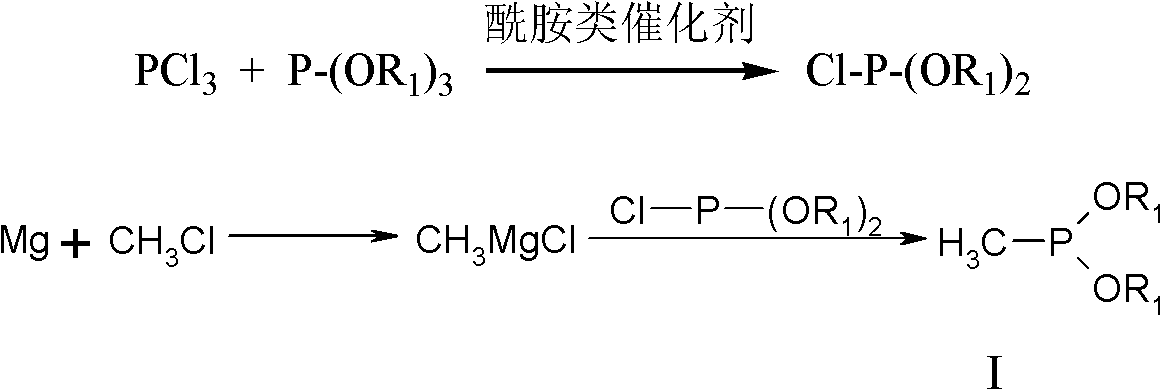
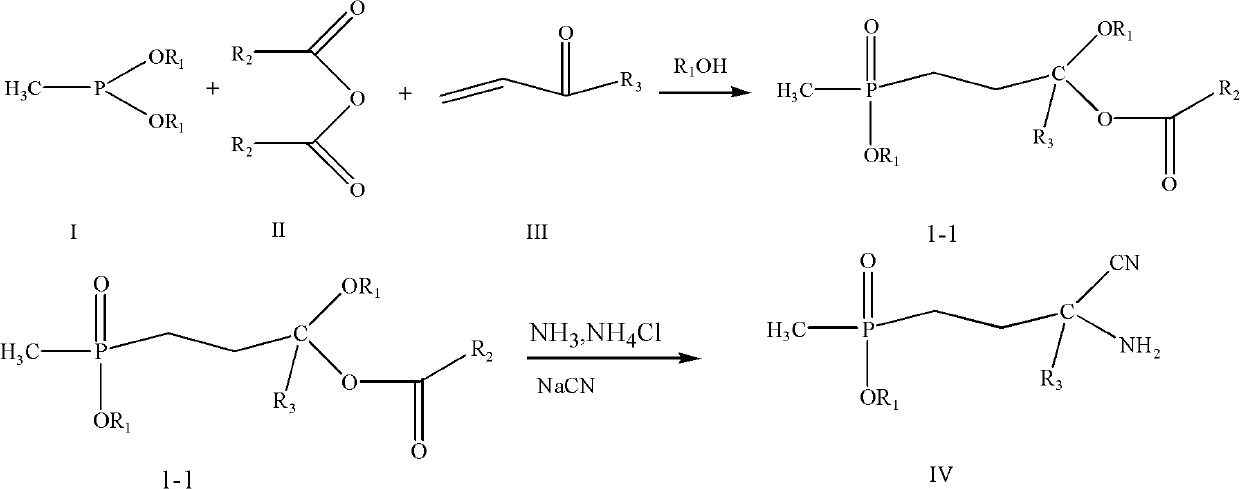
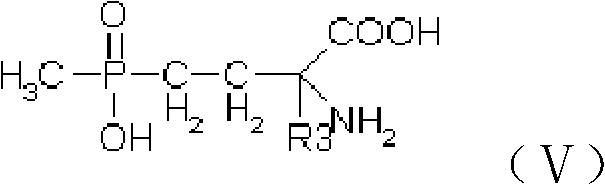Synthesis method for glufosinate and analogue thereof
An analogue, glufosinate-ammonium technology, applied in the field of compound synthesis, can solve problems such as high risk, difficult to meet production requirements, and harsh manufacturing process requirements, so as to reduce the generation of three wastes, reduce the cost of three wastes treatment, and improve The effect of synthesis yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] In a 500ml four-neck flask, add 23.5g of fresh magnesium chips (0.98mol), add THF100g, heat to 35°C and add 1g of methyl bromide dropwise for initiation. Chloromethane 49.5g (0.98mol). The process of passing through the chloromethane maintains a slight reflux state, and maintains a slight reflux state for 2 hours at the end of the passage, until there is almost no visible magnesium chips, and it is ready for use.
[0037] Add 110.7g (0.67mol) of triethyl phosphinate to another 1000ml four-neck flask, add 6g of caprolactam, add 45.8g (0.33mol) of phosphorus trichloride dropwise at 20-25°C, and keep warm for 2 hours after the dropping Diethyl chlorophosphonite is obtained.
[0038] After the above is completed, under strong stirring, add the Grignard reagent dropwise into the diethyl chlorophosphonite, the temperature of the addition is controlled at -10~-5°C, and the drop is completed within 3~4 hours. After the dropwise addition, continue to keep warm for 3 hours. Af...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Into a 500ml four-neck flask, add 23.2g of fresh magnesium chips (0.965mol), add THF100g, heat to 35°C and add 1g of methyl bromide dropwise for initiation. Chloromethane 48.7g (0.965mol). The process of passing through the chloromethane maintains a slight reflux state, and maintains a slight reflux state for 2 hours at the end of the passage, until there is almost no visible magnesium chips, and it is ready for use.
[0041] Add 110.7g (0.67mol) of triethyl phosphinate to another 1000ml four-neck flask, add 6g of hexamethylphosphonic acid triamide, add dropwise 45.8g (0.33mol) of phosphorus trichloride at 20-25°C, At the end of the dropwise addition, keep warm for 2 hours to obtain diethyl chlorophosphonite.
[0042] After the above is completed, add the Grignard reagent dropwise into the diethyl chlorophosphonite under strong stirring, and the dropping temperature is controlled at -10~-5°C, and the drop is completed in 4~6hr. After the dropwise addition, continue to...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Add 11.42g of freshly distilled acrolein (0.204mol) to 20.81g of acetic anhydride (0.204mol) at 20-30°C, and mix well. Then it was added dropwise to a mixture of 27.2g diethyl methylphosphonite (0.2mol) and 9.2g ethanol (0.2mol) under vigorous stirring, the dropping time was controlled for about 2hr, and the dropping temperature was controlled at 15-20°C. After the dropwise addition, continue the heat preservation reaction at this temperature for 2 hours, and then remove the light components under negative pressure to 100°C / -0.095Mpa. Add the residual material dropwise to 9.8g of sodium cyanide (0.2mol) and 21.4g of ammonium chloride (0.4mol) in 100ml of 25% ammonia solution. After the addition was completed, the insulation reaction was continued for 4 hr. The material was added to 400ml of 30% hydrochloric acid without separation, heated to reflux for 3 hours, and dehydrated to 60°C / -0.095Mpa under negative pressure. Add 120g of methanol and 15g of deionized water to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com