Method of recycling residual alkali from sodium tungstate solution in tungsten smelting
A technology of solution recovery and sodium tungstate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal compounds, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve the problems of not considering residual alkali recovery, low degree of automation, and low marginal income, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of energy saving and low labor intensity, high degree of automation, reducing consumption and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
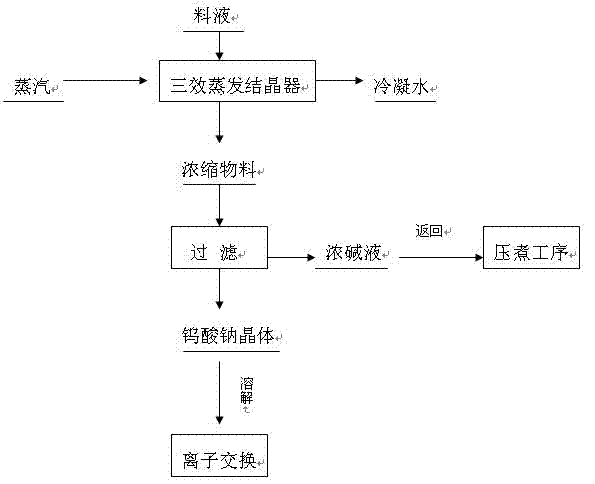
[0017] The sodium tungstate liquid coming out of the pressure cooker contains tungsten trioxide 100g / L, sodium hydroxide concentration 40 g / L, and the volume of the solution is 5000mL. The steam pressure at the inlet of the first-effect evaporation crystallizer is 0.4MPa, and the temperature is 155°C. The sodium tungstate crystals precipitated from the second-effect evaporation crystallizer and the third-effect evaporation crystallizer are sent to the plate and frame filter press for solid-liquid separation, and the filtrate is returned to pressure cooking Process, the filter residue is dissolved and sent to the ion exchange process, and the condensed water is used as dilution water for the main process. The concentration of sodium hydroxide in the filtrate is 355g / L, and the concentration of tungsten trioxide is 35.6g / L. The direct recovery rate of tungsten is 96%, and the recovery rate of alkali is 97.5%.
Embodiment 2
[0019] The sodium tungstate liquid coming out of the autoclave contains 100g / L tungsten trioxide, 45 g / L sodium hydroxide, and a solution volume of 5000mL. The steam pressure at the inlet of the first-effect evaporation crystallizer is 0.4MPa, and the temperature is 155°C. The sodium tungstate crystals precipitated from the second-effect evaporation crystallizer and the third-effect evaporation crystallizer are sent to the plate and frame filter press for solid-liquid separation, and the filtrate is returned to pressure cooking Process, the filter residue is dissolved and sent to the ion exchange process, the condensed water is used as dilution water for the main process, the concentration of sodium hydroxide in the filtrate is 385 g / L, and the concentration of tungsten trioxide is 25.5 g / L. The direct recovery rate of tungsten is 97%, and the alkali recovery rate is 96.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0021] The sodium tungstate liquid coming out of the pressure cooker contains tungsten trioxide 100g / L, sodium hydroxide concentration 50 g / L, and the volume of the solution is 5000mL. The steam pressure at the inlet of the first-effect evaporation crystallizer is 0.4MPa, and the temperature is 155°C. The sodium tungstate crystals precipitated from the second-effect evaporation crystallizer and the third-effect evaporation crystallizer are sent to the plate and frame filter press for solid-liquid separation, and the filtrate is returned to pressure cooking Process, the filter residue is dissolved and sent to the ion exchange process, and the condensed water is used as dilution water for the main process. The concentration of sodium hydroxide in the filtrate is 390.5 g / L, and the concentration of tungsten trioxide is 23.6 g / L. The direct recovery rate of tungsten is 97%, and the alkali recovery rate is 97.1%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com