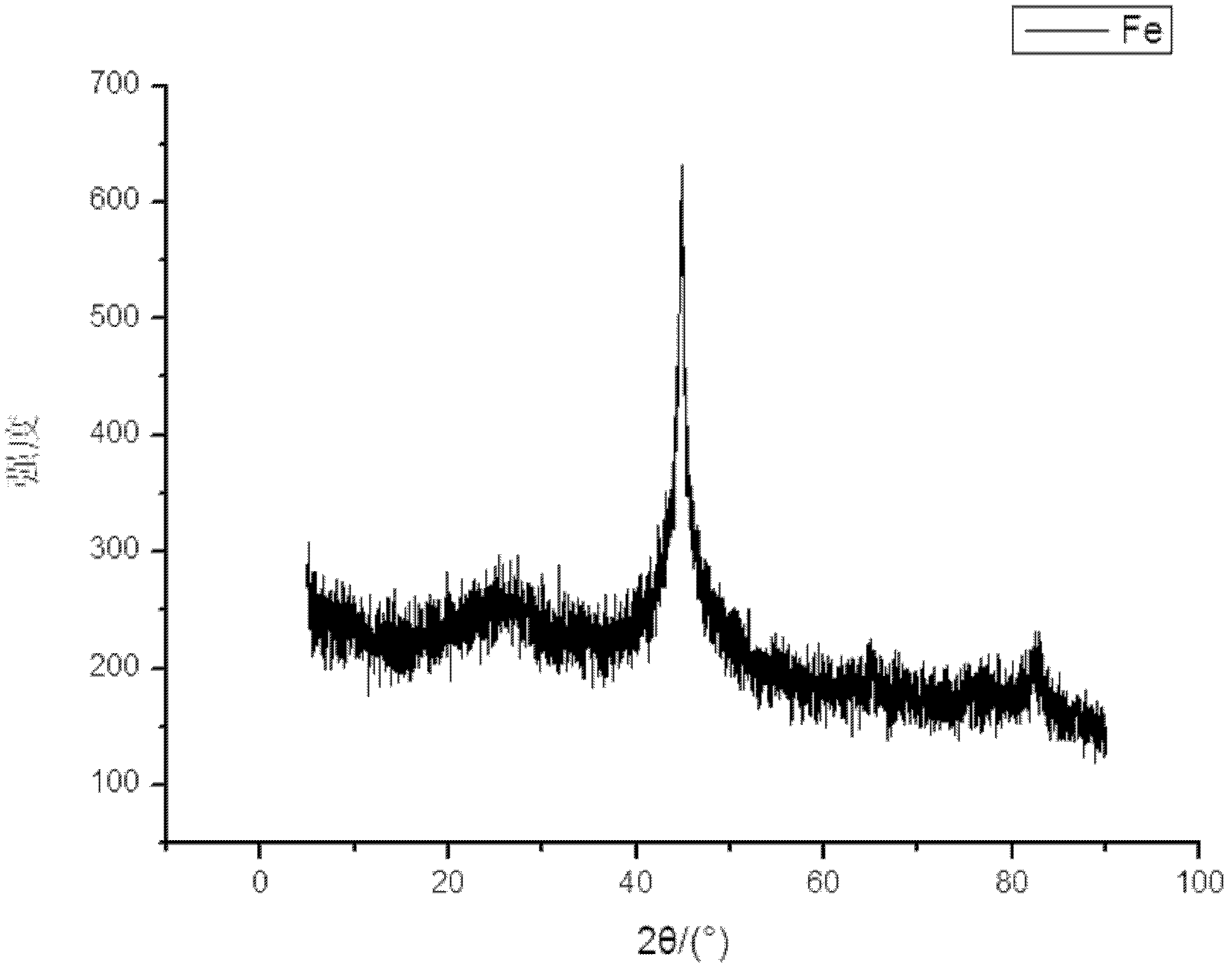
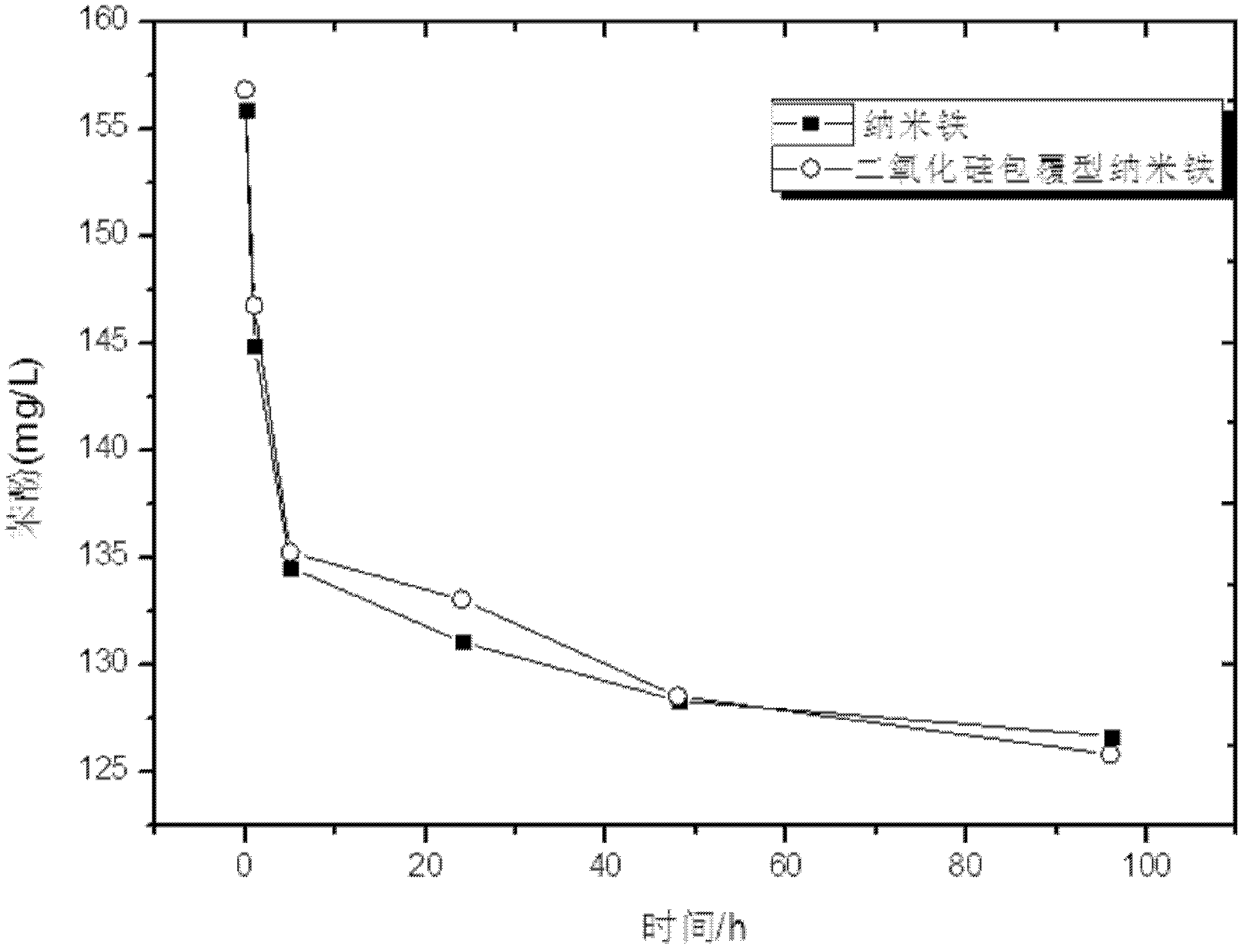
A kind of nano zero-valent iron stable in air and preparation method thereof
A nano-zero-valent iron and stable technology, applied in the direction of nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for materials and surface science, can solve problems such as complicated steps, expensive precious metal materials, and reduced efficiency of nano-iron use, and achieve technological The conditions are easy to control, the effect of improving the surface hydrophobicity and improving the antioxidant capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Weigh 3.0g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate into a three-necked flask, and add 180mL of isopropanol aqueous solution (the volume ratio of isopropanol to water is 2:1), then pass in nitrogen gas, stir mechanically for 15min, and drop while stirring Add 40 mL of sodium borohydride solution with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L, add 1 mL of polyethylene glycol (PEG-400) after the dropwise addition, continue to stir and react for 30 min, and add 1 mL of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS ), continuously stirred for 1 hour, and continued to pass nitrogen in the whole reaction process. After the reaction was completed, vacuum filtration after standing for 5 minutes, and then washed 3 times with absolute ethanol and deionized water respectively, and the obtained nano-iron was transferred to a vacuum Dry at 80°C for 12 hours in a drying oven to obtain stable nano-sized zero-valent iron.