Extracellular vesicles derived from gram-positive bacteria and uses thereof
A cell and application technology, applied in the field of extracellular vesicles, which can solve the problems of not disclosing relevant information and having no outer membrane
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
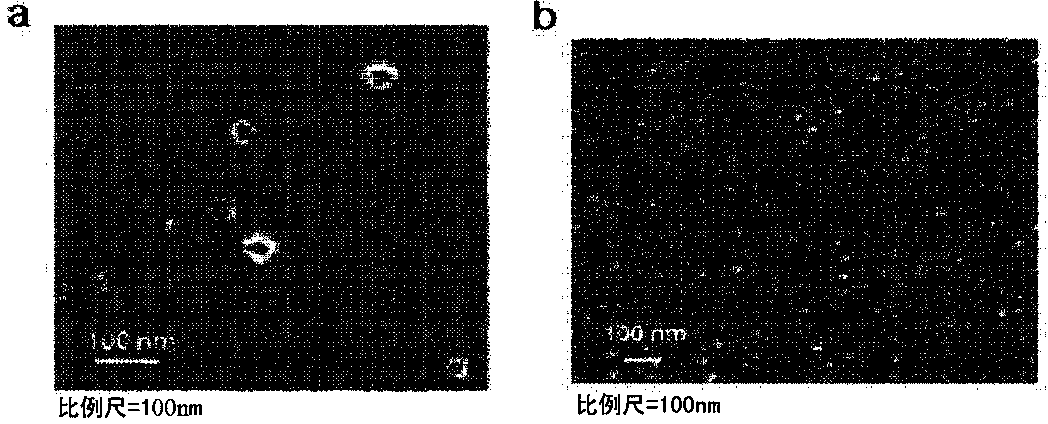
[0152] Example 1. Observation of Staphylococcus aureus cells by electron microscopy
[0153] Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC14458) was cultured in nutrient broth until the absorbance (600 nm) value reached 1.0, and the culture broth was centrifuged at 10,000 x g for 20 minutes. The precipitated Staphylococcus aureus cells were fixed (fix) with 2.5% glutaraldehyde (glutaraldehyde) for 2 hours, and then post-fixed (post-fix) with 1% osmium tetroxide (osmium tetroxide) for 1 hour, and then, with ethanol (ethanol) was dehydrated in stages to make epoxy resin modules, and ultrathin sections were made with a thickness of 70 nm. Cell slices were placed on a glow-discharged carbon-coated copper grid for 3 minutes and then stained with 2% uranyl acetate and lead calcium citrate ( staining), and observed by JEM101 (Jeol, Japan) transmission electron microscope (transmission electron microscope, TEM). Such as figure 1 As shown in the transmission electron microscope image of the Staphyloc...
Embodiment 2
[0156] Example 2. Preparation of extracellular vesicles derived from Staphylococcus aureus
[0157] [Common Extracellular Vesicle Isolation Method]
[0158] Staphylococcus aureus was inoculated in a test tube containing 3 ml of nutrient solution at 37 o C for 6 hours, transfer 5 ml of it into a 2 L Erlenmeyer flask filled with 500 ml of nutrient solution, at 37 o Incubate for 4 hours under C condition to make the absorbance (600 nm) value reach 1.0. Put the culture solution into a 500 ml capacity high speed centrifuge tube (high speed centrifuge tube), in 4 o Under C conditions, centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 20 minutes. The supernatant from which bacteria were removed was filtered once through a membrane filter (membrane filter) with a pore size of 0.45 μm, and then concentrated 25 times using an ultrafiltration system (Quixstand system) equipped with a membrane capable of removing proteins with a molecular weight of less than 100 kDa , the concentrated solution was filtere...
Embodiment 3
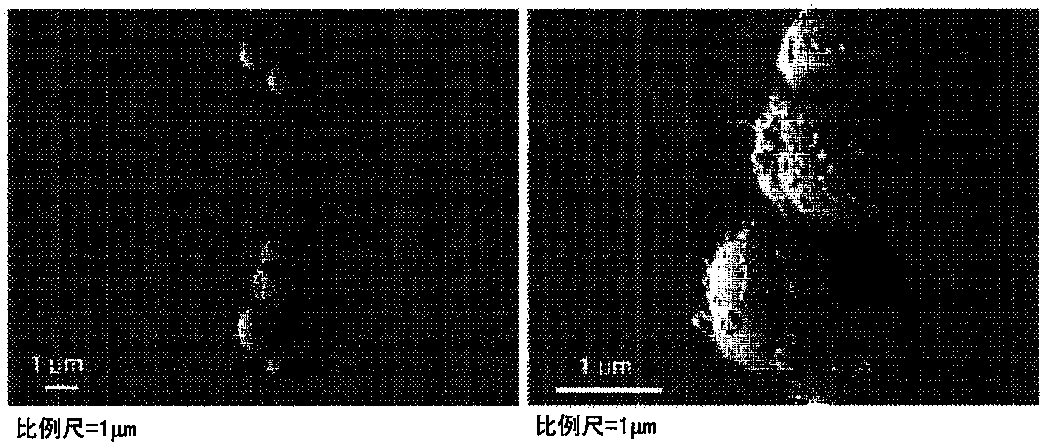
[0161] Example 3. Characterization of extracellular vesicles derived from Staphylococcus aureus
[0162] The extracellular vesicles isolated from Staphylococcus aureus according to the method described in Example 2 were placed on a glow discharge carbon-coated copper grid for adsorption for 3 minutes, the grid was rinsed with distilled water, and stained with 2% uranyl acetate. And observed by JEM101 transmission electron microscope.
[0163] Such as image 3 The transmission electron microscope image of a shows that the extracellular vesicles derived from S. aureus form closed spheres with a size of 20-100 nm. The isolated extracellular vesicles were pasted on a cover glass, fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde for 1 hour, post-fixed with 1% osmium tetroxide for 1 hour, dehydrated in stages with ethanol, and then , using CO 2 The system performs critical point drying. The cover glass with extracellular vesicles was placed on the sample stage and coated with platinum, and then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com