Bacillus subtilis
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and strains, applied in the direction of bacteria, enzymes, animal feed, etc., can solve the problems of limited development, difficult direct absorption by animals, etc., and achieve the effects of good stability, mild degradation and fermentation conditions, and high enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Take the soil where feathers have been piled up for a long time in Hunan Agricultural University, put it into sterile distilled water, mix it, let it stand, and after clarification, take the supernatant and apply it to solid inorganic salt feather medium, culture at 37°C for 2-3 days, and obtain colonies . Pick and isolate the colony obtained by coating with a toothpick, inoculate it in the inorganic salt feather culture solution, culture it at 37°C for 48 hours, observe the degradation degree of the feather, screen out the effective strains, dip it in the culture solution for multiple streak cultures, and then Pick a single colony and culture it in inorganic salt feather culture solution for repeated screening to obtain a pure strain with better degradation effect. Finally, inoculate a single colony in gelatin medium and culture at 37°C for 12 hours to obtain the strain of the present invention.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2: the thalline staining of bacterial strain of the present invention, electron microscope observation, colony morphological feature observation experiment
[0030] The bacterial strain of the present invention is cultured and grown by streaking in LB liquid medium at 37° C., and the colony is round, with a moist surface, rough and opaque, with irregular, white or yellowish edges. Pick single bacterium colony wherein, carry out Gram staining, after Gram staining, be purple, short rod-shaped explanation bacterial strain of the present invention is Gram-positive bacteria, as figure 1 . Observed in the electron microscope, the bacterium is rod-shaped, the size of a single cell is 0.6-0.7×2-3 microns, and the coloring is uniform. uncapsulated, such as figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
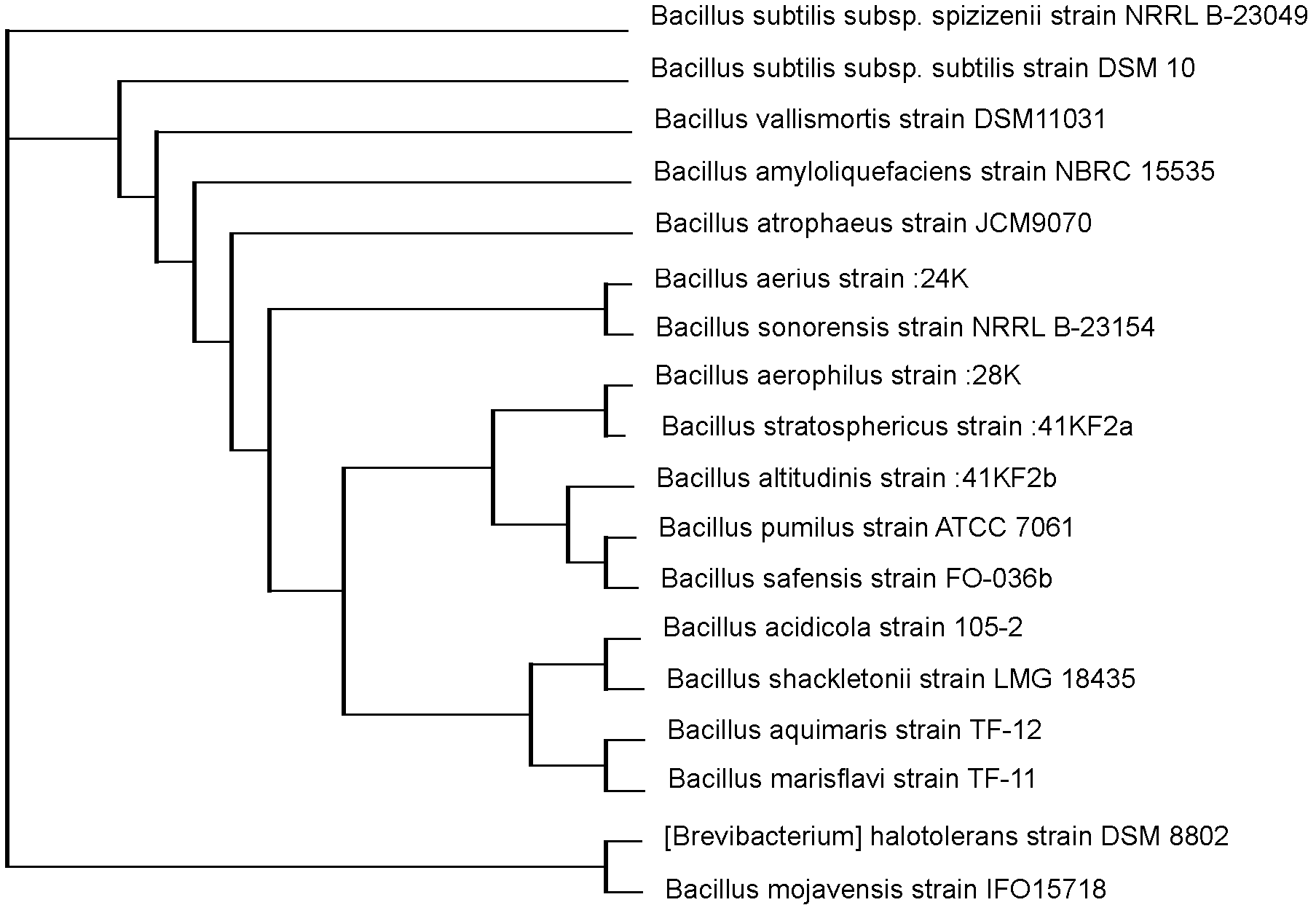
[0031] Embodiment 3: 16SrDNA identification and the construction of phylogenetic tree of bacterial strain of the present invention
[0032] In the present invention, the EDTA method is used to extract the genomic DNA of the strain of the present invention, and the 16S rDNA primer F: agtggccattacggccagagtttgatcmtggctcag (as shown in SEQ ID No: 1); R: agaggccgaggcggcctacgggytaccttgttacgactt (as shown in SEQ ID No: 2) is used to obtain the high-fidelity sequence of the dominant strain , the PCR system is: ddH 2 O: 40.0ul, 10×Buffer (Mg 2+ plus): 5ul, d NTPs: 1ul, F: 1.0ul, R: 1.0ul, Taq enzyme: 1ul, DNA template: 1ul, total volume50ul, pre-denaturation at 95°C for 4min, denaturation at 95°C for 30s, annealing at 55°C for 45s, 72 30 cycles of extension at ℃ for 1.5 min, final extension at 72 °C for 15 min, and 4 °C to ∞. After the PCR was completed, a brighter band at about 1500p was detected by electrophoresis, and the QlAquick Gel Extraction Kit was used for gel extraction an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com