Method for manufacturing thin line with relatively small edge roughness
A technology with edge roughness and thin lines, applied in the field of VLSI manufacturing, it can solve the problems of lack of advantages, limited development, and long time-consuming, and achieve the effect of short process time, strong operability, and LER improvement.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
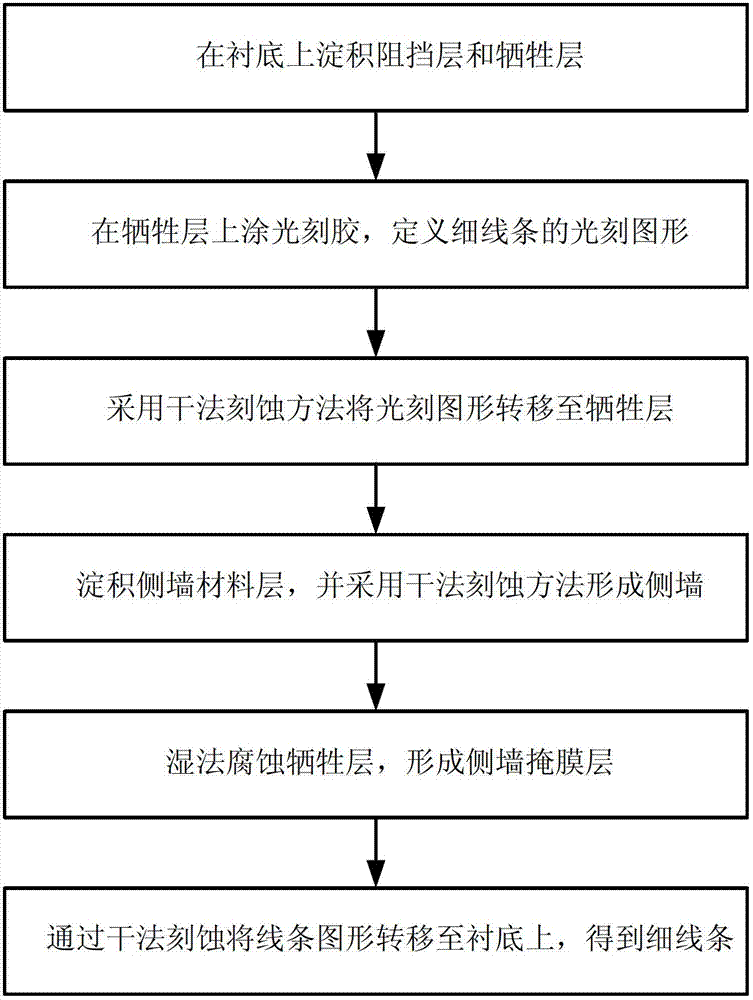
[0029] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the steps of the method for preparing thin lines with less edge roughness in this embodiment. The process can be further summarized into the following three major steps:
[0030] 1) Deposit a barrier layer and a sacrificial layer on the substrate, and define the lithographic pattern of the lines.
[0031] The material of the blocking layer is silicon oxide, which acts as a blocking layer of the substrate during the subsequent etching of the sacrificial layer and etching of the sacrificial layer. The material of the sacrificial layer is polysilicon, which serves as a support layer for subsequent deposition of side walls. The specific process steps include:
[0032] a) Depositing a barrier layer of silicon oxide to block subsequent etching and corrosion;
[0033] b) depositing a layer of polysilicon film;
[0034] c) Coating a layer of photoresist on the polysilicon, and defining thin lines by photolithography;
[0035] d) Dry etching ...