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Weigh 3.0g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate into a three-necked flask, and add 180mL of isopropanol aqueous solution (the volume ratio of isopropanol to water is 1:2), then pass in nitrogen gas, stir mechanically for 15min, and drop while stirring Add 40 mL of sodium borohydride solution with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L, add 3 mL of polyethylene glycol (PEG-400) after the dropwise addition, continue to stir and react for 30 min, and add 3 mL of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS ) and 8mL of 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, stirred continuously for 1 hour, and continued to pass nitrogen gas during the whole reaction process. Three times, the obtained nano-iron was transferred to a vacuum drying oven at 80° C. for 12 h to obtain stable nano-sized zero-valent iron.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Weigh 3.0g of ferrous sulfate heptahydrate into a three-necked flask, and add 180mL of isopropanol aqueous solution (the volume ratio of isopropanol to water is 1:2), then pass in nitrogen gas, stir mechanically for 15min, and drop while stirring Add 40 mL of sodium borohydride solution with a concentration of 0.5 mol / L, add 4 mL of polyethylene glycol (PEG-400) after the dropwise addition, continue stirring for 30 min, and add 3 mL of tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS ) and 4mL of 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide solution, stirred continuously for 3 hours, and continued to pass nitrogen gas during the whole reaction process. Three times, the obtained nano-iron was transferred to a vacuum drying oven at 80° C. for 12 h to obtain stable nano-sized zero-valent iron.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com