Method for preparing polyvinylidene fluoride ultra-filtration membranes
A technology of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane and polyvinylidene fluoride, which is applied in the field of preparation of polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane, can solve the problems that the ultrafiltration membrane with separation precision cannot be produced, and achieve easy extraction of diluent, high separation precision, The effect of high porosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The method for preparing polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membrane provided by the present invention is carried out according to the following steps:
[0029] 1) mixing polyvinylidene fluoride with a diluent; wherein the mass percentage of polyvinylidene fluoride is 20% to 40%, and the mass percentage of the diluent is 80% to 60%;
[0030] 2) Add the mixture in step 1) into the stirred tank, heat up to 100°C-160°C to form a homogeneous solution, and let it stand for defoaming;
[0031] 3) The homogeneous solution obtained in step 2) is directly scraped and coated on the support net to form a casting solution in the shape of a flat plate or spun into a hollow fiber shape through a spinneret, and then the casting solution is immersed in a cooling liquid to cool, so that The casting solution undergoes phase separation and finally solidifies to form a film;
[0032] 4) Remove the diluent in the membrane obtained in step 3) with an extractant to obtain a polyvinylide...
Embodiment 1
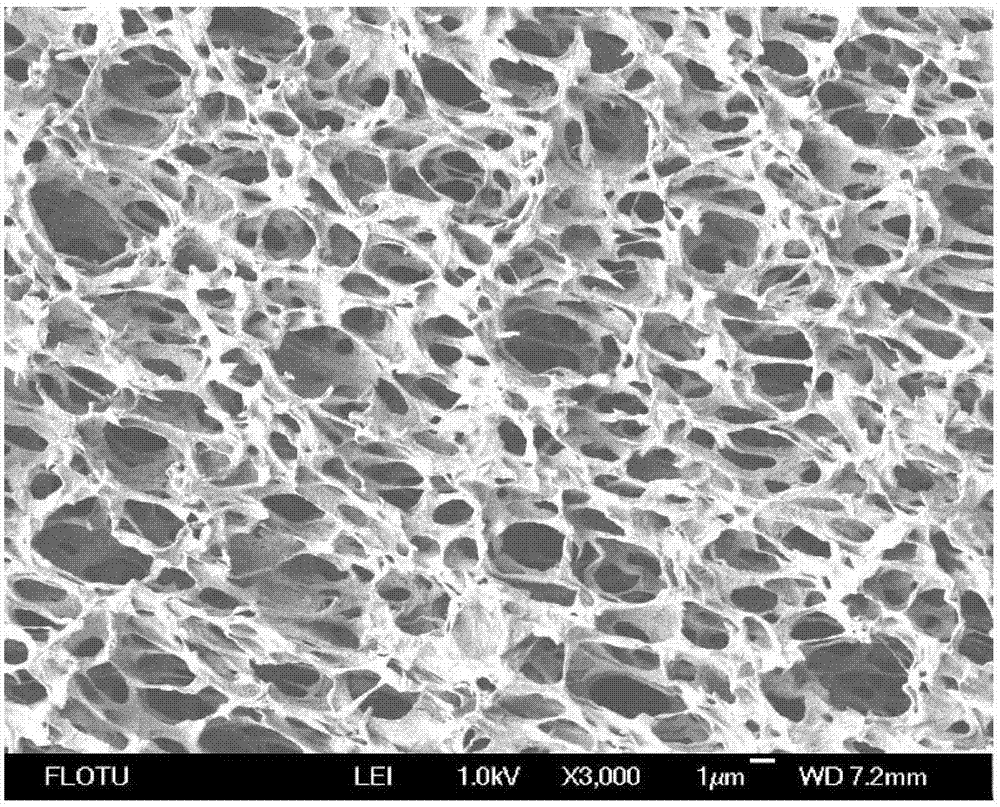
[0040] Put polyvinylidene fluoride (weight average molecular weight 100000), tributyl citrate and diethylene glycol into a high-temperature stirred tank and heat up to 100°C, stir and mix evenly to form a polymer homogeneous solution, and let stand for 2 hours; The mass percentage of polyvinylidene fluoride is 20%, the mass percentage of tributyl citrate is 24%, and the mass percentage of diethylene glycol is 56%. Then the polymer homogeneous solution was directly hang-coated on the support net to form a flat film with a film thickness of 200 μm, and entered into a cooling liquid bath at 30° C. to separate and solidify the solution into a film. The cooling liquid was water. The solidified flat film is dried after being extracted with an extractant, and the extractant is ethanol.
