Method for separating rutin, hyperoside, isoquercitrin and quercetin from lotus leaves
A technology of hyperoside and isoquercitrin, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of sugar derivatives, sugar derivatives, etc., can solve problems such as difficult and effective separation, unsuitable separation, and low separation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
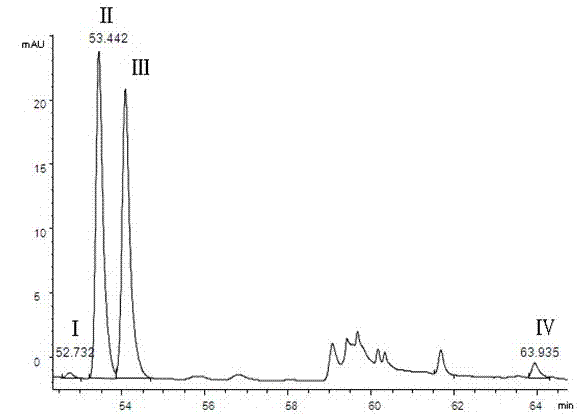
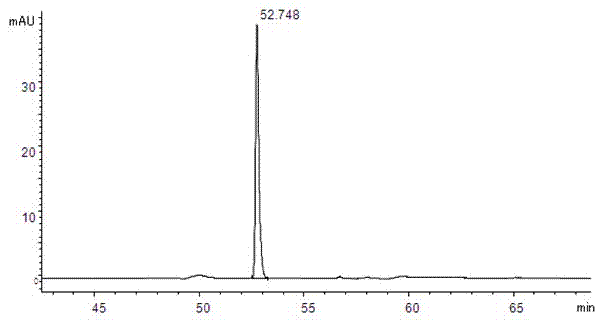
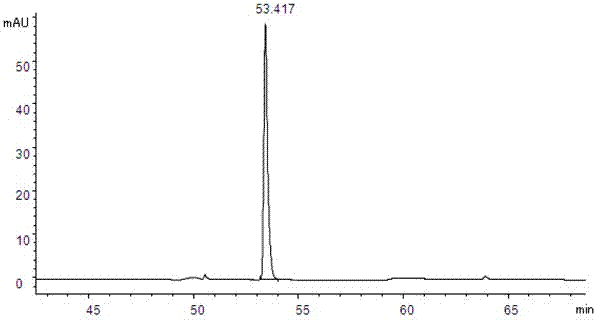
[0026] 1 Instruments and reagents
[0027] Agilent 1100 high performance liquid chromatography; Isoquercitrin reference substance (batch number 10391, purity 93.0%, German HWI ANALYTIK company); quercetin reference substance (batch number 100081-200406, China Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products) ; Rutin reference substance (batch number is 100080-200707, National Institute for the Control of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products); Acetonitrile (chromatographically pure, German Merck company); dried, crushed, and passed through a No. 5 sieve); the rest of the reagents are analytically pure.
[0028] 2 Methods and results
[0029] 2.1 Chromatographic conditions
[0030] Chromatographic column: Agilent C18 column (250mm×4.6mm, 5μm) with a column temperature of 30°C. Mobile phase A: pH4.0 phosphate buffer (0.2% phosphoric acid solution, adjust the pH value to 4.0 with 10% sodium hydroxide solution); mobile phase B: acetonitrile; see Table 1 for ...
Embodiment 2
[0054] The same as in Example 1, the difference is that the volume ratio of mobile phase A to mobile phase B, that is, the gradient elution conditions, is shown in Table 3 at different times. The phosphate buffer solution is prepared by mixing 0.15% phosphoric acid solution and 8% sodium hydroxide solution to a pH value of 3.5. The lotus leaf powder was first dissolved with 75% methanol solution and ultrasonicated for 28 minutes, then dissolved with 85% methanol solution and filtered, and the filtrate was used as the separation liquid for the column chromatography.
[0055] The measured yield of rutin was 96.5% with a purity of 90.5%; the yield of hyperoside was 97.3% with a purity of 89%; the yield of isoquercitrin was 99% with a purity of 92.3%; the yield of quercetin It is 98.4%, and the purity reaches 90.4%.
[0056] Table 3 Example two gradient elution table
[0057]
Embodiment 3
[0059] The same as in Example 1, the difference is that the volume ratio of mobile phase A to mobile phase B, that is, the gradient elution conditions, is shown in Table 4 at different times.
[0060] The measured yield of rutin was 96.2% with a purity of 89.9%; the yield of hyperoside was 97.1% with a purity of 89.4%; the yield of isoquercitrin was 98.9% with a purity of 91.8%; the yield of quercetin It is 97.8%, and the purity reaches 90.1%.
[0061] Table 4 Example three gradient elution table
[0062]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com