Method for treating waste fused salt produced in production of TiCl4
A processing method and technology of molten salt, applied in the direction of chlorine/hydrogen chloride, calcium carbonate/strontium/barium, energy input, etc., can solve the problems of large amount of waste molten salt, polluted groundwater, polluted groundwater salinized land, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
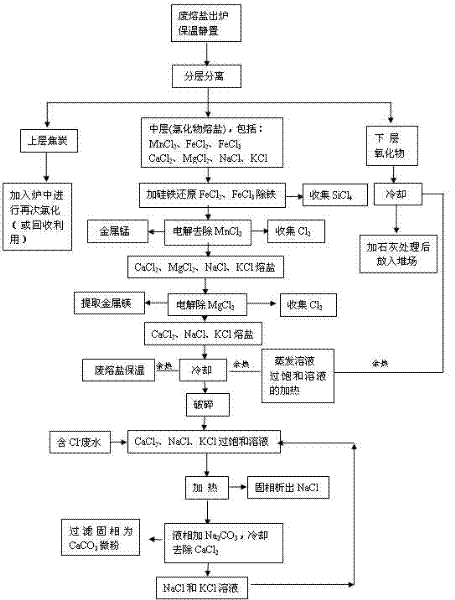
[0033] Example 1: Such as the process flow of waste molten salt treatment figure 1 As shown, the waste molten salt that comes out of the furnace is directly kept at 500-900°C for heat preservation and standing, so that the waste molten salt is divided into three layers, namely the upper layer (floating layer), the middle layer (molten salt layer) and the lower layer (precipitation layer).
[0034] After the middle layer is separated from the upper and lower layers, its composition is: MgCl 2 +KCl+CaCl 2 +NaCl accounts for 76.0-80.0%, manganese chloride accounts for 13.0-14.5% and iron chloride accounts for 5.5-11.0%, adding ferrosilicon powder accounting for 1.7-3.5% of the molten salt weight, after removing iron chloride, Dust collection of SiCl through dry closed piping system 4 , the bottom of the molten salt is metal Fe and some precipitates; after separation, the MnCl in the molten salt 2 , MgCl 2 , KCl, CaCl 2 And the content of NaCl is 97.0-99.0%.
[0035] The mol...
example 2
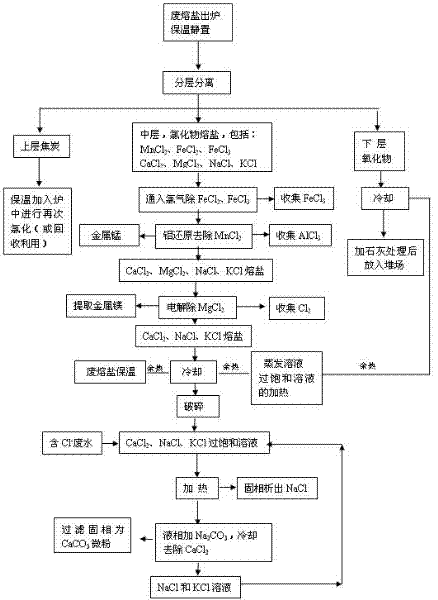
[0038]Example 2: Such as the process flow of waste molten salt treatment figure 2 As shown, after the chloride molten salt in the middle layer is separated from the upper and lower layers, Cl is introduced into the molten salt 2 , kept at 820°C for 2.5 hours to make FeCl 2 into FeCl 3 Evaporate in the liquid phase to remove iron chloride, and collect FeCl through the dust removal system 3 , the content of iron in the molten salt is less than 0.5% at this time; MnCl in the molten salt 2 , MgCl 2 , KCl, CaCl 2 And the content of NaCl is 96.5-99.0%.
[0039] Under stirring conditions, gradually add aluminum powder accounting for 2.5-3.5% of the total weight of the molten salt to the molten salt after iron removal to remove MnCl in the molten salt 2 , AlCl is collected by the dust removal system 3 , recover manganese metal at the bottom of molten salt.
[0040] Then the molten salt is at 680-720°C, the cell voltage is 4.3-4.5V, the pole spacing is 68.0-71.0mm, and the cat...
example 3
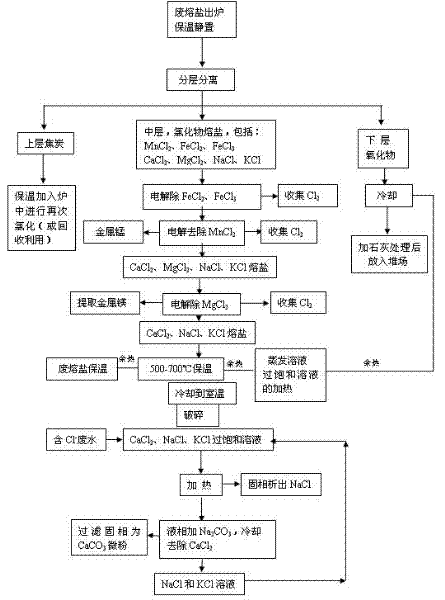
[0042] Example 3: The molten salt from which coke and oxides have been separated is at 680-720°C, the cell voltage is 2.0-2.2V, the pole spacing is 47-49mm, and the cathode current density is 0.5-0.85A / mm 2 Electrolysis under the condition of iron to remove iron chloride; and FeCl can be obtained in the dust removal system 3 , the anode collects chlorine gas, and the cathode plate obtains metallic iron with a content greater than 95.0%.
[0043] After removal of iron chloride, MnCl in molten salt 2 , MgCl 2 , KCl, CaCl 2 And the content of NaCl is 95.0-98.0%.
[0044] Then the molten salt is at 680-720°C, the cell voltage is 2.8-3.1V, the pole spacing is 47-49mm, and the cathode current density is 0.5-0.85A / mm 2 Under the conditions of electrolysis, remove MnCl 2 , The anode can collect chlorine gas, and the cathode can obtain metal manganese with a content greater than 95.0%.
[0045] After the molten salt and metal manganese are separated, the molten salt is at 680-720...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com