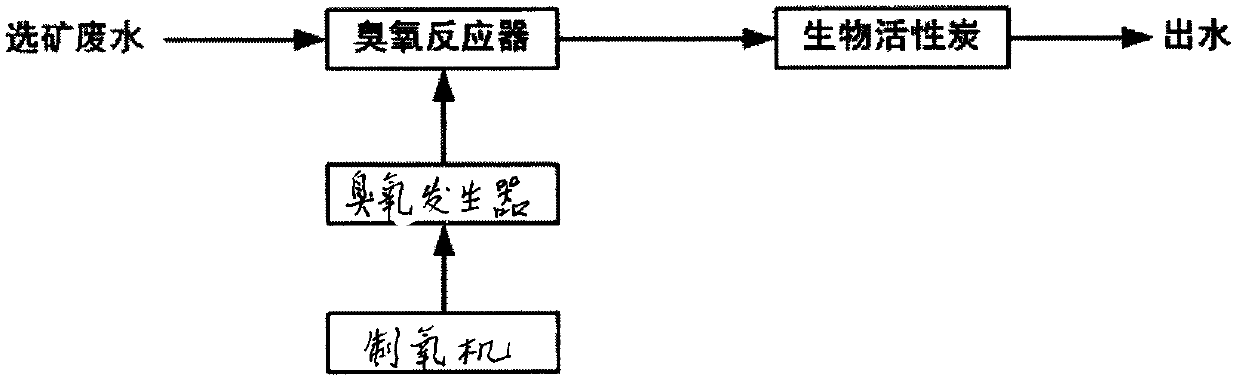
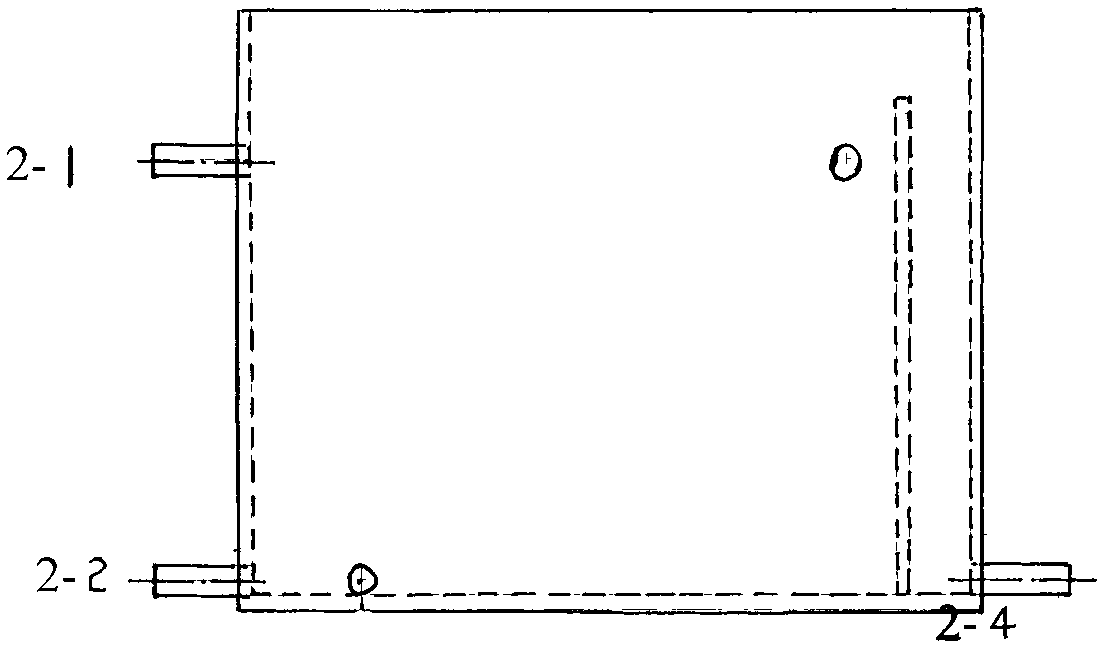
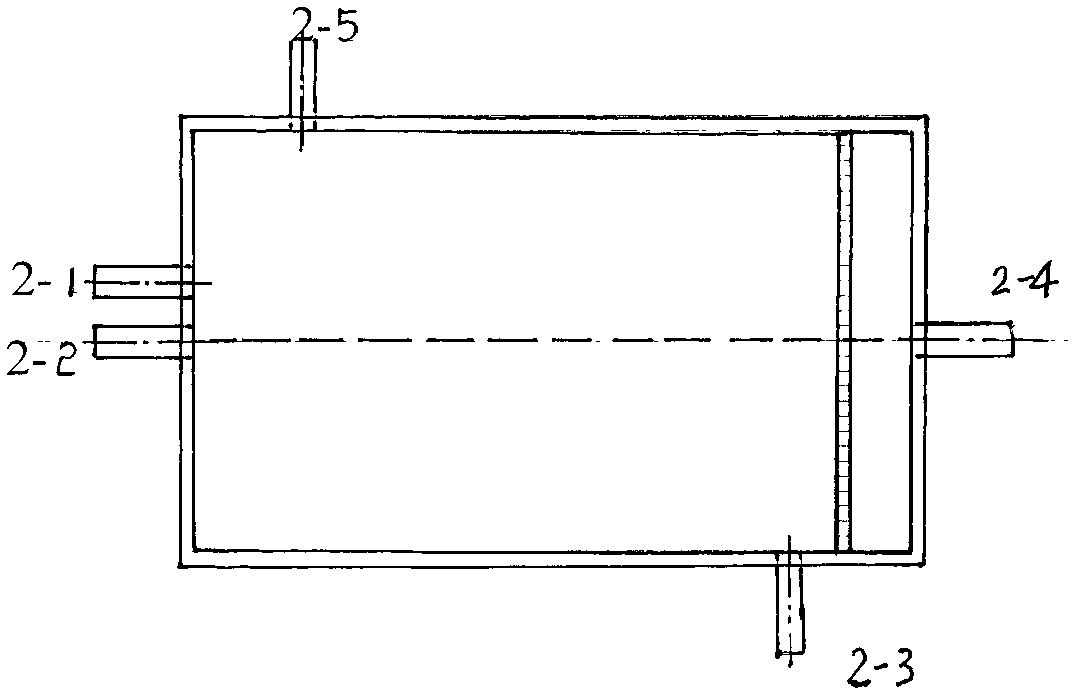
Process for treating and recycling beneficiation waste water of lead and zinc sulfide ores
A technology for beneficiation wastewater and sulfide ore, applied in the field of water treatment, can solve problems such as deterioration of beneficiation effect, inability to reuse lead for beneficiation, etc., and achieve the effects of short reaction time and high reaction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The ore of a lead-zinc mine in Hebei was used for the mineral processing test. The mineral processing process was to select lead first, then zinc, and only lead was selected for backwater verification. For the beneficiation process of wastewater output, see Figure 4 , the raw ore is first crushed to -200 mesh 70%, adding 15g / ton of kerosene and 5g / ton of No. 2 oil to decarburize first, and then adding 3000g / ton of calcium oxide, 3000g / ton of zinc sulfate, 1500g / ton of sodium sulfite, 20g / ton of sodium cyanide, 40g / ton of sulfur and nitrogen No. 9, 10g / ton of butylamine and 15g / ton of No. 2 oil to select lead coarse concentrate, and then add 40g / ton of sulfur and nitrogen No. 9 and 5g / ton of No. 2 Oil separation of lead medium ore, followed by adding 2000g / ton of calcium oxide, 20g / ton of sodium cyanide, 150g / ton of copper sulfate, 50g / ton of butyl xanthate, 15 grams of No. 2 oil separation zinc concentrate, tailings pressure The filtered return water is used as waste ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com