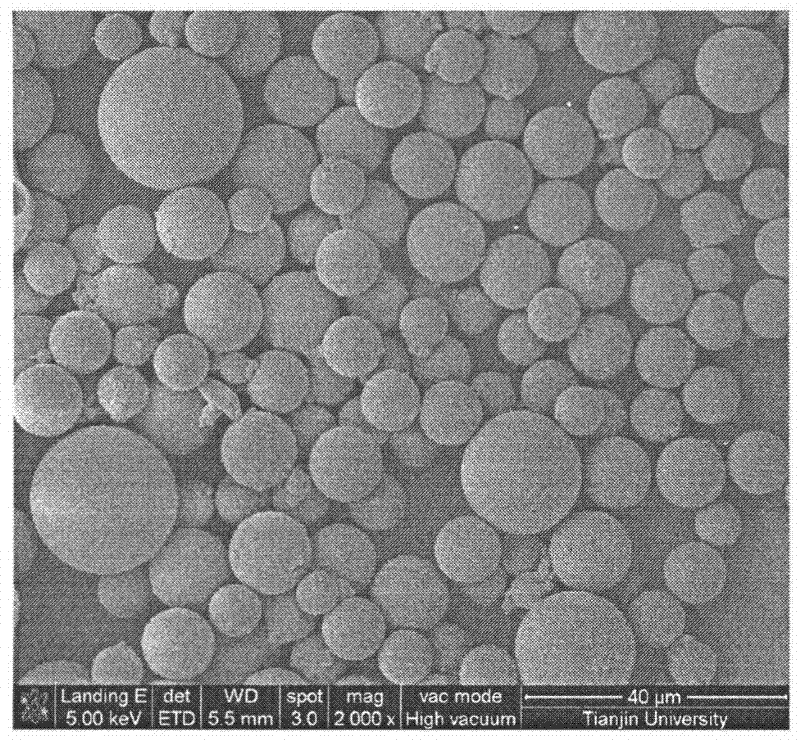
Supercooling phase change-inhibiting alkane microcapsule and preparation and application thereof
A technology of microcapsules and alkanes, which is applied in the field of phase change materials, can solve the problems of destroying the morphology of microcapsules, increasing the temperature range of phase transition, rough surface, etc., and achieve the effects of suppressing supercooling, improving thermal efficiency, and smoothing the surface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
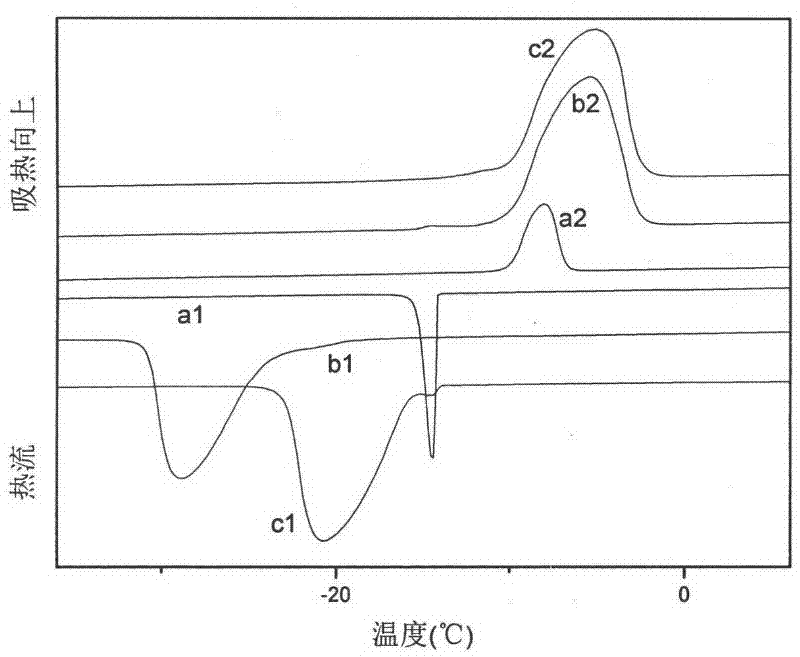
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Dissolve 5g of SMA in 95mL of deionized water, adjust the pH value to 8 with 1M NaOH solution, set the temperature at 60°C, and stir at a stirring speed of 600rpm until the solid powder is completely dissolved and the solution is clear to obtain a SMA solution. Mix 5g of melamine, 8.6mL of formaldehyde solution with a mass fraction of 37%, and 20mL of deionized water, control the temperature at 60°C, adjust the pH value to between 8 and 9 with 1M NaOH solution, and stir at a stirring speed of 600rpm until the solution After clarification, a PMF prepolymer solution was obtained. Mix 15g of n-dodecane and 0.45g of n-hexadecane evenly, add the above SMA solution, stir at 60°C at a stirring speed of 3000rpm for 10min to obtain an emulsion, then continue stirring at a stirring speed of 1200rpm, adjust with 1M citric acid The pH was 4.6 and the emulsion was cooled to 45°C. Slowly add the PMF resin prepolymer to the emulsion dropwise, and the dropwise addition is completed wi...
Embodiment 2
[0028]Dissolve 6 g of SMA in 95 mL of deionized water, adjust the pH value to 8 with 1M NaOH solution, set the temperature at 60 ° C, and stir at a stirring speed of 600 rpm until the solid powder is completely dissolved and the solution is clear to obtain a SMA solution. Mix 4g of melamine, 8mL of formaldehyde solution with a mass fraction of 37%, and 25mL of deionized water, control the temperature at 60°C, adjust the pH value to between 8 and 9 with 1M NaOH solution, and stir at a stirring speed of 600rpm until the solution is clear , to obtain the PMF prepolymer solution. Mix 10g of n-dodecane, 5g of n-tetradecane and 0.45g of n-tetradecane evenly, add the above SMA solution, stir at 55°C at a speed of 2700rpm for 15min to obtain an emulsion, then continue stirring at a speed of about 1300rpm, and use 1M citric acid was used to adjust the pH to 4.4, and the emulsion was cooled to 40°C. Slowly add the PMF resin prepolymer to the emulsion dropwise, and the dropwise addition...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Dissolve 7g of SMA in 100mL of deionized water, adjust the pH value to 8 with 1M NaOH solution, set the temperature at 60°C, and stir at a stirring speed of 400rpm until the solid powder is completely dissolved and the solution is clear to obtain an SMA solution. Mix 6g of melamine, 9mL of formaldehyde solution with a mass fraction of 40%, and 18mL of deionized water, control the temperature at 60°C, adjust the pH value to between 8 and 9 with 1M NaOH solution, and stir at a stirring speed of 500rpm until the solution is clear , to obtain the PMF prepolymer solution. Mix 5g of n-dodecane, 10g of n-tetradecane and 0.15g of n-octadecane evenly, add the above SMA solution, stir at 65°C at a speed of 2400rpm for 12min to obtain an emulsion, then continue stirring at a speed of about 800rpm, and use The pH was adjusted to 4.5 with 1M citric acid, and the emulsion was cooled to 45°C. Slowly add the PMF resin prepolymer to the emulsion dropwise, and the dropwise addition is c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com