Polypeptide drug sustained-release microsphere preparation and preparation method thereof
A technology of slow-release microsphere preparations and drugs, which is applied in the direction of drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulas, and medical preparations of non-active ingredients. The effect of embedding rate and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
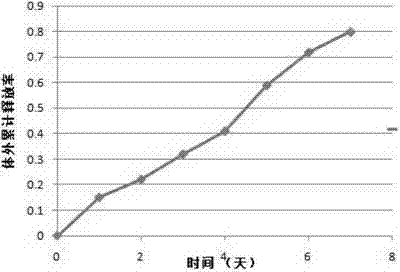
Embodiment 1
[0055] A preparation method for exenatide slow-release microspheres, comprising the following steps:
[0056] (1) 1.0 g of polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (molecular weight 15000, glycolide:lactide=75:25, carboxyl terminal) was dissolved in 5 ml of anhydrous acetic acid to form polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer solution;
[0057] (2) Weigh 50 mg of exenatide and dissolve 30 mg of sucrose in 0.5 mL of sterile water;
[0058] (3) Mix the polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer solution in step (1) with the exenatide solution in step (2), and stir with a magnetic stirrer until a completely uniform, clear, transparent mixed solution is formed as the organic phase ;
[0059] (4) prepare 50ml of liquid paraffin containing 2wt% lecithin, as the oil phase;
[0060] (5) Homogeneously emulsifying the mixed solution of step (3) and the oil phase of step (4) for 5-15 minutes to form an O / O type emulsion;
[0061] (6) Stir and volatilize the emulsion of step (5) to remove ...
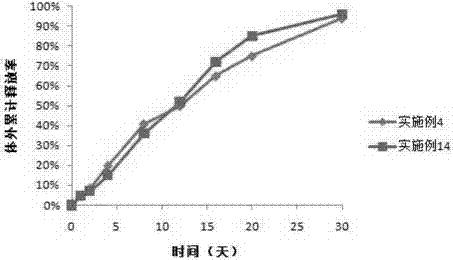
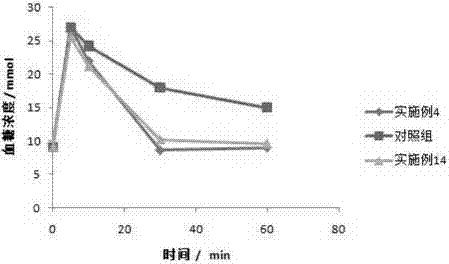
Embodiment 2
[0063] Except that PLGA is replaced by carboxyl-terminated PLGA with end-blocked PLGA, the specific steps are the same as in Example 1, and the particle size of exenatide sustained-release microspheres is in the range of 5 to 30 microns, the drug loading is 4.58%, and the encapsulation efficiency is 90.49%. %.
Embodiment 3
[0065] Except that PLGA was replaced by MPEG-PLGA with end-blocked PLGA, the specific steps were the same as in Example 1, and the obtained exenatide sustained-release microspheres had a particle size in the range of 5 to 30 microns, a drug loading of 4.22%, and an encapsulation efficiency of 88.45. %.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com