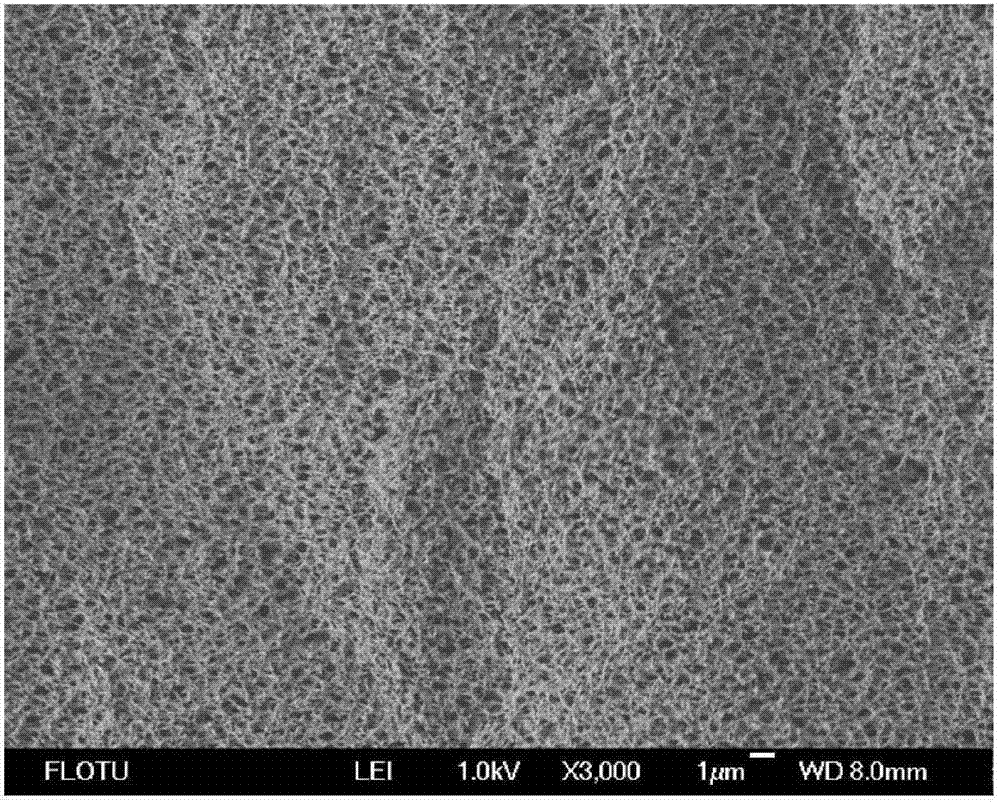
[0041] The cross-section of the membrane is a uniform sponge-like structure, with a porosity of 81%, a breaking strength of 4.51MPa, a bubble point pressure of 0.16MPa, an average surface pore diamet...
Embodiment 2
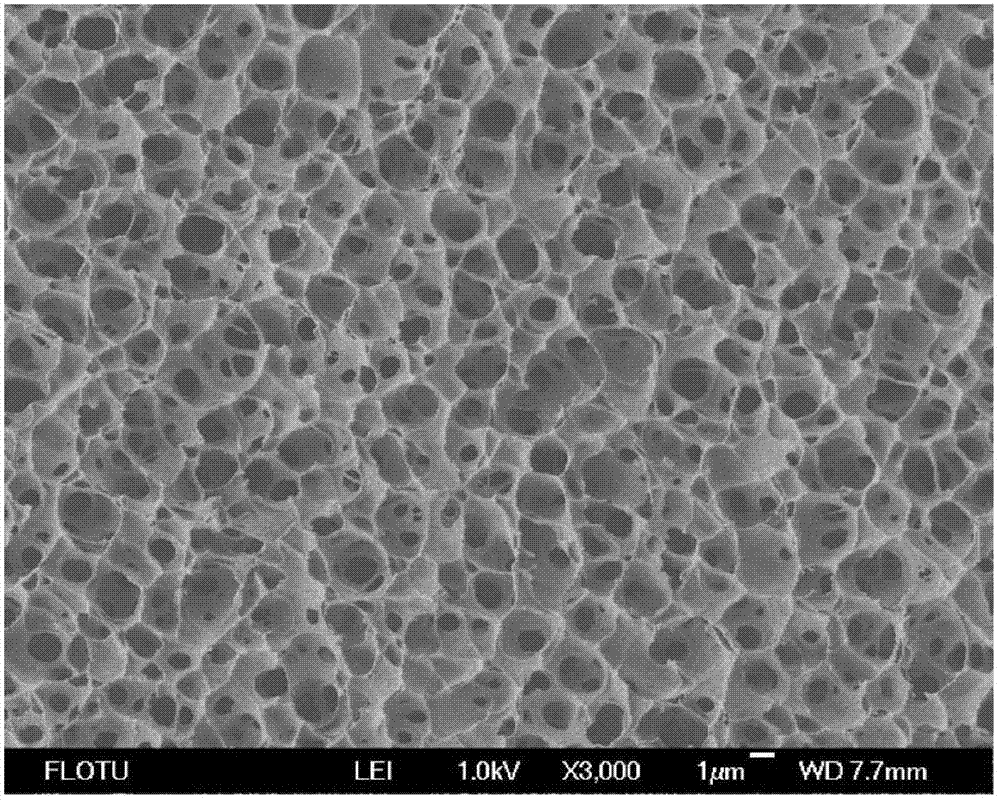
[0043] Put vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene copolymer (weight average molecular weight 420000), diethylene glycol ethyl ether and 1-octanol into a high-temperature stirring tank and heat up to 140°C, stir and mix evenly to form a homogeneous polymer solution. Stand still for 2 hours; wherein, the mass percentage of vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene copolymer is 30%, the mass percentage of diethylene glycol ether is 35%, and the mass percentage of 1-octanol is 35%. Then hang-coat the polymer homogeneous solution directly on the support net to form a flat film with a film thickness of 200 μm, and enter the cooling liquid bath at 30 ° C to solidify the solution into a film by phase separation. The cooling liquid is dibutyl phthalate . The solidified flat film is dried after being extracted with an extractant, and the extractant is benzyl alcohol.
[0044] The cross-section of the membrane is a uniform sponge-like structure, with a porosity of 69%, a breaking strengt...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bubble point pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com