Embodiment 1
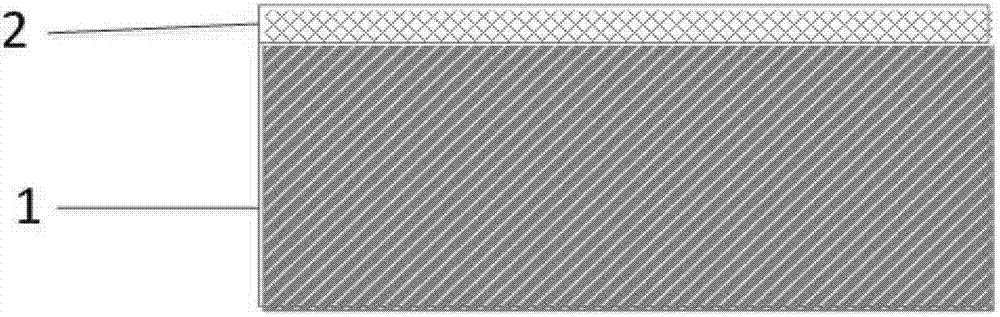
[0049] 1. Chemical vapor deposition of a silicon oxide film on a (100) / bulk silicon substrate with a thickness of As shown in Figure 2(a).
[0050] 2. Chemical vapor deposition of a layer of polysilicon film on the silicon oxide film with a thickness of As shown in Figure 2(b);
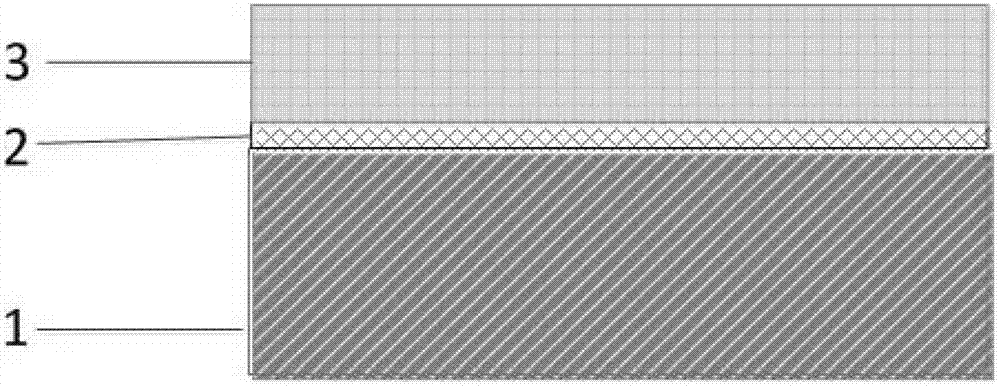
[0051] 3. Coating photoresist on the polysilicon film, as shown in Figure 2(c);
[0052] 4. Photolithography defines the area to be used as the sacrificial layer, as shown in Figure 2(d);
[0053] 5. Anisotropic dry etching of the polysilicon film, and finally transfer the pattern on the photoresist to the polysilicon film material, as shown in Figure 2(e);
[0054] 6. Remove the photoresist, as shown in Figure 2(f);
[0055] 7. Chemical vapor deposition of silicon nitride on the surface of silicon oxide film and polysilicon film, with a thickness of As shown in Figure 2(g);
[0056] 8. Anisotropic dry etching of silicon nitride to form silicon nitride sidewalls, as shown in Figure 2(h);
...
Embodiment 2
[0063] This example provides process parameters for producing thinner lines with smaller dimensions. To produce thinner lines with smaller dimensions, the thickness of the polysilicon sacrificial layer can be increased. In this way, when silicon nitride is etched to form sidewalls, the size of the silicon nitride hard mask is smaller due to the more serious lateral undercutting, and the size of the finally prepared thin lines is also smaller, which can reach below 10nm. Specific steps are as follows:
[0064] 1. Chemical vapor deposition of a silicon oxide film on a (100) / bulk silicon substrate with a thickness of As shown in Figure 2(a).
[0065] 2. Chemical vapor deposition of a layer of polysilicon film on the silicon oxide film with a thickness of As shown in Figure 2(b);
[0066] 3. Coating photoresist on the polysilicon film, as shown in Figure 2(c);
[0067] 4. Photolithography defines the area to be used as the sacrificial layer, as shown in Figure 2(d);
[00...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com