind of hydrothermal synthesis method of copper-zinc-tin-sulfur photoelectric material, concrete steps are as follows:
[0046] 1) take by weighing 1 mmol zinc chloride, 0.33 mmol stannous chloride, 0.67 mmol cupric chloride, 4 mmol thiourea, 0.26 gram cetyltrimethylammonium bromide, 20 milliliters of water respectively, Stir magnetically to make it evenly mixed to obtain a precursor solution.
[0047] 2) The precursor solution obtained in step 1) was transferred to a stainless steel reactor lined with polytetrafluoroethylene, and reacted at a constant temperature of 220° C. for 16 hours. After the reaction was completed, it was naturally cooled to room temperature. The obtained product was washed 6 times with absolute ethanol at room temperature and then centrifuged. After the separated product is dried, the powder body of the copper-zinc-tin-sulfur photoelectric material is obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com